As a seasoned researcher with years of experience troubleshooting and optimizing computer performance, I can confidently say that understanding drive activity is crucial for maintaining system health and efficiency. While most modern systems have switched to SSDs, these drives are not invincible, and they do require regular monitoring to ensure optimal performance.
On Windows 11, you can keep track of your system drive’s performance by observing metrics like data transfer rates and reaction times to get insights into its behavior during specific periods. In this tutorial, I will demonstrate two methods for accomplishing this task without relying on external applications.
Although most laptops and desktop computers have switched to Solid-State Drives (SSDs), which are a lot faster than traditional Hard Disk Drives (HDDs), regardless of the storage technology, depending on the application and the task at hand, it will generate a number of reads and writes that can affect performance.
To examine the behavior of your drives for insight into performance or to diagnose storage problems in Windows 11, you can utilize the Task Manager and Performance Monitor. These tools will enable you to observe live data such as transfer speeds, reaction times, and additional details.
In this tutorial, I will walk you through simple methods for assessing your Windows 11 drive activity. This guide offers two straightforward approaches to evaluate your drive’s performance instantaneously. These steps can be utilized for testing drive performance, or alternatively, I have prepared another guide to help you analyze the condition of an SSD.
How to monitor drive activity from Task Manager
To check the drive activity through Task Manager, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Task Manager and click the top result to open the app.
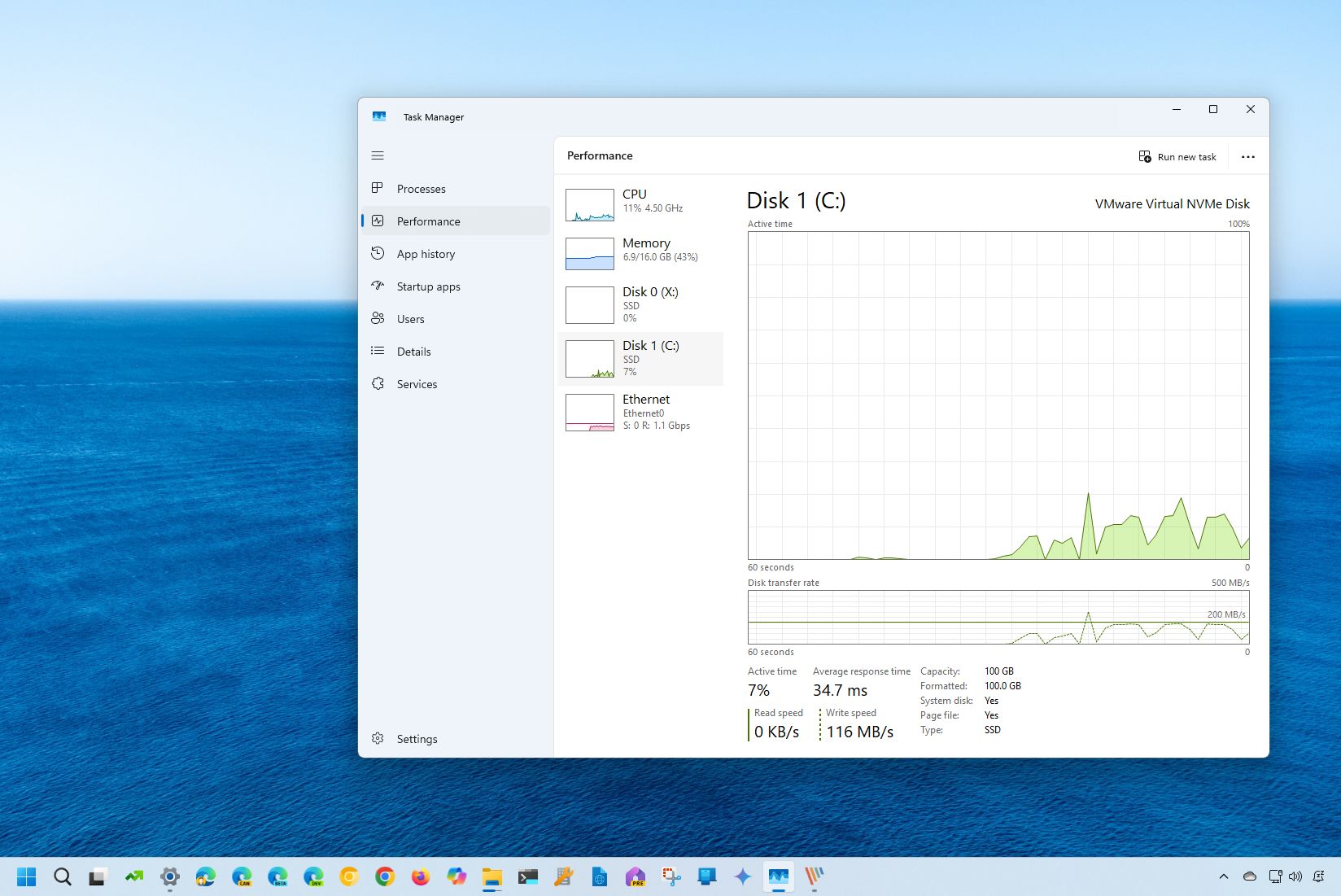
- Click on Performance from the left pane.
- Select the drive from the left side.
- Check the “Active time” section to review the percentage of reads and writes over time (every 60 seconds).
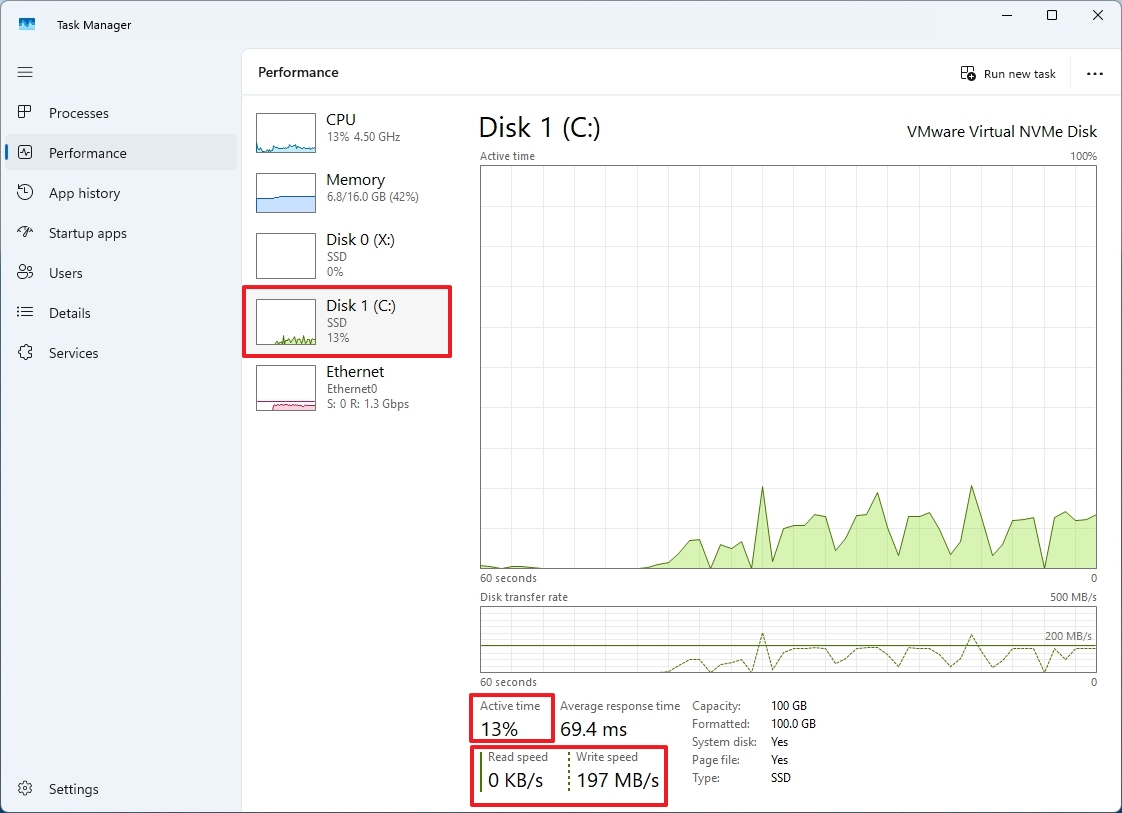
- Quick note: This information is also represented in the main “Active time” graph.
- Check the “Average response time” information, which is the amount of time it takes for a hard drive or solid-state drive to respond to a read or write request from the operating system.
- Check the “Read speed” and “Write speed” to determine the current speeds (Kilobytes or Megabytes per second) of the drive.
- Quick note: This information is also represented in the main “Disk transfer rate” graph.
Once you complete the steps, you will have an overview of the overall performance of the drive.
How to monitor drive activity from Performance Monitor
To monitor the drive activity with the legacy Performance Monitor app, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Resource Monitor and click the top result to open the app.
- Click the Disk tab.
- Check the “Processes with Disk Activity” section to read and write speeds (Bytes per second) for processes that are currently using or have recently used disk resources.
- Click on Disk Activity.
- Check the read and write speeds for each of the system processes.
- Check the overall operations per second (IOPS) or bandwidth in the “Disk Activity” tab header.
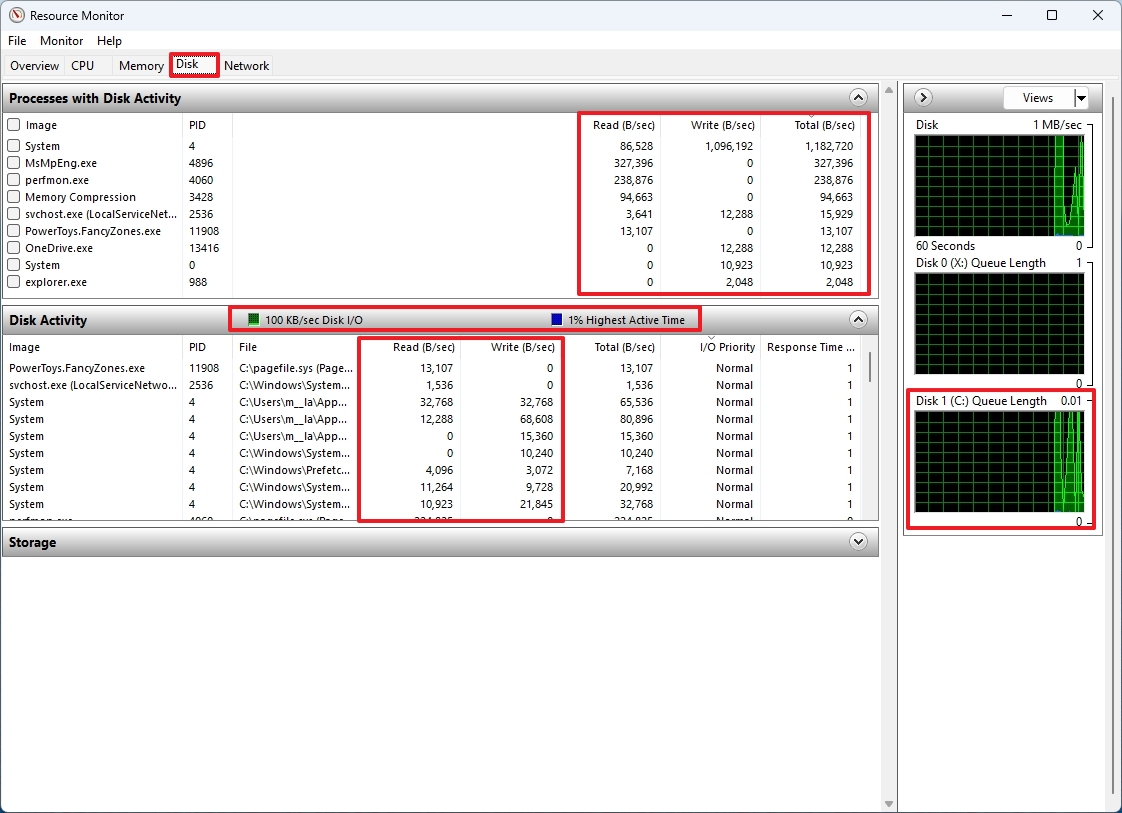
On the right panel, you’ll see individual graphs representing each drive connected to your computer. At the top, you’ll find a graph showing Input/Output Operations Per Second (IOPS) for these drives. Below it, Queue Length graphs provide insights into the performance of each drive.
As a tech enthusiast, I’ve noticed when a queue is long, it typically indicates my storage device is struggling to cope with the influx of read and write demands. Essentially, this implies numerous requests are stacking up, waiting for their turn to be handled, causing noticeable delays. This situation often translates into slower drive performance, which isn’t ideal when you’re trying to access or transfer data promptly.
Conversely, a short queue length suggests that the disk is effectively managing read and write requests. Since there’s minimal, if any, delay in processing these requests, programs can easily retrieve data promptly. Typically, a short queue length implies efficient drive performance.
It’s worth mentioning that it’s never recommended to use a computer with a full drive, since this can slow performance significantly. Typically, once the storage capacity reaches 70 percent, you want to start freeing up space or think about upgrading the drive with a larger capacity.
More resources
Read More
- PI PREDICTION. PI cryptocurrency
- Gold Rate Forecast
- WCT PREDICTION. WCT cryptocurrency
- LPT PREDICTION. LPT cryptocurrency
- Guide: 18 PS5, PS4 Games You Should Buy in PS Store’s Extended Play Sale
- Solo Leveling Arise Tawata Kanae Guide
- Despite Bitcoin’s $64K surprise, some major concerns persist
- Jack Dorsey’s Block to use 10% of Bitcoin profit to buy BTC every month
- Elden Ring Nightreign Recluse guide and abilities explained
- Shrek Fans Have Mixed Feelings About New Shrek 5 Character Designs (And There’s A Good Reason)
2024-09-14 13:39