What you need to know
- AMD’s latest Ryzen 9000 Series desktop processors are delayed on their planned July launch until at least August 8, 2024.
- Of the four planned chips, at least the Ryzen 7 9700X and Ryzen 5 9600X have exhibited production issues.
- While AMD vaguely confirms the problems, it comes alongside Intel’s struggles with widespread and permanent damages to its 13th and 14th Gen Raptor Lake processors caused by microcode (firmware) errors.
As a long-time tech enthusiast and custom PC builder, I’ve grown accustomed to the ebbs and flows of the semiconductor industry – the thrill of new releases, the anticipation of groundbreaking technology, and the occasional setbacks that accompany progress. However, recent news regarding AMD’s Ryzen 9000 Series desktop processors and Intel’s Raptor Lake chips has left me with a mix of excitement and frustration.
Custom PC builders are facing choppy waters as they wait for AMD’s latest desktop processors, the Ryzen 9000 series. Originally slated for a late July debut, AMD has announced that the new Zen 5 APUs will experience a slight delay due to not meeting “our” complete quality standards. AMD’s Senior Vice President and General Manager of Computing and Graphics, Jack Huynh, confirmed the earliest availability dates: August 8 for the Ryzen 7 9600X and Ryzen 5 9700X with a 65W TDP, and August 15 for the Ryzen 9 9900X and 9950X with a 120W TDP.
To ensure the best possible experience for all Ryzen users and out of careful precaution, we’re collaborating with our retail partners to exchange the initial shipments with new ones.
An AMD representative discussed with Tom’s Hardware their discovery of a problem in the testing procedure for Ryzen 9000 series processors, without providing further information. However, leaks soon revealed that a possible cause for this sudden recall was a less serious issue than initially feared. Erroneous engraving on at least two 4nm APUs, specifically the Ryzen 7 9700X and Ryzen 5 9600X, led to their inadvertent labeling as more potent Ryzen 9 models. It remains uncertain if this mistake extends to the retail packaging of these processors, but even such a seemingly trivial error could result in a launch postponement.
What’s wrong with Intel’s 13th/14th Gen chips?

It’s hopeful that AMD’s issues with the Ryzen 9000 chips were merely typographical errors in the labels instead of more significant production issues related to the processor dies. In contrast, Intel’s Raptor Lake processors have encountered problems due to a microcode (firmware) bug, causing their 13th Gen and 14th Gen Core i9 desktop chips to exceed safe voltage levels and potentially result in permanent damage.
According to Tom’s Hardware, a disappointing find is that users encountering recurring crashes with Raptor Lake chips in their computers will not gain relief from Intel’s corrective microcode update. Determining any potential deterioration is an exceedingly challenging or impossible task, thus impacted consumers are advised to contact Intel’s support team for a return merchandise authorization (RMA) and adhere to Intel’s suggested power settings based on their processor and motherboard configuration.
What do we know about Ryzen 9000 chips?
The upcoming Ryzen 9000 Series processors from AMD, similar to their predecessor, the Ryzen 8000G Series, will only work with motherboards featuring an AM5 socket. This is a prerequisite that began with AMD’s Zen 4 Ryzen 7000 Series. This new lineup marks the first time AMD’s advanced Zen 5 architecture and the Ryzen AI 300 Series for mobile devices are utilized together. These processors support PCIe 5.0 for up-to-date expansion cards, USB4 for swift plug-and-play devices, and Wi-Fi 7 networking technology.
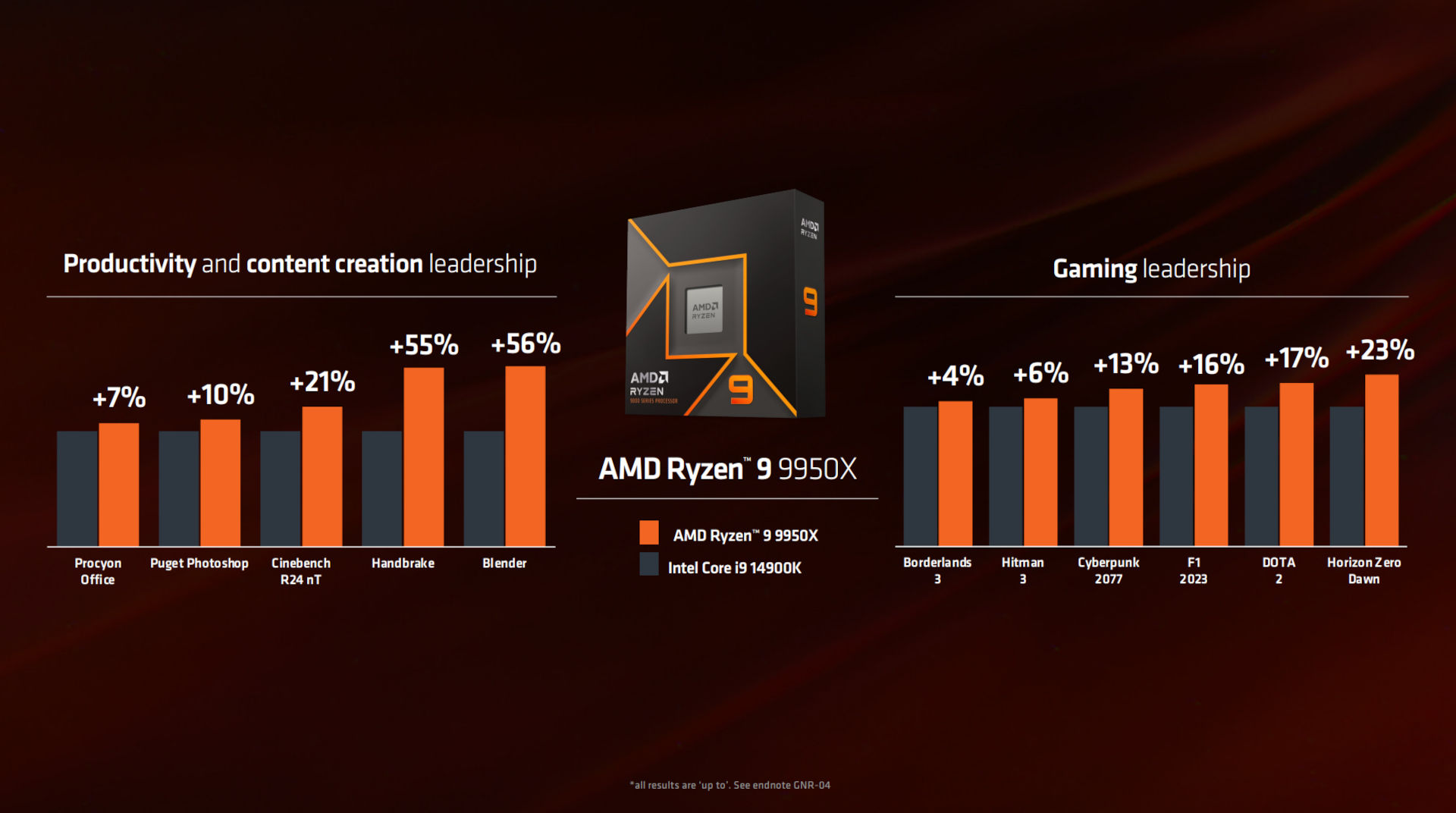
The Ryzen 9000 Series desktop processors from AMD can be categorized into three groups based on their Thermal Design Power (TDP). This ranges from a 6-core, 12-thread Ryzen 5 9600X APU which has a power consumption of 65W, all the way up to a 16-core, 32-thread Ryzen 9 9950X that consumes 170W. For several years, AMD’s Ryzen 5 5600X and Ryzen 7 5800X stood out as excellent value choices for gaming, while the Ryzen 7 7800X3D took over as a premium pick. The Ryzen 7 8700G, the successor to these processors, offers integrated Radeon 780M graphics and sits in the middle with impressive performance that can run modern titles like Cyberpunk 2077 at ‘low’ graphic settings.
Labeled “Granite Ridge,” the upcoming Ryzen 9000 Series processors boast the same powerful Radeon 800M Series graphics unit as laptops such as ASUS’ Zenbook S 16. These chips could be an ideal integrated option for budget-conscious builders. The specification sheet is intriguing, backed by a solid reputation. I can hardly wait to try out at least one of these new Ryzen 9000 processors once they hit the market (hopefully without significant flaws).
Read More
- PI PREDICTION. PI cryptocurrency
- WCT PREDICTION. WCT cryptocurrency
- LPT PREDICTION. LPT cryptocurrency
- Guide: 18 PS5, PS4 Games You Should Buy in PS Store’s Extended Play Sale
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Shrek Fans Have Mixed Feelings About New Shrek 5 Character Designs (And There’s A Good Reason)
- SOL PREDICTION. SOL cryptocurrency
- FANTASY LIFE i: The Girl Who Steals Time digital pre-orders now available for PS5, PS4, Xbox Series, and PC
- Playmates’ Power Rangers Toyline Teaser Reveals First Lineup of Figures
- Solo Leveling Arise Tawata Kanae Guide
2024-07-29 18:10