
As a seasoned tech enthusiast with years of experience under my belt, I must say that Microsoft’s new feature – Windows Recall – has caught my attention. This innovative tool promises to revolutionize how we interact with our devices, making it easier than ever to find what we need when we need it.
In the Windows 11 Version 24H2 (2024 Update), there’s a novel functionality called Windows Recall, which uses artificial intelligence to follow and remember all your activities on the computer.
Instead of thinking of it as a photographic memory, you can consider this feature as an on-screen activity logger. It operates by capturing screenshots of your actions at regular intervals, employing multiple AI models embedded within the device to analyze the data. The information is then made searchable using conversational language through the “Recall” app.
As I delve into this novel system, it’s crucial that I take the time to acquaint myself with its interface and adjustable options, ensuring a richer and more rewarding user experience.
It’s worth mentioning that this specific function is exclusive to Copilot+ computers equipped with the most recent AI processors from Qualcomm, AMD, and Intel. By default, it’s turned off. At present, you can access this feature only as a preview through the Windows Insider Program.
This tutorial will walk you through the correct procedures for utilizing the Windows Recall function effectively on Windows 11.
How to configure and manage settings on Windows Recall
For users with a Copilot+ PC, the operating system provides several options to customize Windows Recall. You can choose whether to enable or disable this feature, adjust storage space, remove saved snapshots, and set preferences for which applications and websites to include.
Opt-in and out
The automatic activation of the Recall AI feature on your computer with Windows 11 will not occur; rather, you have the choice to enable it yourself.
To turn Windows Recall on or off, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Privacy & security.
- Click the Recall & snapshots page from the right side.
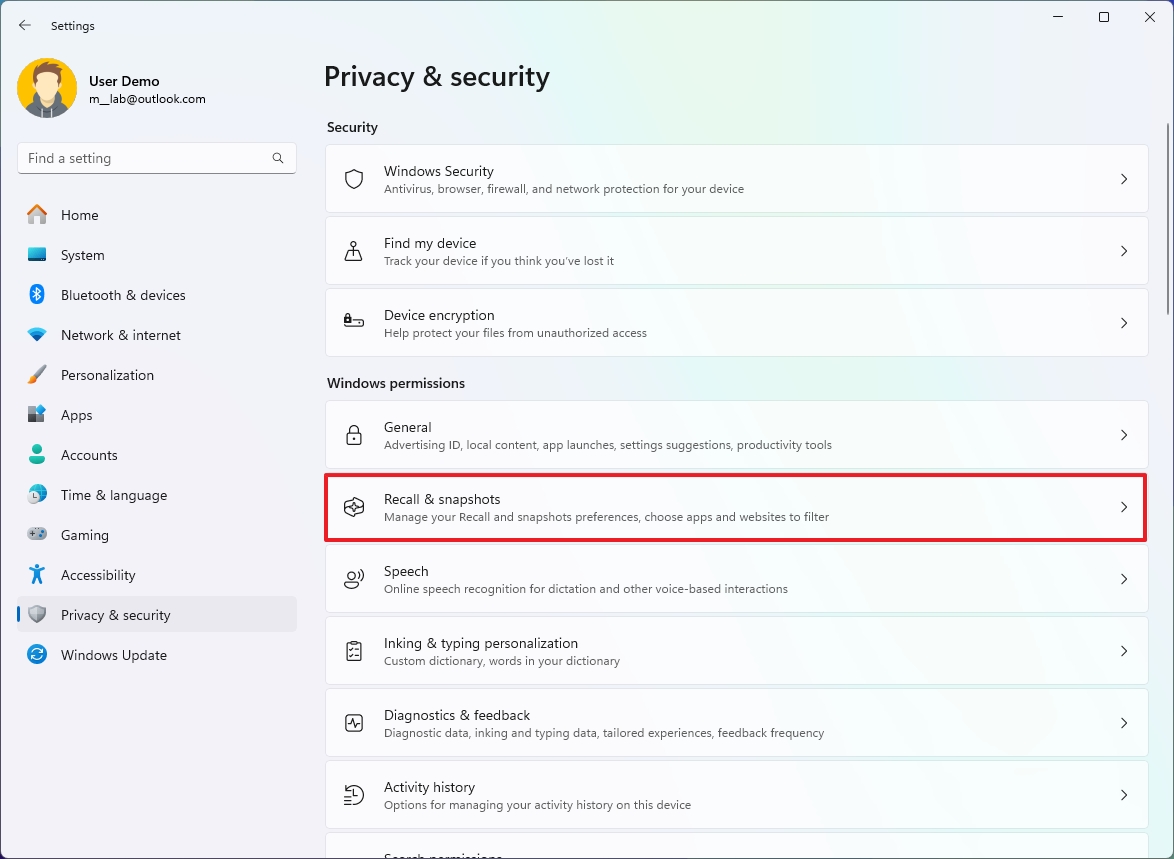
- (Option 1) Turn on the “Save snapshots” toggle switch to enable the feature.
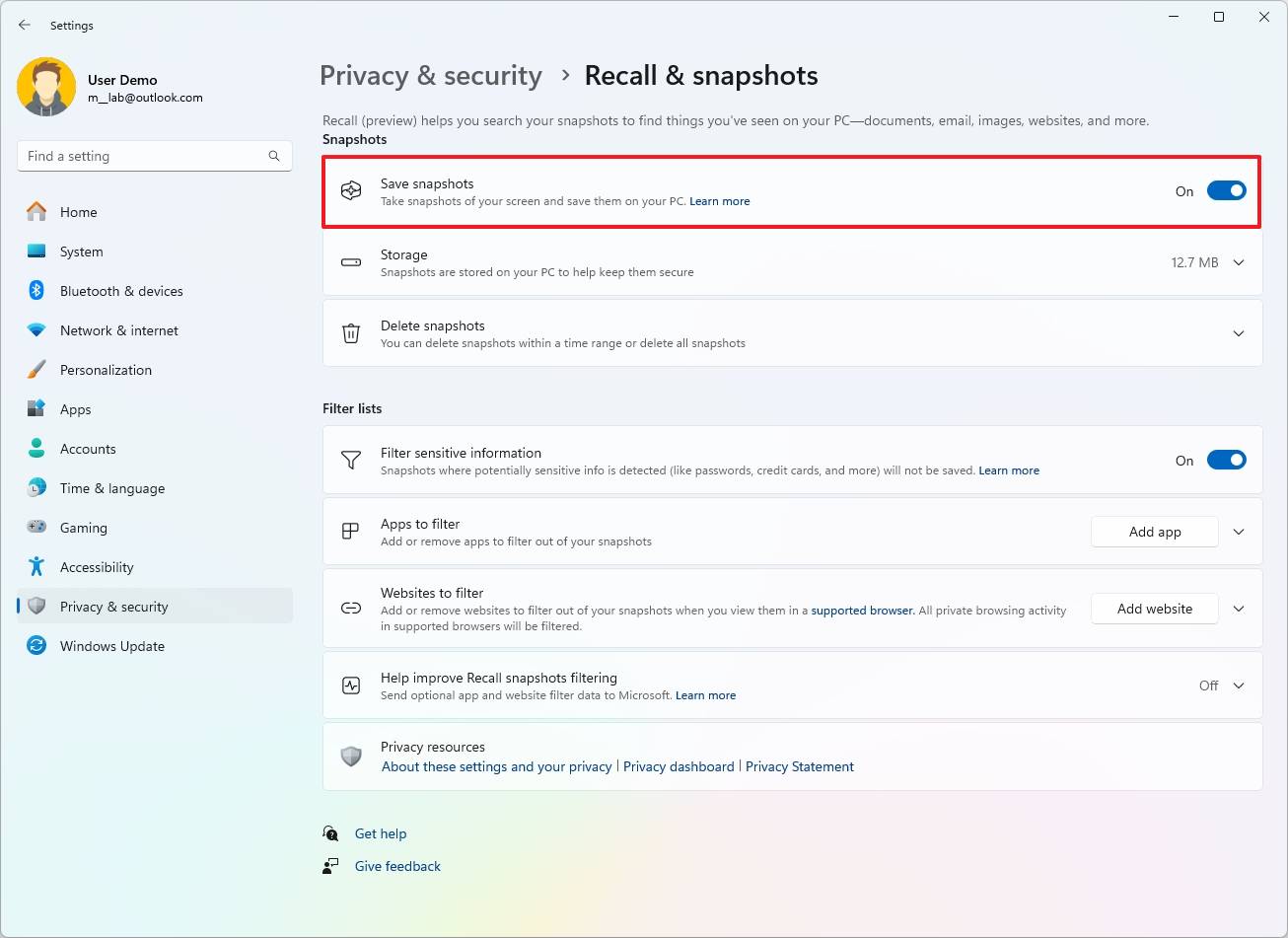
- (Option 2) Turn off the “Save snapshots” toggle switch to disable the feature.
After finishing the steps, the function will either activate or remain inactive, depending on your settings.
Another way to activate this feature is by opening the “Recall” application, then choosing to enable the option that saves screenshots directly onto your computer.
Change storage settings
By setup, Windows Reservation automatically sets aside approximately 25GB, 75GB, and 150GB of storage on devices sporting a 256GB, 512GB, and 1TB Solid State Drive (SSD) respectively. Nonetheless, you can adjust this allocation using the guidance provided below.
To change the storage allocation for Windows Recall, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Privacy & security.
- Click the Recall & snapshots page from the right side.

- Click the Storage setting.
- Choose the storage allocation size using the “Maximum storage for snapshots” setting.
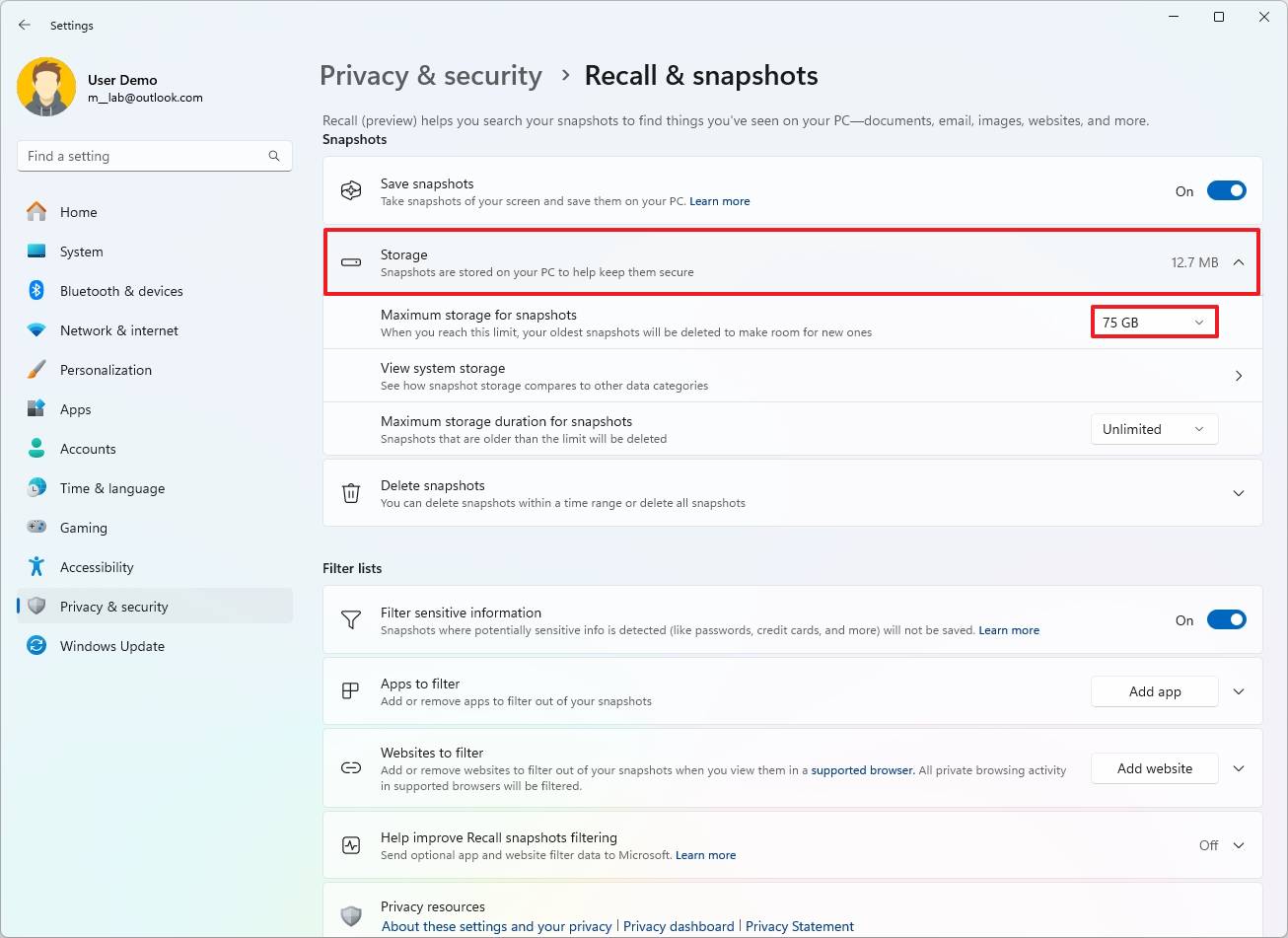
- (Optional) Click the “View system storage” settings to open the Storage settings to view the drive usage of Recall AI.
- Quick tip: The Storage settings in the “Recall & snapshots” page show this information.
- Choose the data retention time range (Unlimited, 30, 60, 90, or 180 days) in the “Maximum storage duration for snapshots” setting.
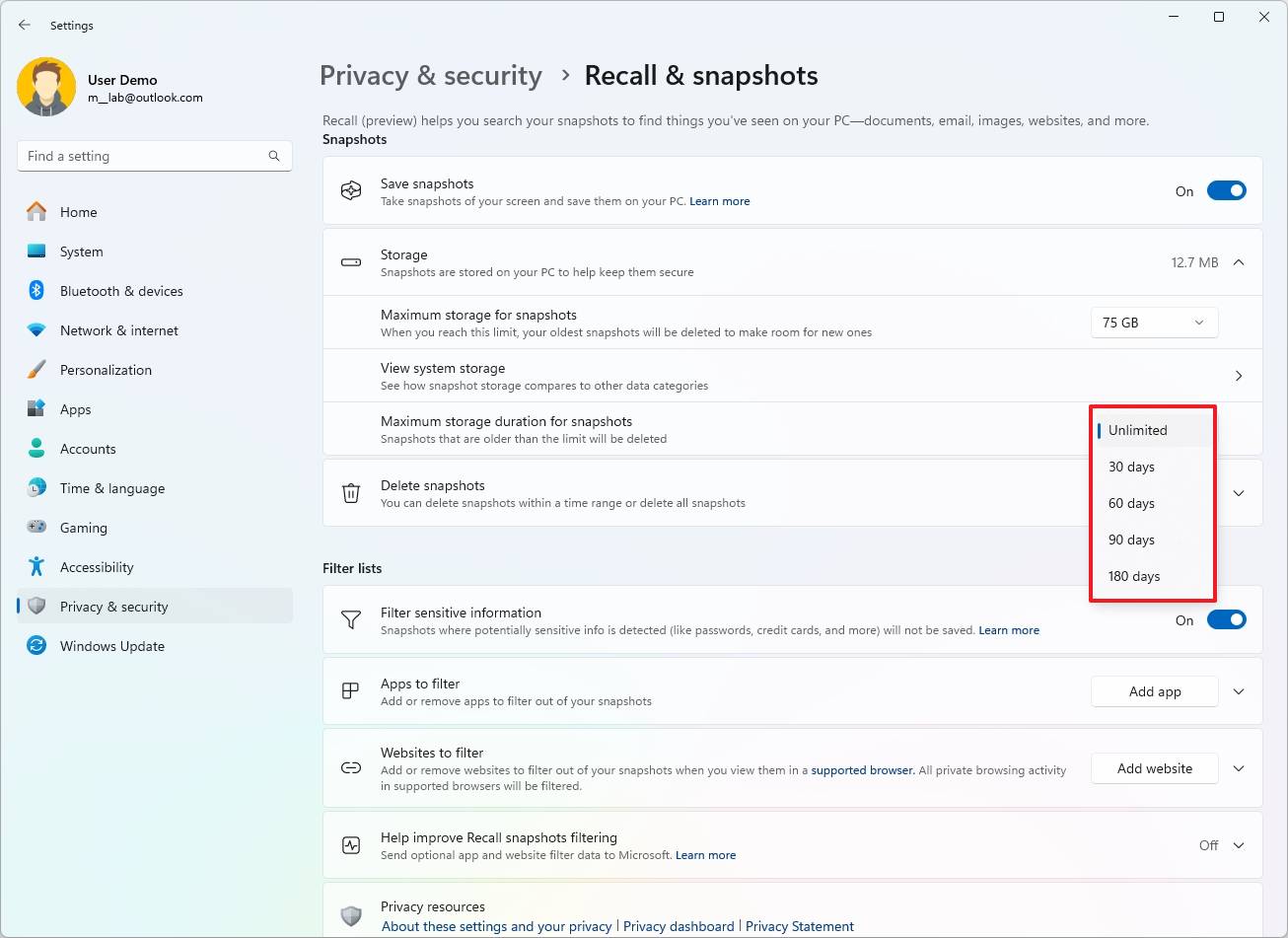
After you complete the steps, the system will apply the new storage allocation.
Delete snapshots
The Windows Recall function captures images of the screen intermittently to monitor user activity and improve the Windows Semantic Search engine. As these captured images might contain confidential information, Microsoft has created an option for users to erase certain or all images that the tool has saved, storing them on your computer if desired.
To delete Windows Recall snapshots on Windows 11, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Privacy & security.
- Click the Recall & snapshots page from the right side.

- Click the Delete setting.
- (Option 1) Choose the timeframe to delete snapshots from the “Delete snapshots from a specific timeframe” setting.
- Click the Delete snapshots button.
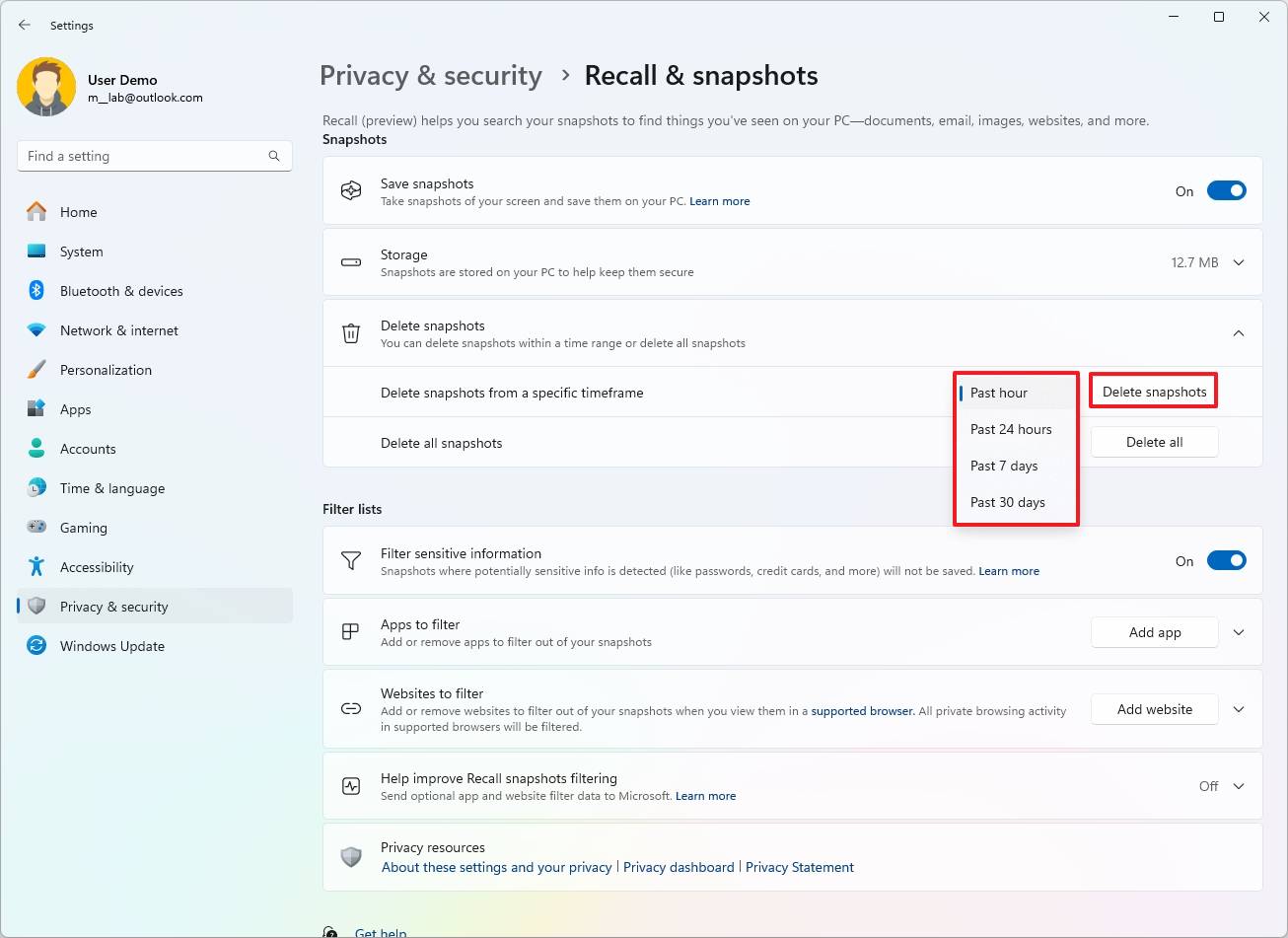
- Click the Delete button again to confirm.
- (Option 2) Click the “Delete all” button to remove the snapshots stored on your computer.
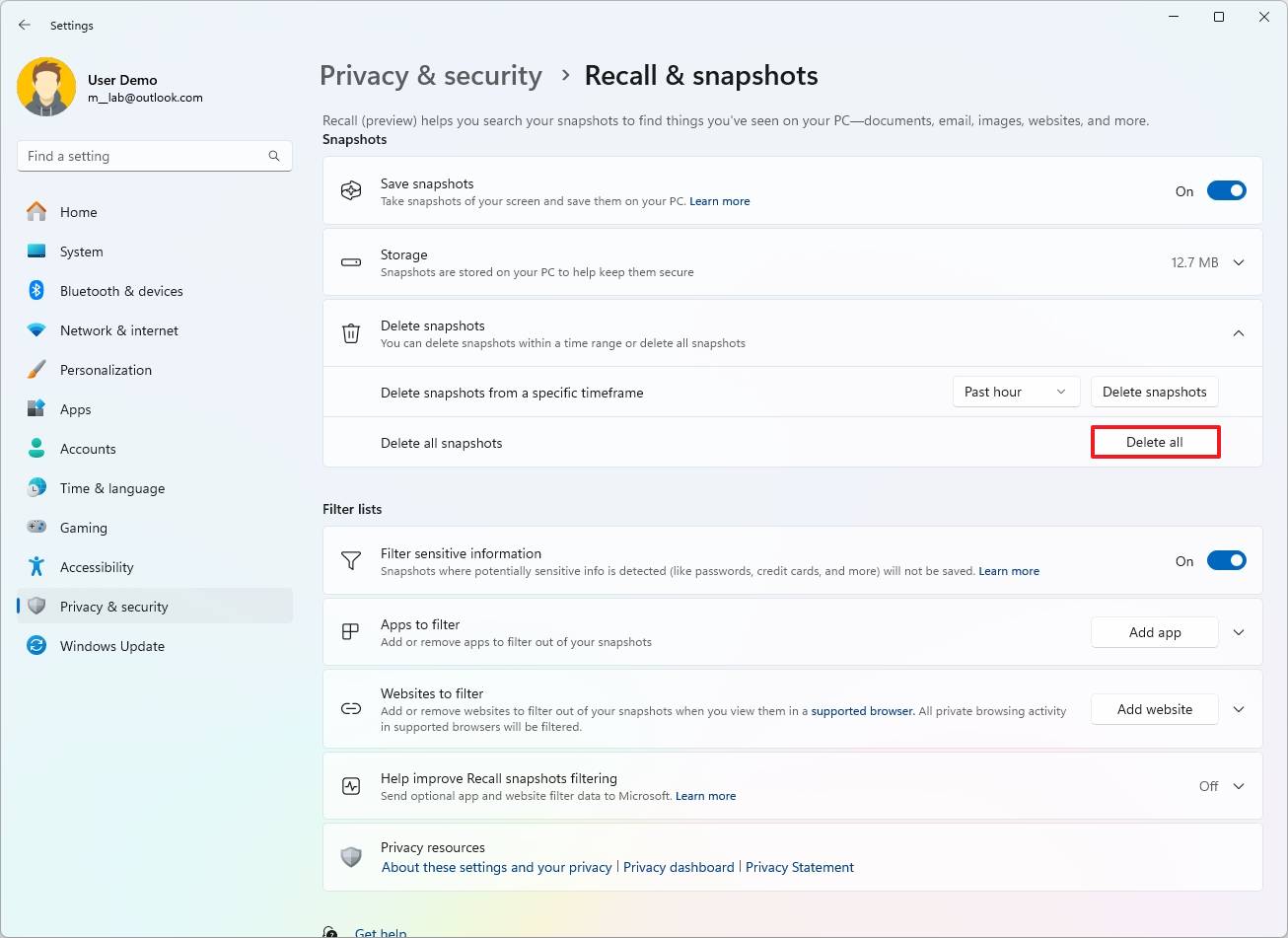
- Click the Delete button again to confirm.
Once you complete the steps, the Recall data will be deleted according to your configuration.
Filter sensitive information
To enhance user privacy and security, Recall AI offers an automatic feature that identifies and hides sensitive data like passwords or credit card numbers. This feature is activated by default, but users have the freedom to adjust it according to their preferences under the “Recall & Snapshots” settings.
To enable or disable the filter for sensitive information, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Privacy & security.
- Click the Recall & snapshots page from the right side.

- (Option 1) Turn on the “Filter sensitive information” toggle switch to enable the feature.
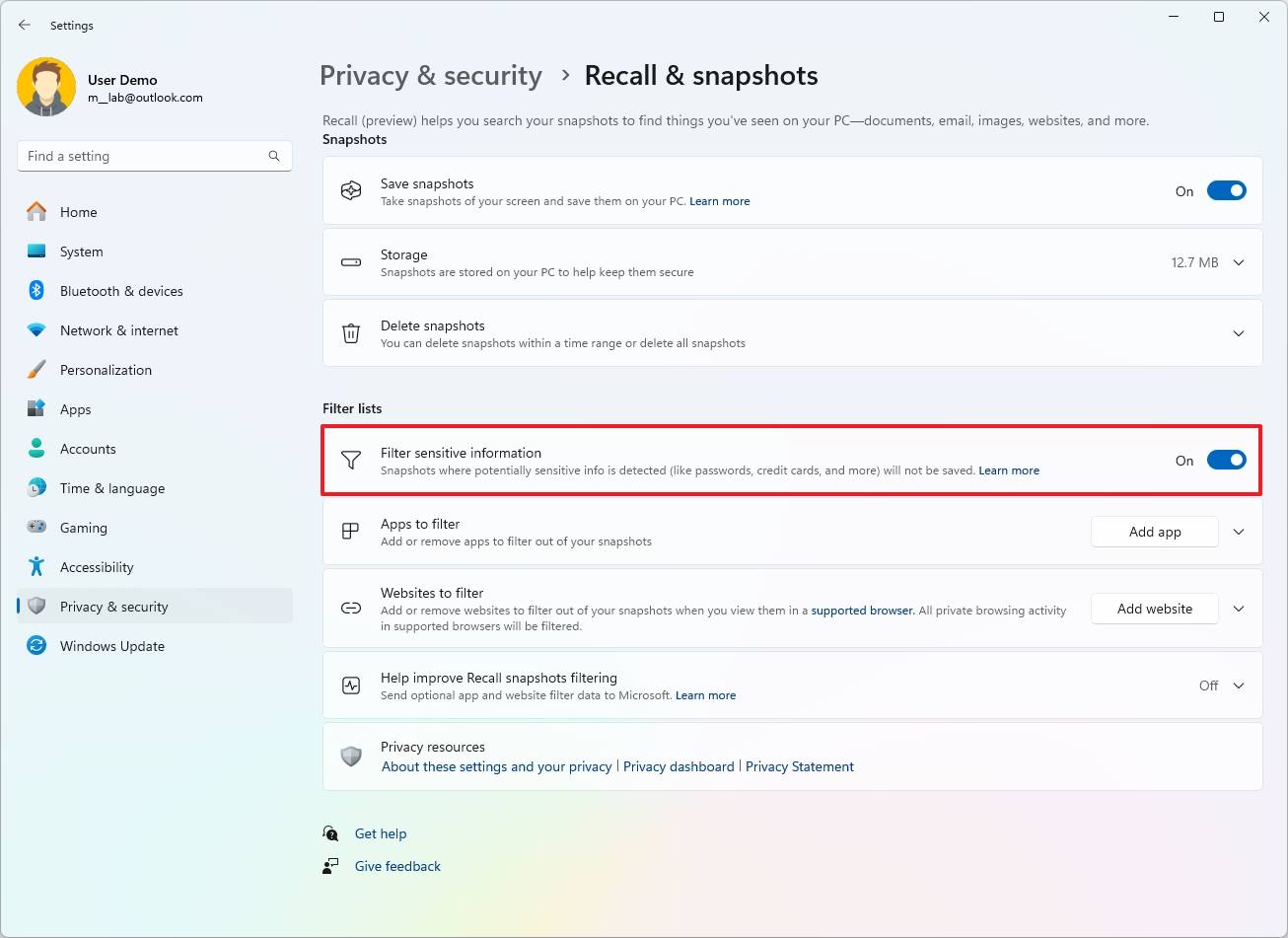
- (Option 2) Turn off the “Filter sensitive information” toggle switch to disable the feature.
After finishing the given instructions, the function will cease capturing screenshots containing confidential data on your PC.
Filter apps from Recall
While Windows Recall largely captures all activities on your computer, Microsoft is introducing a few options to customize which applications and websites are excluded from this feature.
By its standard settings, the feature does not track activities when using Chromium-based browsers such as Microsoft Edge, Google Chrome, Mozilla Firefox, and Opera in their private modes (Incognito or InPrivate). Additionally, Windows Recall doesn’t capture any content protected by Digital Rights Management (DRM).
To exclude apps from being recorded by Windows Recall, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Privacy & security.
- Click the Recall & snapshots page from the right side.

- Click the Add app button to filter an app.
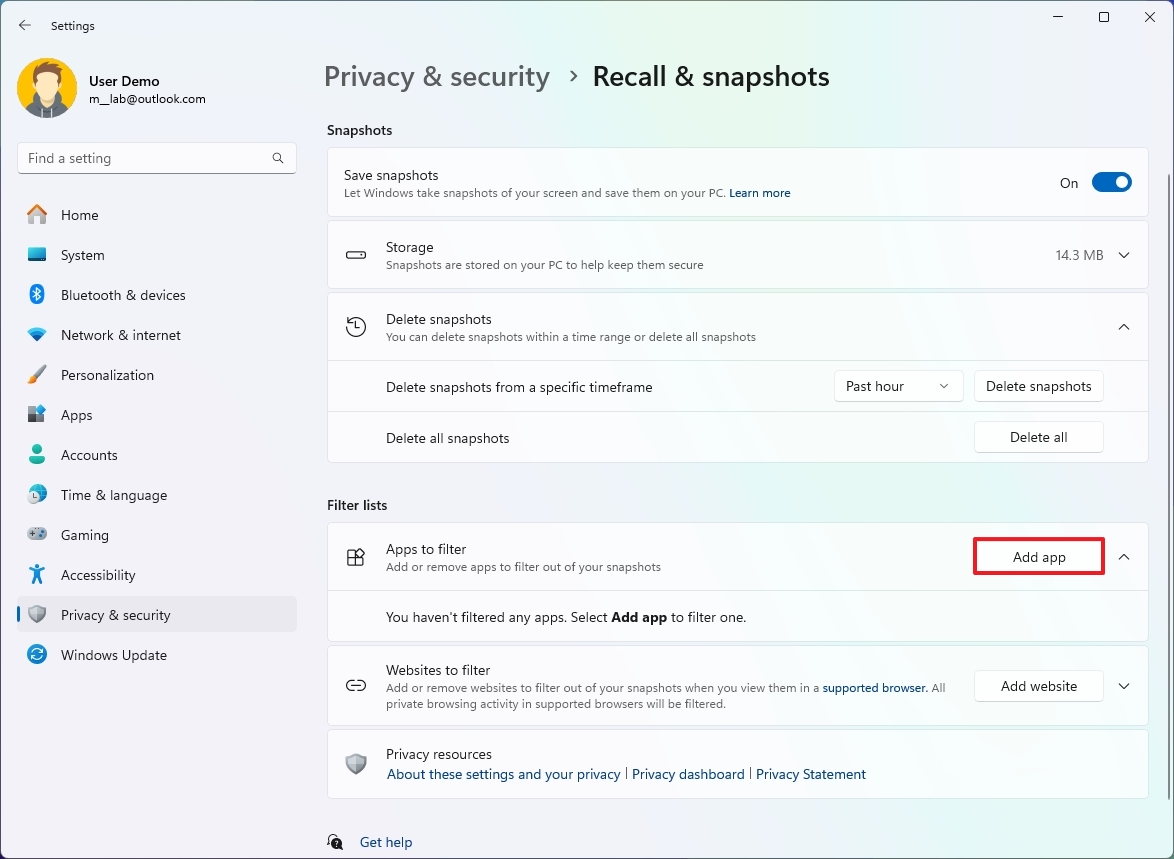
- Select the app from the list.
- Click the Add button.
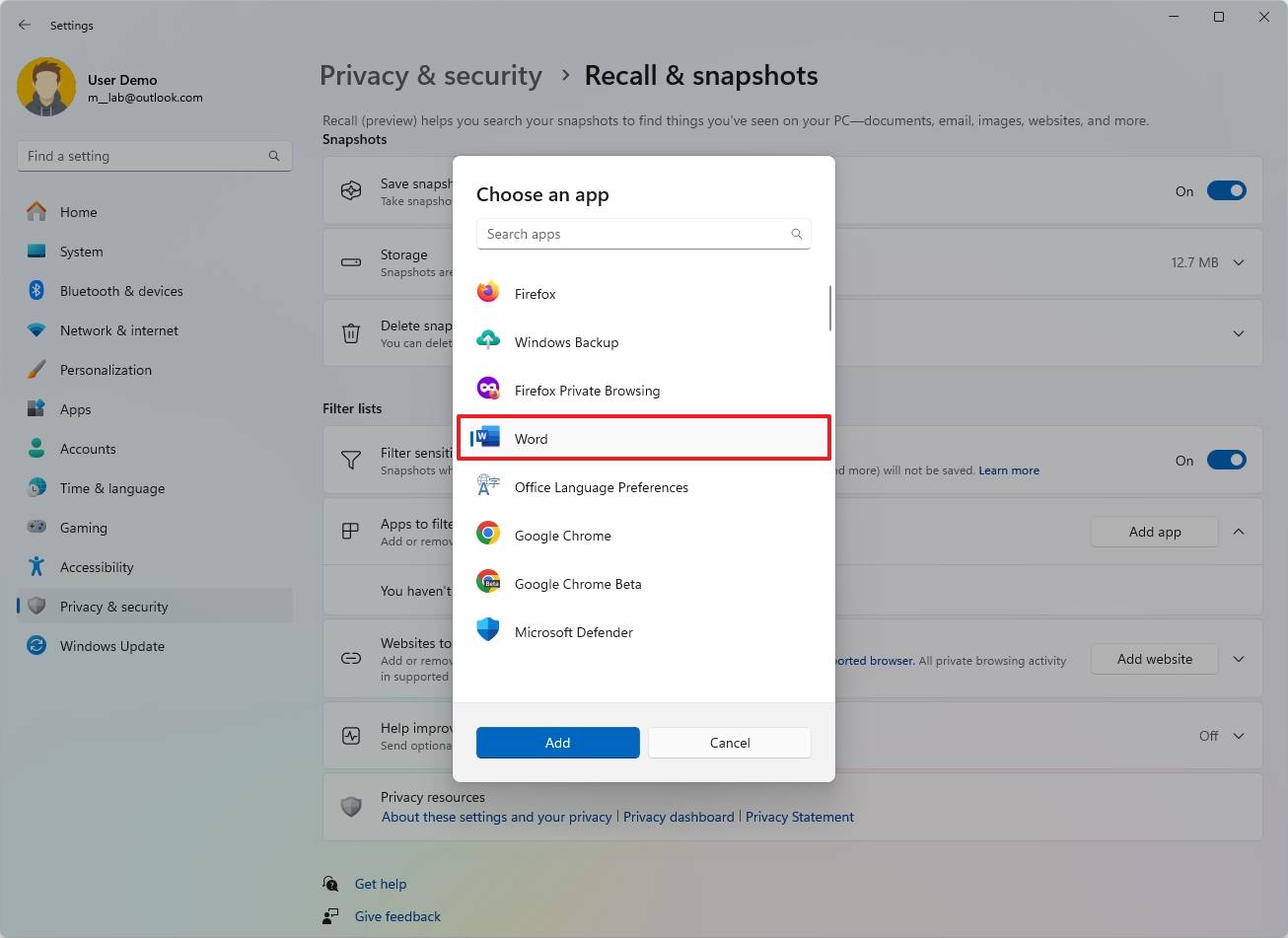
In step 4, click on the “Filter Apps” option, then hit the “Delete” button for the app you wish to eliminate.
Filter websites from Recall
To exclude websites from being recorded by Windows Recall, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
- Click on Privacy & security.
- Click the Recall & snapshots page from the right side.

- Click the Add website button to filter an app.
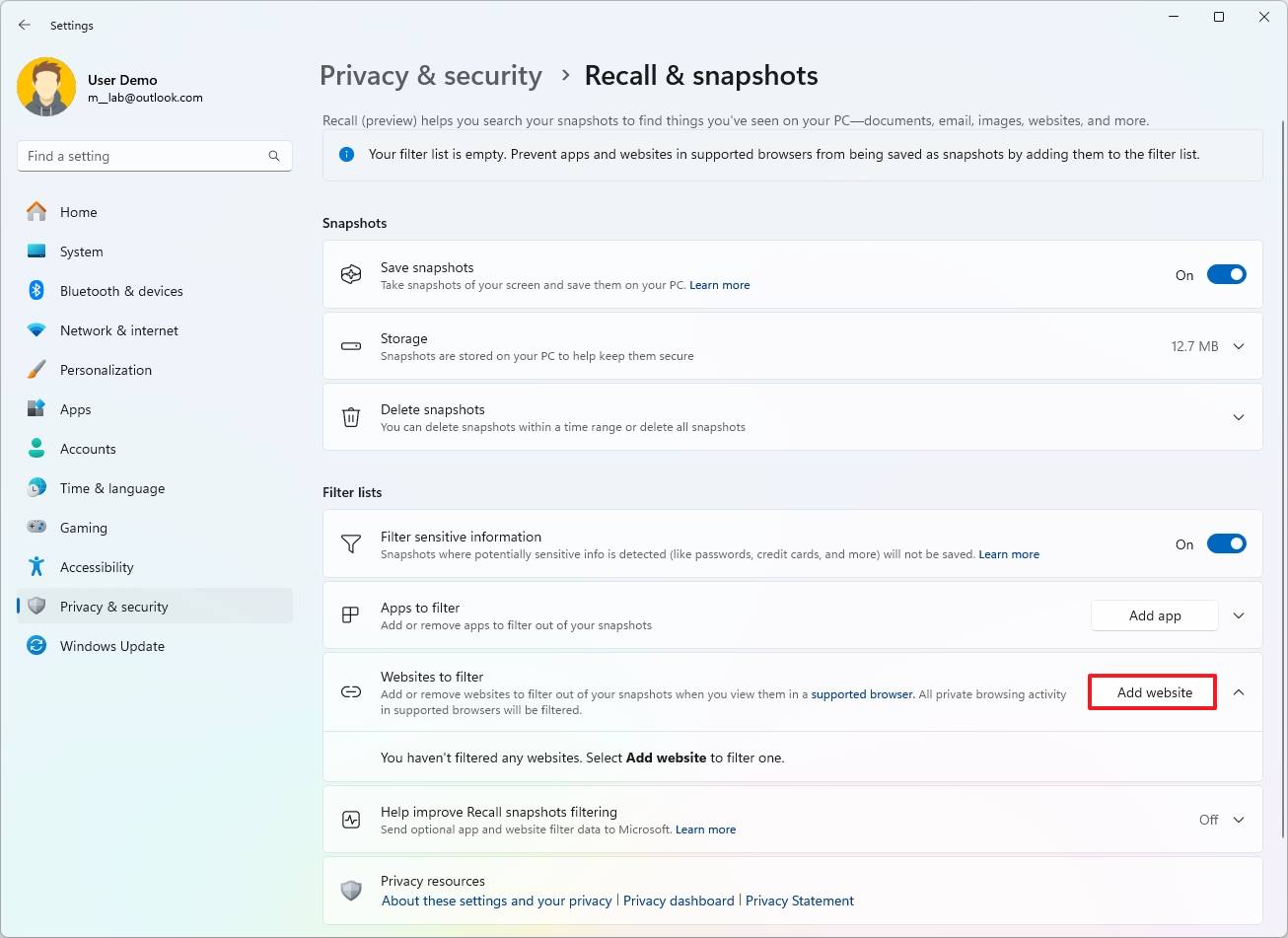
- Confirm the website to exclude.
- Click the Add button.
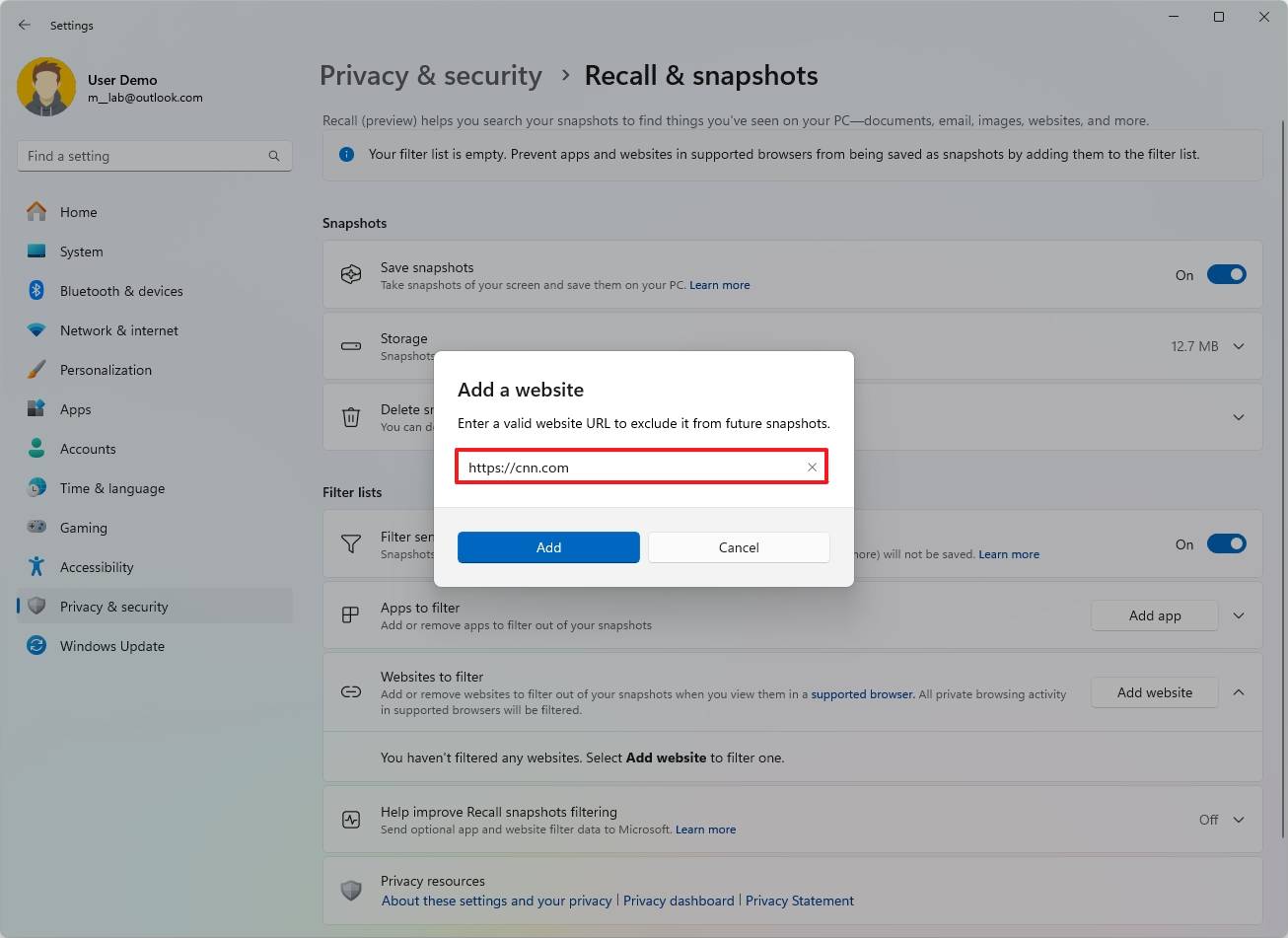
In step 4, instead of clicking on “Websites to filter”, tap the “Settings” option, then look for the “website removal” feature and select the unwanted site by tapping the “Delete” or “Remove” button associated with it.
Keep in mind that if you use an incognito mode or a site or app not included in our system, and click the “Now” button, the function will capture a screenshot of the current content. However, these screenshots are only kept temporarily in your account’s “Temp” folder before they are automatically deleted when you switch to another snapshot.
Pause and resume
It’s also possible to pause and resume the Recall snapshots with these instructions:
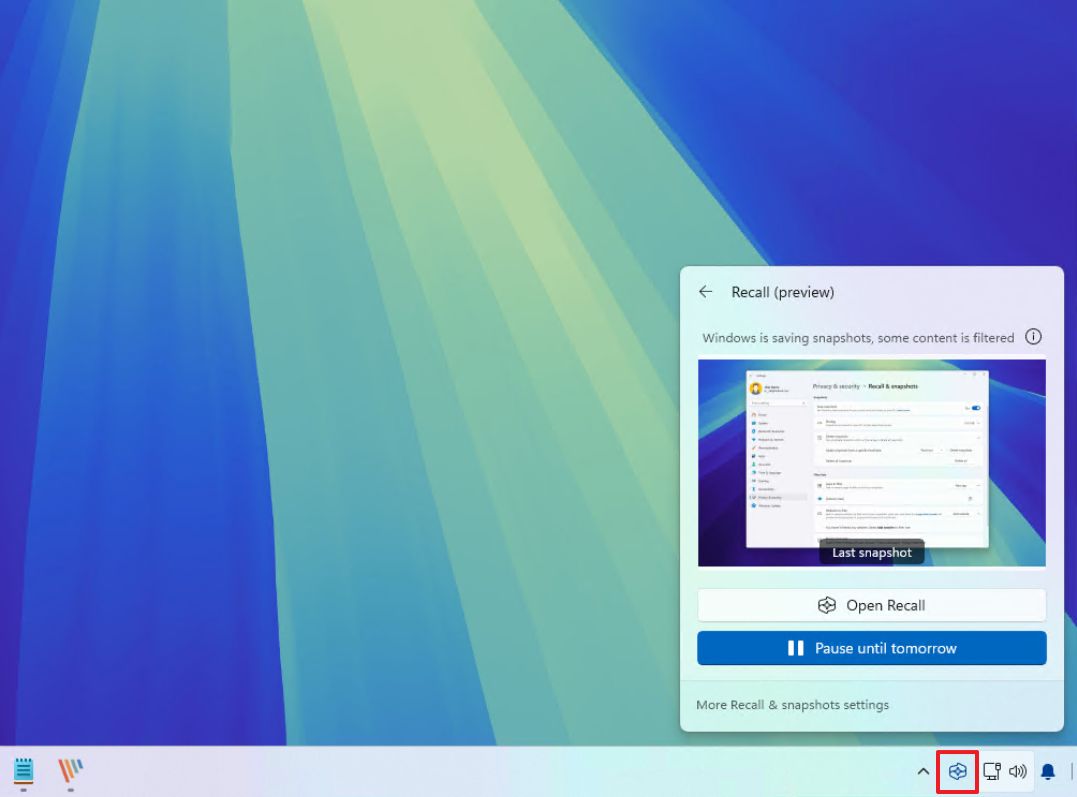
- Click the Windows Recall button from the System Tray.
- (Option 1) Click the “Pause until tomorrow” button to turn off the feature until the next day at 12AM.
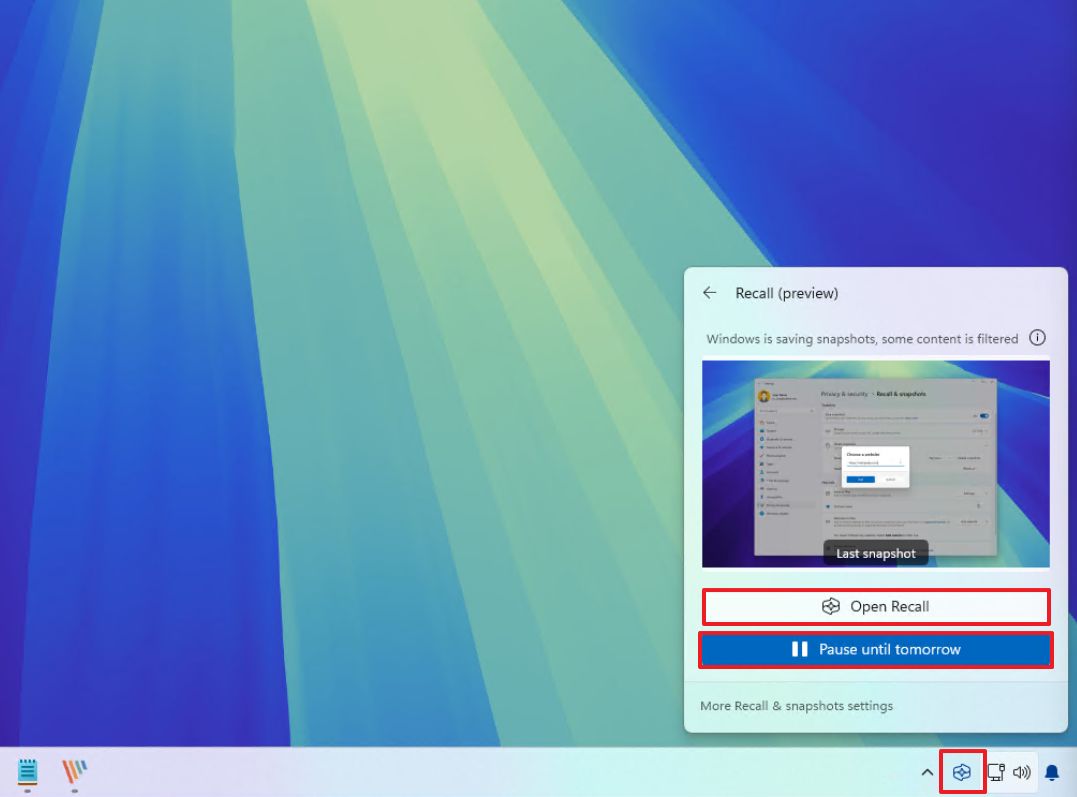
- (Option 2) Click the “Resume snapshots” button to manually turn on the feature.
In the Recall menu’s dropdown, you can see the most recent screenshot the feature captured along with its current state.
Additionally, you have the option to access the feature page within the Settings app by clicking on “‘Expand Recall & Snapshots settings’“.
How to search and find activities on Windows Recall
Windows Recall is a straightforward feature once it’s configured, but there are some details you need to know.
Start a search
To use search with Recall AI, use these steps:
- Click the Windows Recall button in the System Tray.
- Sign in with your Microsoft account credentials to access the app.
- Click the Open Recall button.
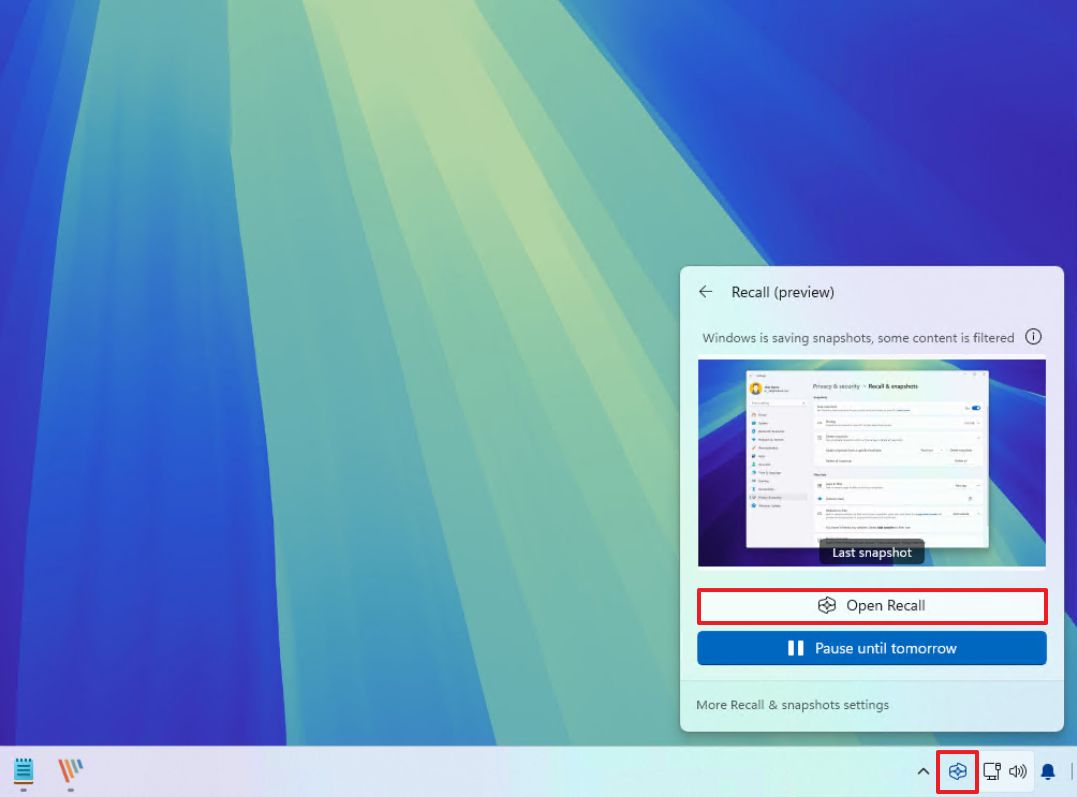
- Quick tip: You can also find the app from the Start menu, and you can right-click the app and pin it to the Taskbar.
- (Option 1) Use the search box to search for an activity using natural language.
- Quick tip: You can also click the “microphone” button and perform a voice search.
- Select the snapshot from the result.
- Quick tip: If the feature can’t find any matches, you can click the “File Explorer results” option to perform a traditional Windows Search.
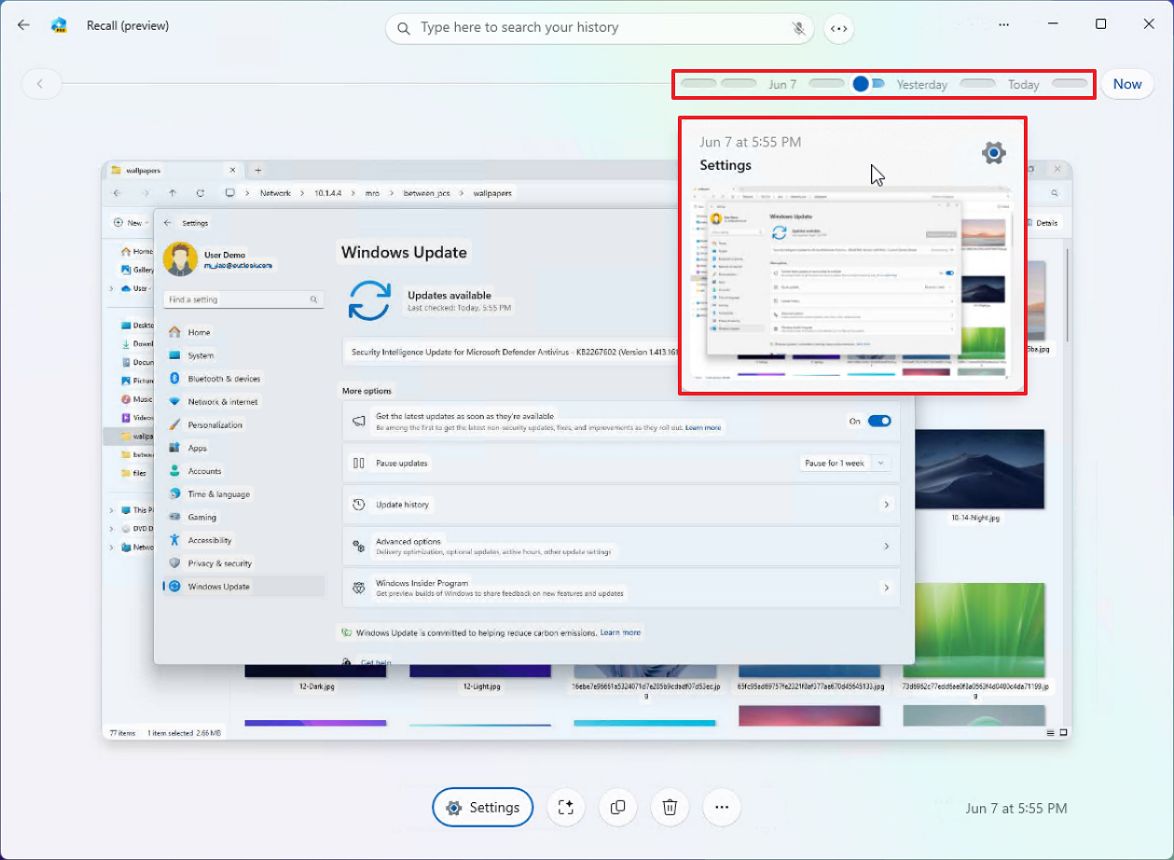
- (Option 2) Use the timeline slider to scroll back in time to find a particular snapshot.
In the search bar, feel free to input your query just as if you were asking someone directly. For example: “Locate the red leather jacket I came across online a few days ago while surfing the web.
When you hit the ‘Enter’ key, the function will delve into your previous actions and present a summary with an image of the red leather jacket included.
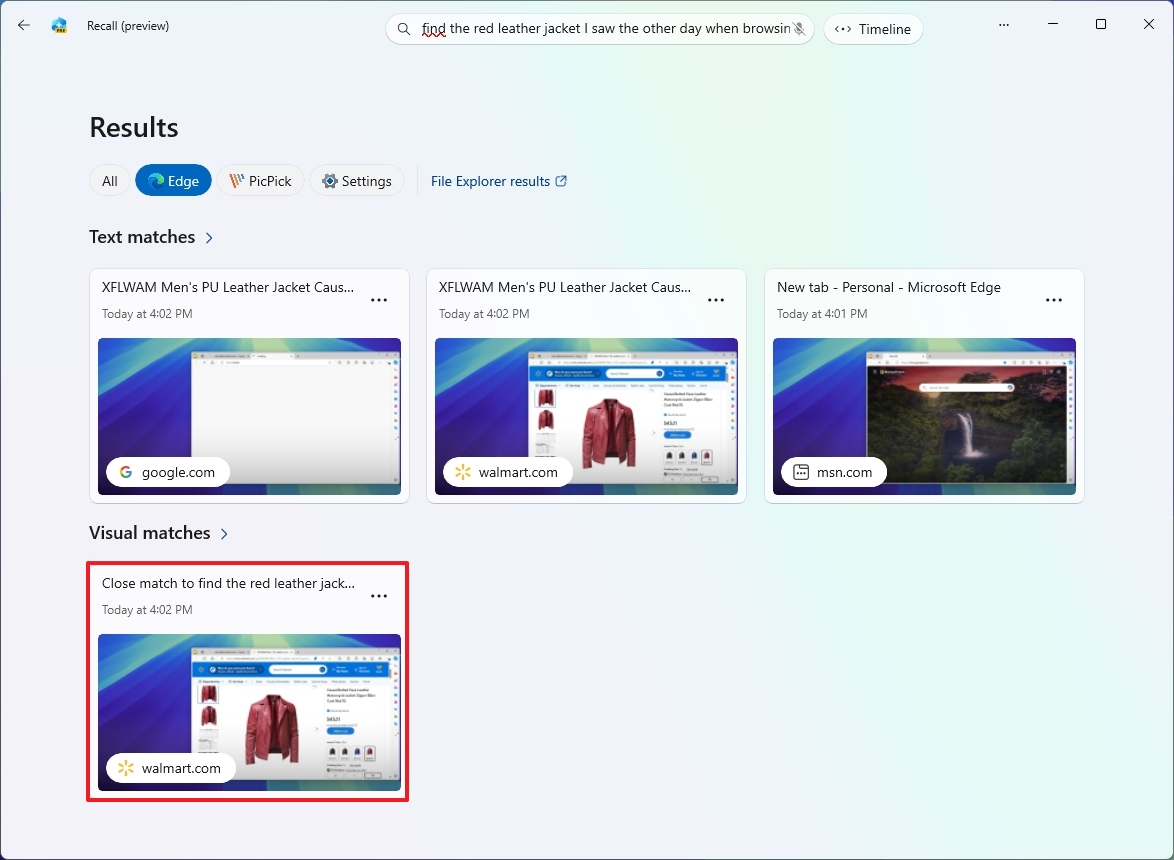
As a devoted user, I’d usually find myself presented with all the outcomes across various applications. However, the good news is that there are handy tools at my disposal to refine my search and hone in on exactly what I need!
Windows Recall delivers text and picture matches that are more closely connected to your inquiry. Additionally, the “‘Close match’” results will contain at least one keyword, phrase, or image from your search term. The “‘Related match’” results may not directly relate to your search term.
By moving the timeline scrollbar, you can navigate directly to a specific point in time when you were engaged in a particular task. The timeline is broken down into various segments and timeframes. Hovering your cursor over the timeline allows you to preview the activities from the selected time period. If the slider isn’t visible, click on the “Timeline” button located next to the search box instead.
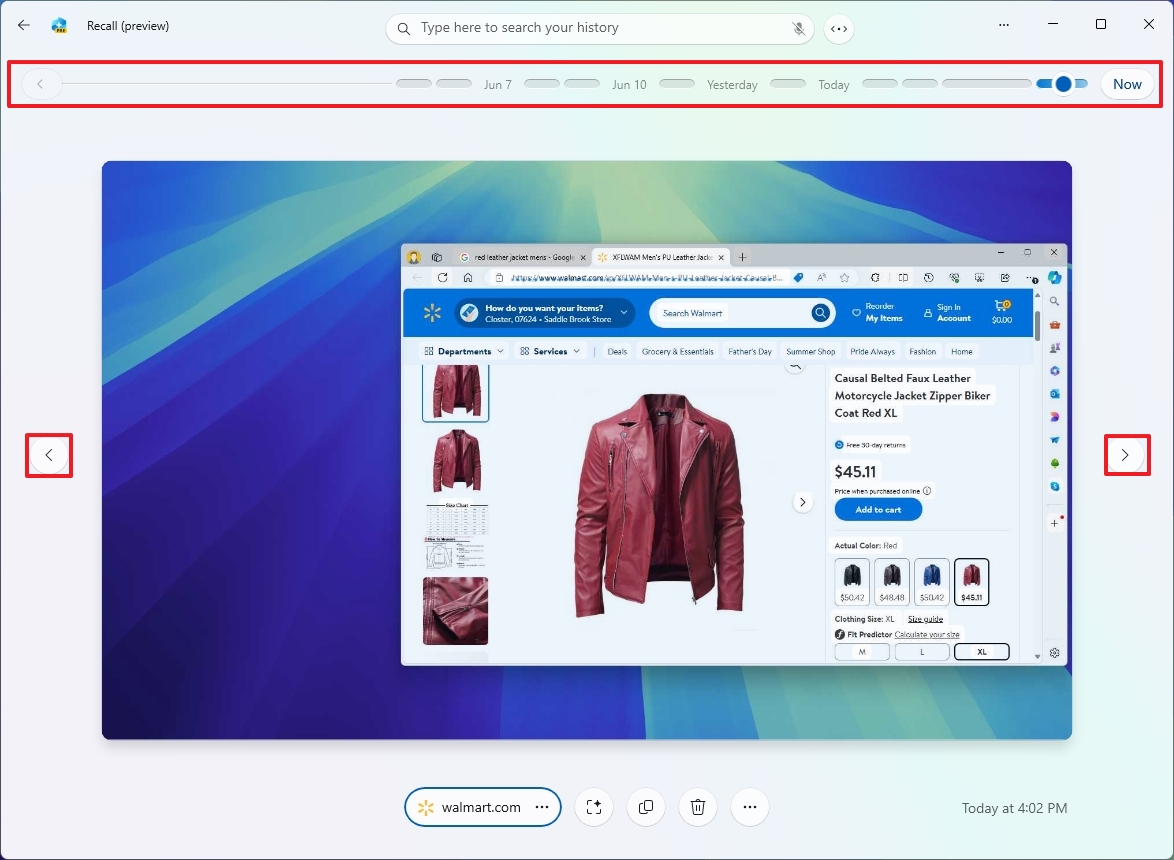
You can also use the navigation buttons on either side of the app to go between snapshots.
When you choose a segment from the timeline or certain actions, Windows Recall will retrieve a saved version (snapshot) for that period.
Clicking the “Now” button captures an image of your current desktop. You’re able to work with this specific screenshot, but it won’t be stored in your Recall history.
Interact with snapshots
It’s worth mentioning that while engaging with snapshots, you’re essentially making use of the “Click-to-Perform” functionality.
The “Click to Do” feature uses AI models directly on your device to analyze screenshots, providing suggestions for various tasks based on the text and visual components within the images you are currently viewing.
To interact with a Recall snapshot with Click to Do, use these steps:
- Open the Windows Recall app.
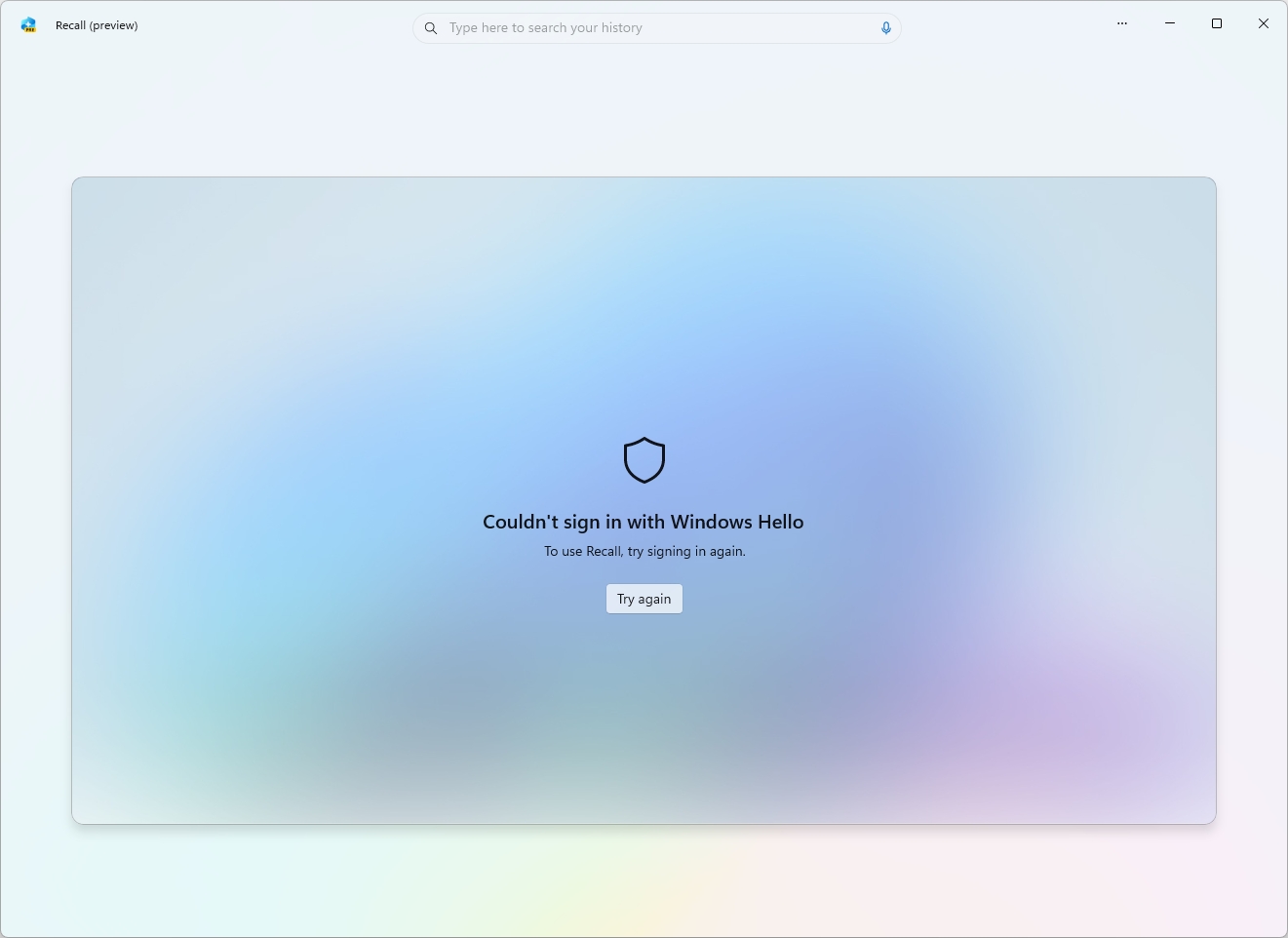
- Sign in using Windows Hello to access the app.
- Perform a search with a text prompt or voice or by using the timeline slider.
- Select the snapshot from the result.
- Quick tip: You can also right-click a snapshot to copy or delete the element from the context menu.
- In the snapshot, you will notice an animation around the element. This is the Click to Do feature analyzing the contents of the element. The snapshot also includes a date and time stamp in the bottom-right corner.
- (Option 1) You can select and copy text, similar to extracting text from images using the Snipping Tool.
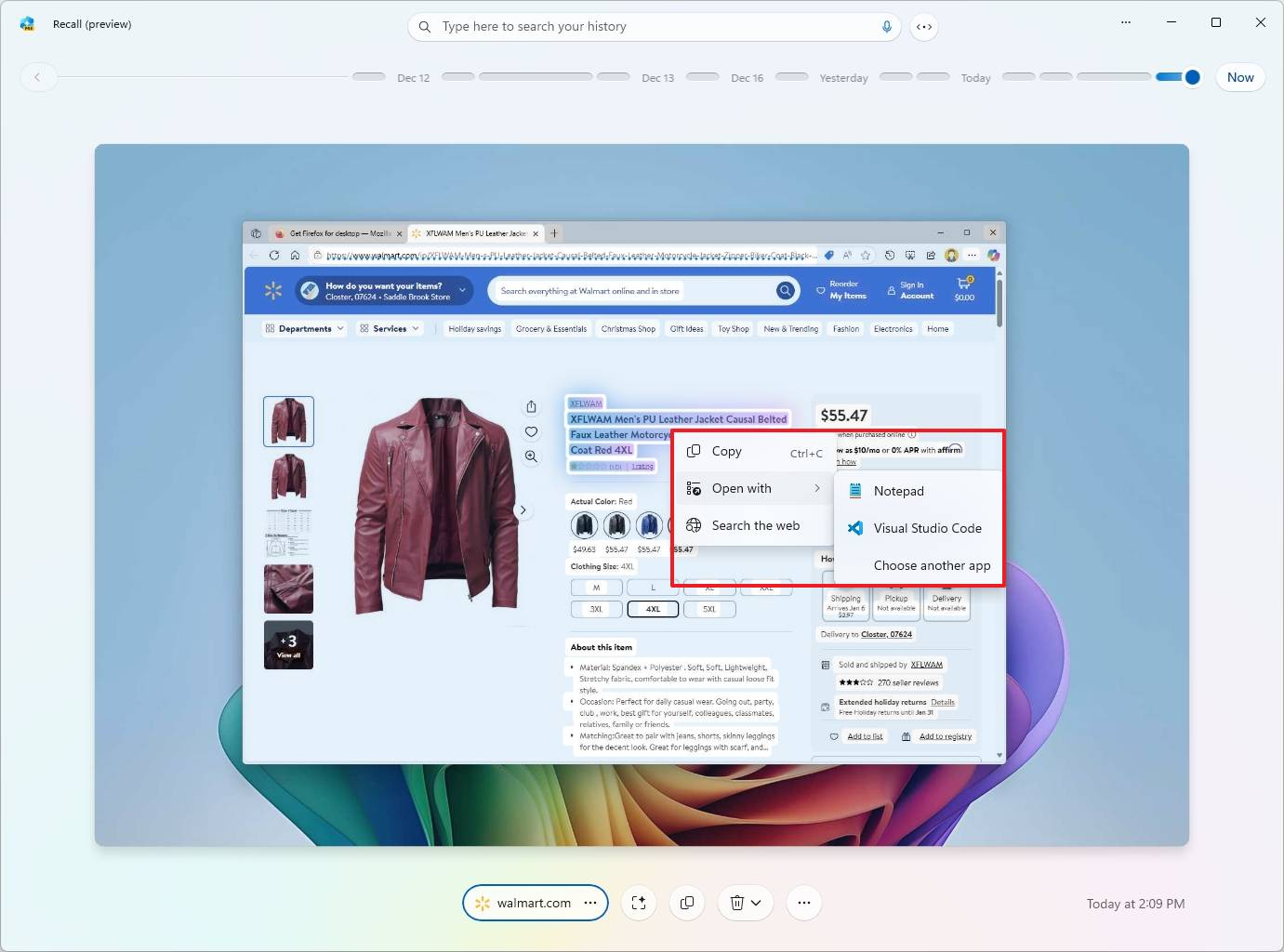
- Select an element from the snapshot to access different options. For example, blur and remove background and erase object.
- Quick tip: When using the Click to Do feature on an object, the options to blur and erase the background will open the screenshot with the Photos app, and the option to remove the background will open with the Microsoft Paint app.
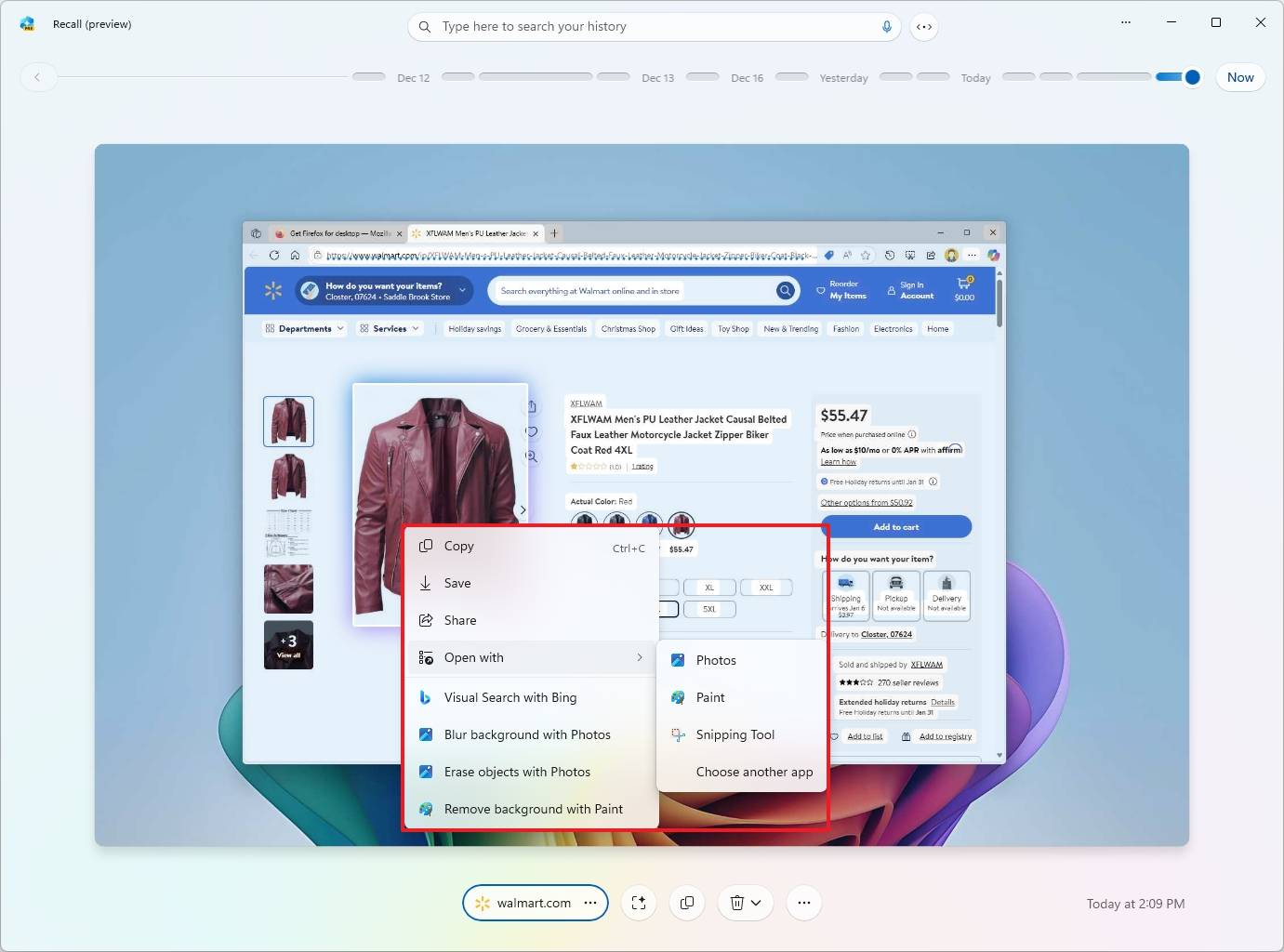
- (Option 2) Click the app button at the bottom of the page to launch the app.
- Quick note: If the feature is capable, it will restore the app in the same location as the app you left off. If you’re dealing with a snapshot of a website, the page on the snapshot will load instead of simplifying opening the web browser.
- (Option 3) Click the “Click to Do” button to turn the feature on or off.
- (Option 4) Click the Copy button to copy the snapshot as a screenshot to the clipboard.
- (Option 5) Click the “Delete” (trash) button to erase the snapshot from the system.
- (Option 6) Click the context menu to access different options. However, currently, you can only choose to open the screenshot with the Snipping Tool.
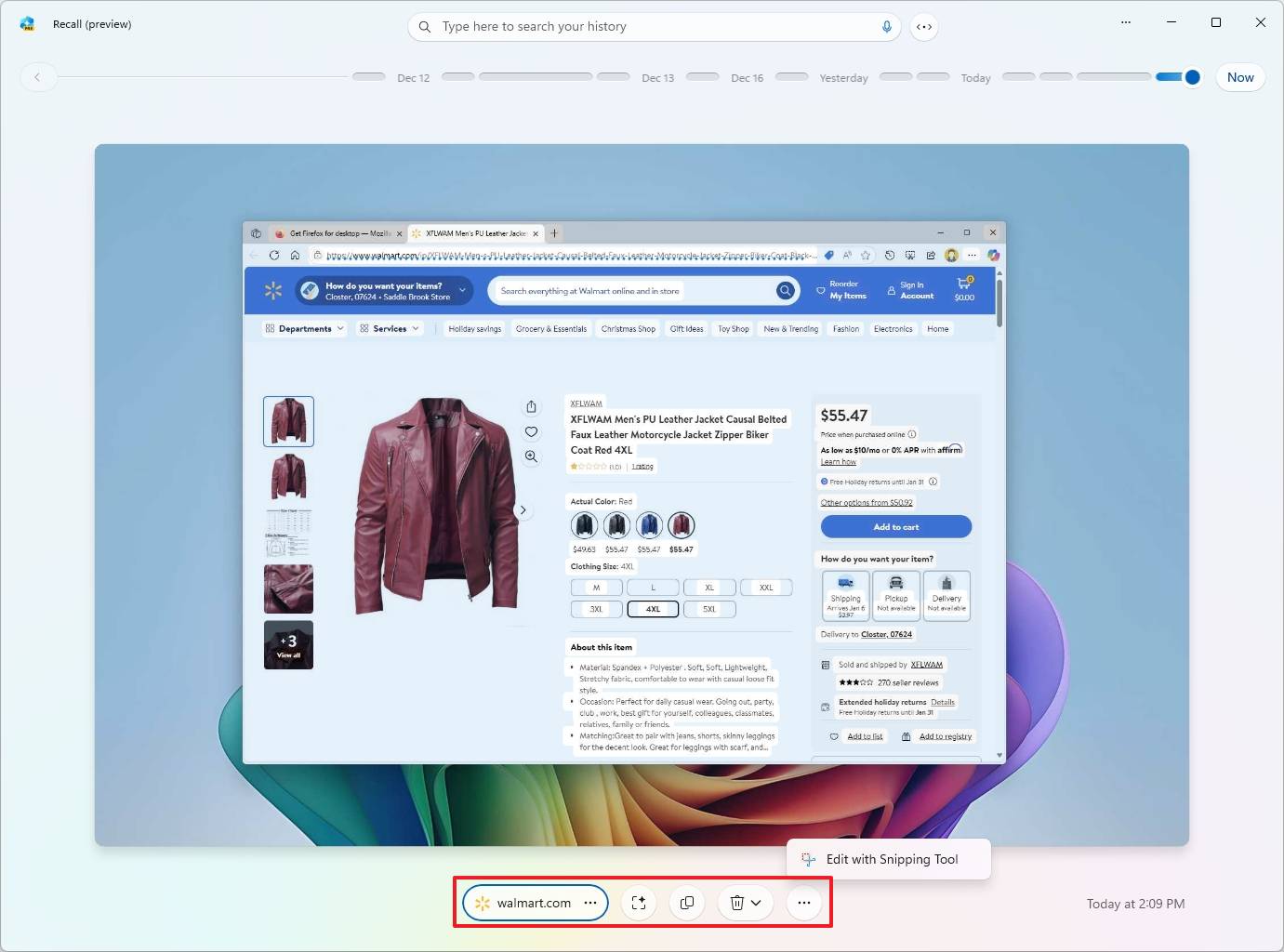
After finishing the process, feel free to move on to a new search or shut down the application for the safety of your information.
Other details about Windows Recall
If you’ve made it this far, you should have a solid understanding of how to apply the Windows Recall function. Nevertheless, I thought you might be interested in some further insights.
The function works only when your device is being actively used; if it remains idle for a while, the function will shut down automatically until you start a new task. You can tell this has happened because the Windows Recall icon in the System Tray will switch to an inactive state.
As a dedicated user, I’ve come to recognize the System Tray icon as my constant reminder that Windows Recall is active on my machine. Just like the location icon that pops up when an app needs access to my whereabouts, this one stays put and can’t be moved or hidden. It’s a reassuring presence, signaling that my computer’s memory is optimized for top performance.
Disabling the Windows Recall feature means it won’t be available again. You won’t see its icon in the System Tray anymore, and it won’t show up in your Start menu either.
Furthermore, disabling the feature won’t cause the data on your computer to be erased automatically. Once you decide to activate it again, the prior history will still be accessible. However, if you wish to wipe the history cache, you’ll need to manually remove the snapshots yourself.
Microsoft is taking some extra precautions after receiving many security concerns from feedback.
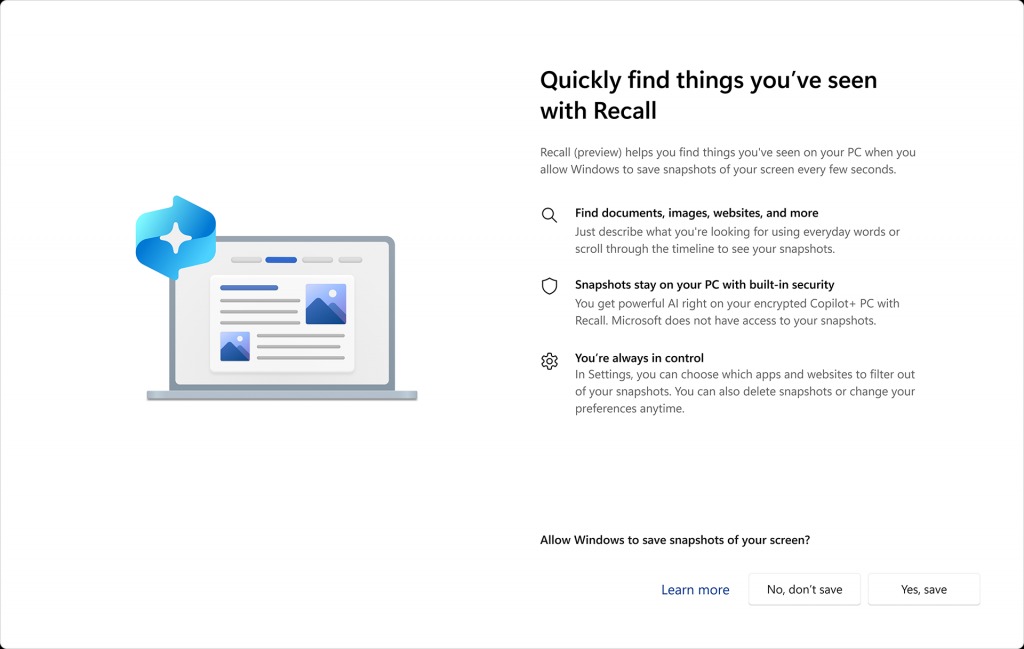
This update introduces a fresh stage during the Windows 11 installation process, where you can choose whether to activate or deactivate a specific setting on your device. Previously, Microsoft intended for this feature to be automatically activated upon setup.
To utilize the AI function, it’s essential to set up Windows Hello authentication method – either PIN, facial recognition, or fingerprint scan – for your user account. Additionally, you’ll be required to log into the “Recall” application to view your activity timeline.
Originally, the Recall database was shielded by a security system; upon signing in, the data appeared in its unencrypted form. But with recent updates, the firm is now scrambling the database and its backups, making them harder to access.
Beyond these modifications, Windows Recall will benefit from the safeguard provided by Secure-core PC firmware, Microsoft’s Pluton security processor, and advanced sign-in security through Windows Hello Enhanced Sign-in Security (ESS). It’s important to note that the computer must have BitLocker (or Device Encryption) enabled in order to activate this feature.
Moreover, Microsoft guarantees that data gathered by Recall remains solely on your device, no information is transferred to the cloud for storage, and they promise not to utilize this data in training their artificial intelligence systems.
Lastly, it’s worth mentioning that at first, the feature is primarily tailored for English, Simplified Chinese, French, German, Japanese, and Spanish languages.
More resources
Read More
2024-12-20 18:11