EA is killing a game I didn’t even know was alive
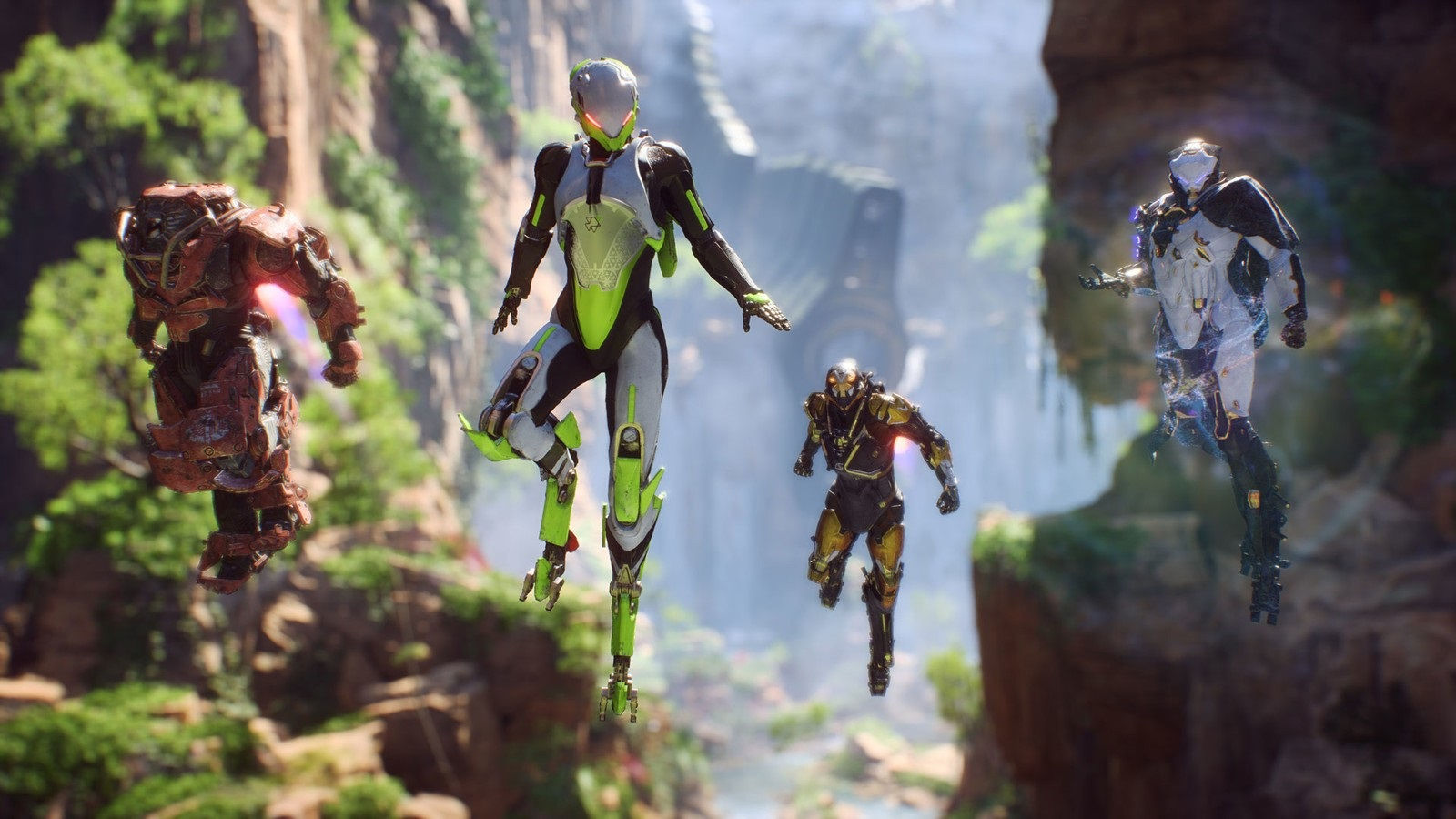

Many people, including myself, were taken aback when we learned that the game was not yet being discontinued, as it seemed to us that it had been shut down long ago due to poor performance in the competitive shooter market since its launch in February 2019 by BioWare and EA.