On Windows 11, when you have more than one hard drive, you can merge them into a single, larger storage space to prevent your data from being scattered manually across the drives automatically.
There are several approaches to setting up this configuration, either through the traditional Disk Management tool or the contemporary Settings application. If you prefer to utilize Disk Management, you can opt for the “Spanned” or “Striped” feature when creating a new volume. These options provide similar functionality but employ distinct methods for data storage on your hard drive.
Through the Settings app method, you can set up two or more drives as a single logical unit by utilizing the “Storage Spaces” feature. This setup allows you to leverage either the “‘Basic’ ” or ‘Error Correction’ ” functions, which are similar to the “Mirrored” and “Raid 5” options. However, while the ‘Basic’ option does not offer data protection, the ‘Error Correction’ feature ensures data security in case of a drive failure as it writes data with parity information.
It’s wise to set up a dependable data backup system if you intend to utilize any of these features. This will ensure that you can restore your files in the event of hardware malfunction or data spoilage.
In this step-by-step tutorial, I’ll walk you through the process of combining several secondary drives into one big drive on your Windows 11 system.
How to span volume across drives using Disk Management
To combine multiple drives into a single large volume through Disk Management, use these steps:
- Open Start.
- Search for Disk Management and click the top result (Create and format hard disk) to open the app.
- Right-click the drive volume and select the Delete volume option (if applicable).
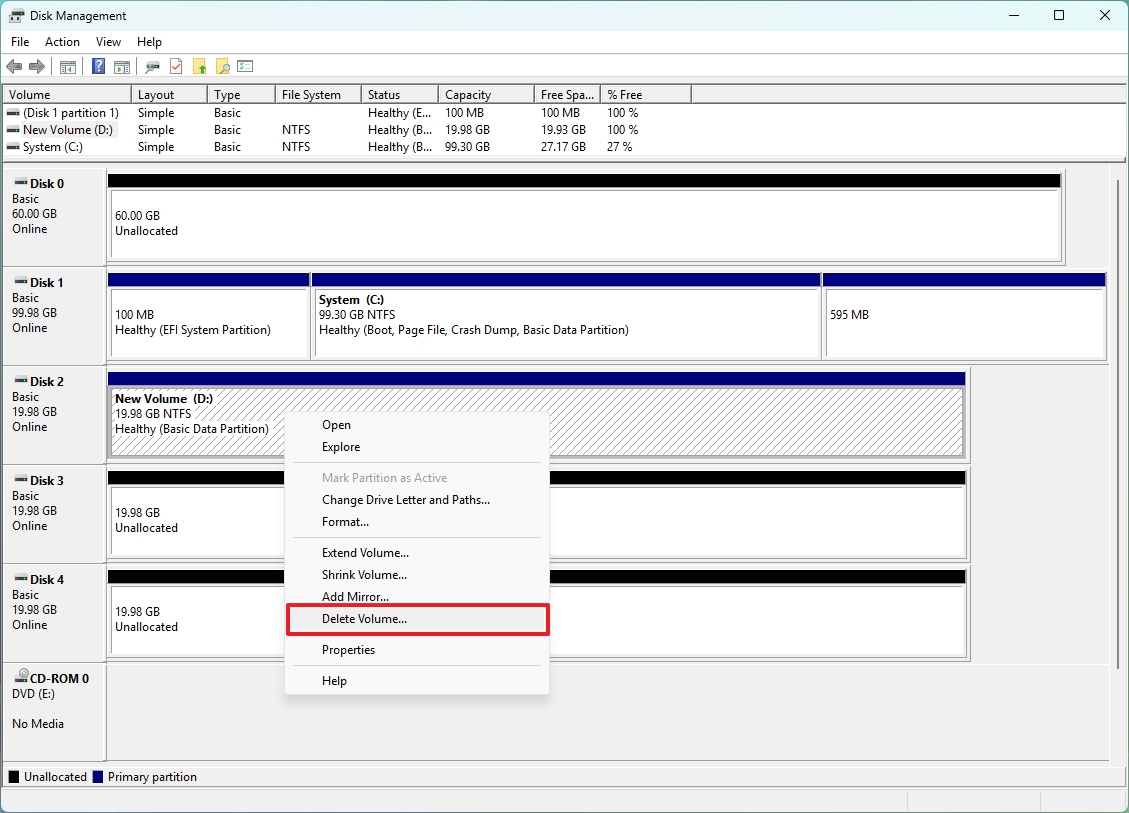
- Click Yes to confirm the deletion of the current volume and the data.
- Repeat steps 3 and 4 on the drives you want to combine.
- Right-click on the unallocated space for one of the drives and choose the “New Spanned Volume” or the “New Striped Volume” option.
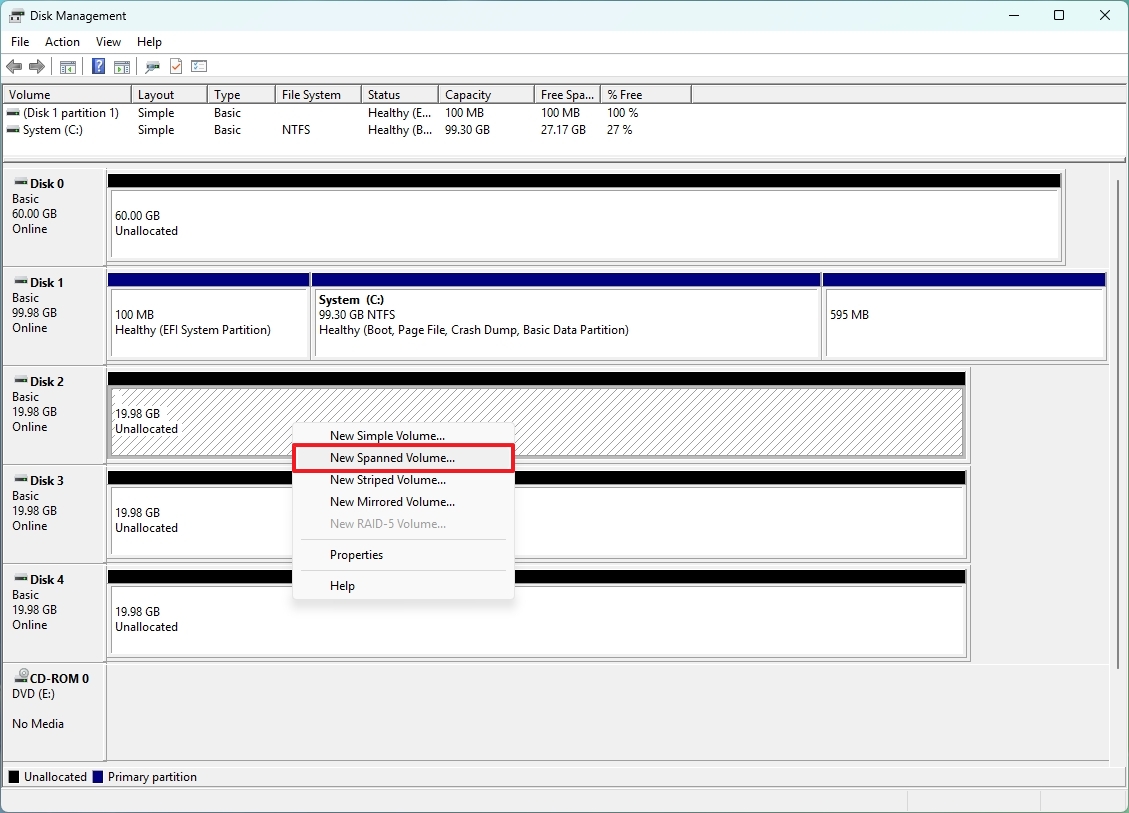
- Click the Next button.
- Choose the drives to include in this process and click the Add button. (You can only add one drive at a time.)
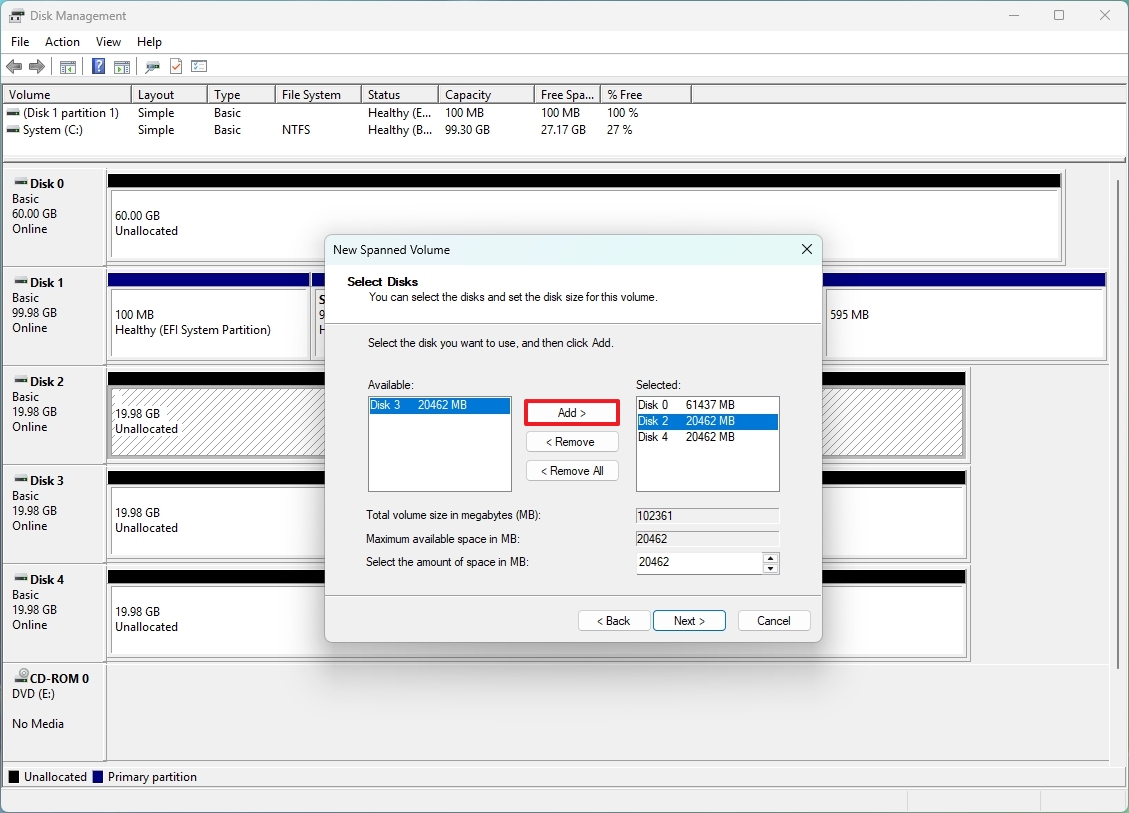
- Click the Next button.
- Select a drive letter in the “Assign the following drive letter” setting.
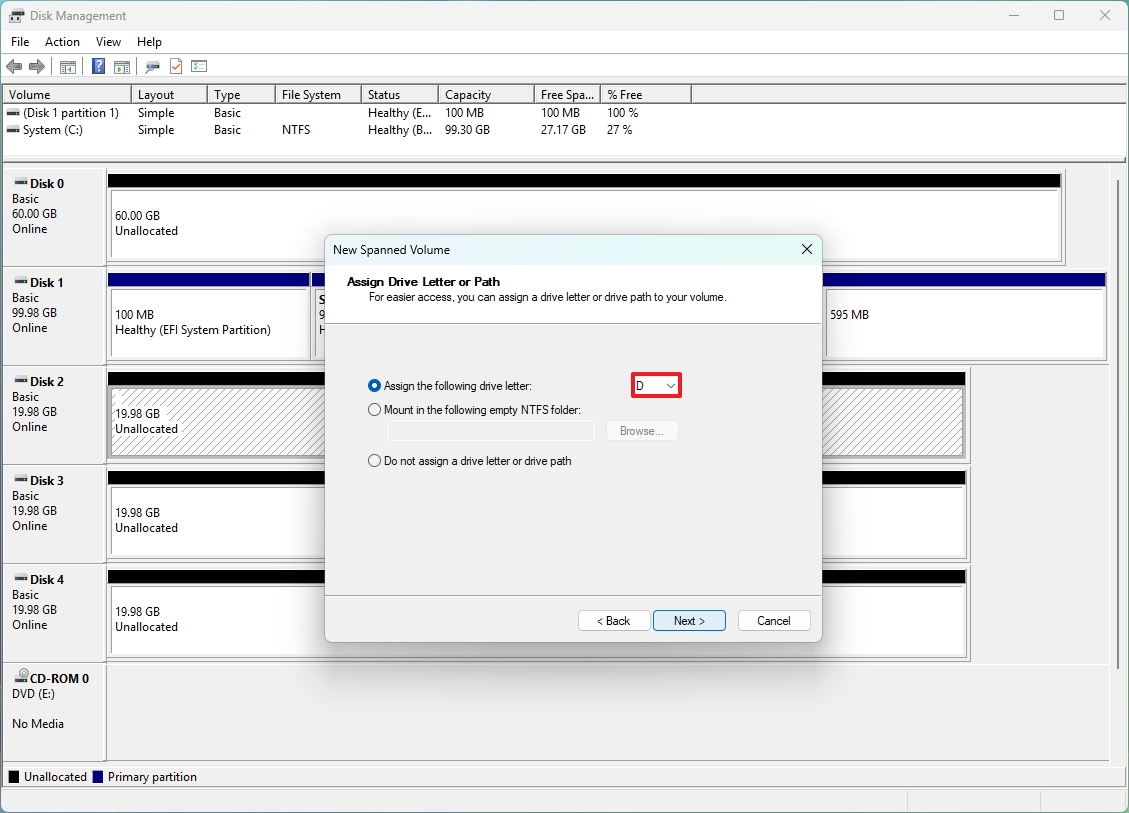
- Click the Next button.
- Use the default file system and allocation unit size.
- Confirm a label for the drive.
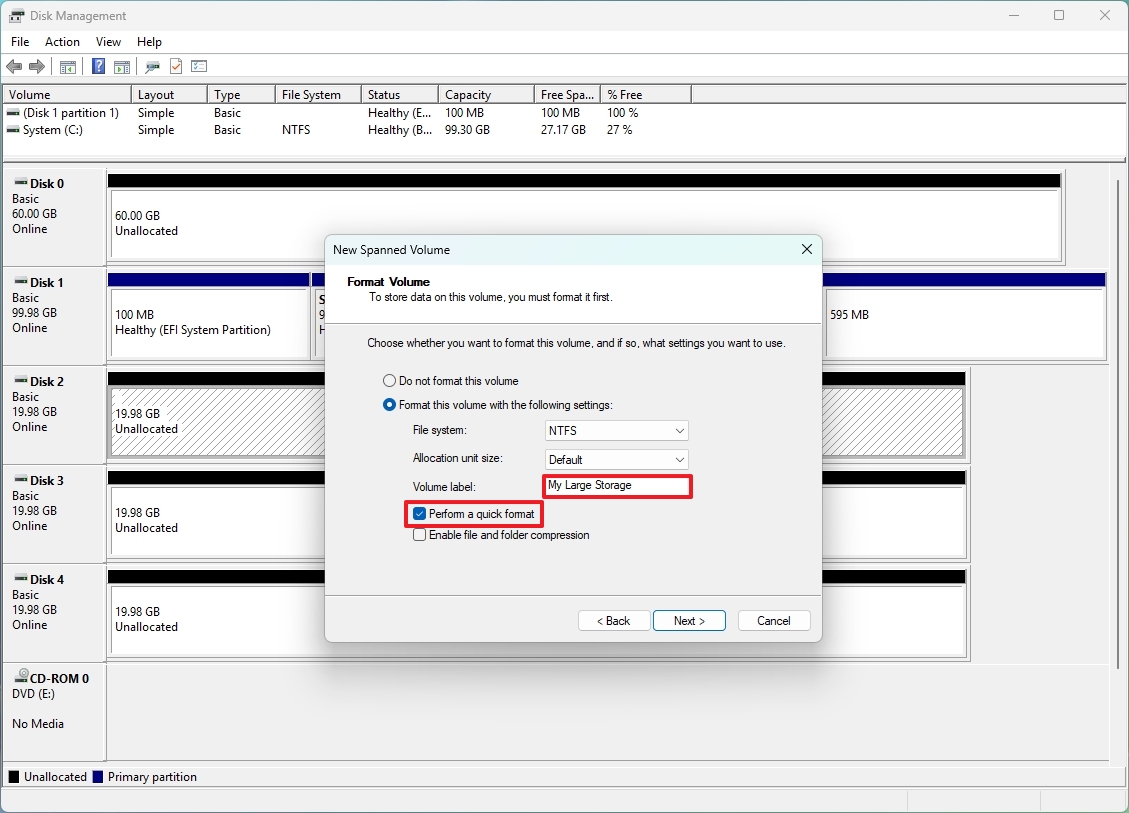
- Check the “Perform a quick format” option.
- Click the Next button.
Once you complete the steps, the system will create a large volume combining the selected drives.
The “New Spanned Volume” feature stores files one after another on every drive involved. This implies that in case a drive malfunctions or fails, the information saved on that specific drive becomes irretrievable. Nevertheless, the data stored on the functioning drives can still be accessed.
Instead, the “New Striped Volume” alternative disperses your data among various hard drives, enhancing both reading and writing speed. Yet, it’s crucial to note that if a drive malfunctions, the entire volume becomes unavailable for use. Furthermore, this option requires at least two or more drives in total.
As I observe, it’s important to point out that while this new feature has some similarities, it doesn’t take the place of a RAID (Redundant Array of Independent Disks) controller. The controller delivers a comparable solution, but with an added advantage: data redundancy and enhanced performance.
Extend volume already with data
If your storage device (drive) currently has a section (partition) filled with data, you can still expand its capacity by utilizing additional hard drives. Here’s an easy method to do so:
- Open Start.
- Search for Disk Management and click the top result (Create and format hard disk) to open the app.
- Right-click the drive volume and select the Extend Volume option.
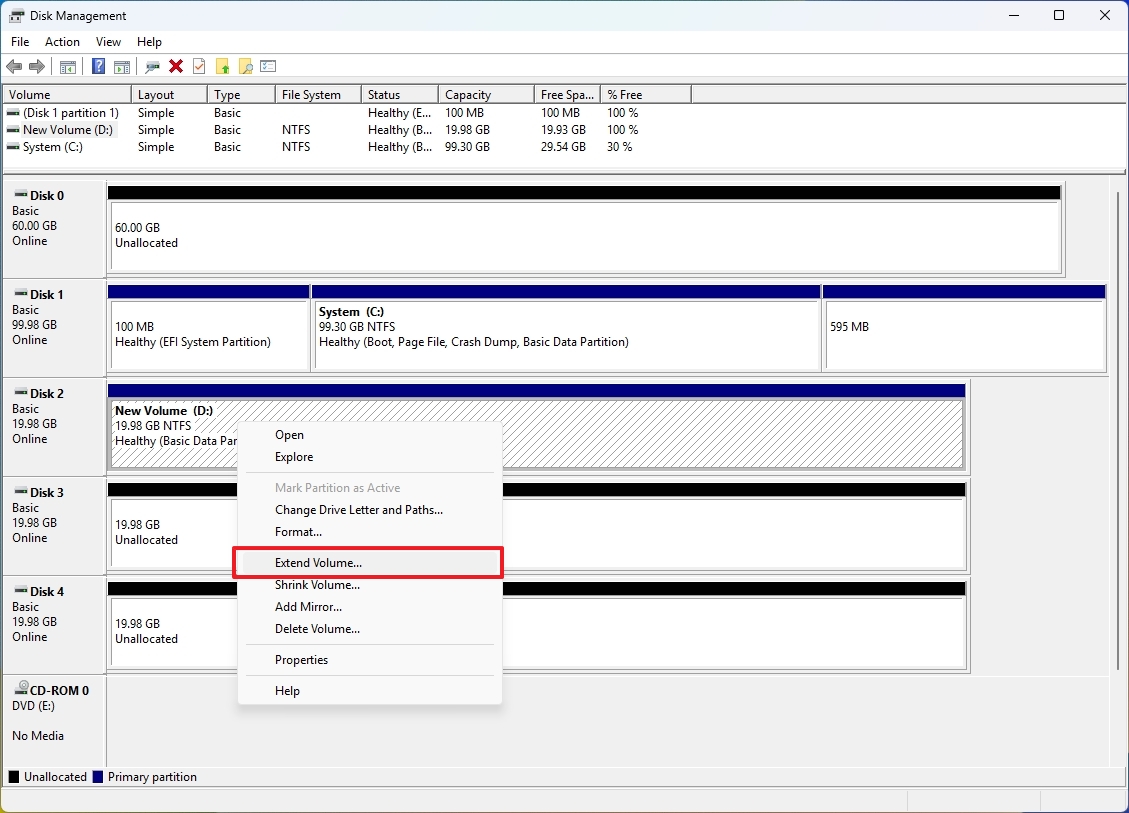
- Click the Next button.
- Choose the drives to include in this process and click the Add button. (You can only add one drive at a time.)
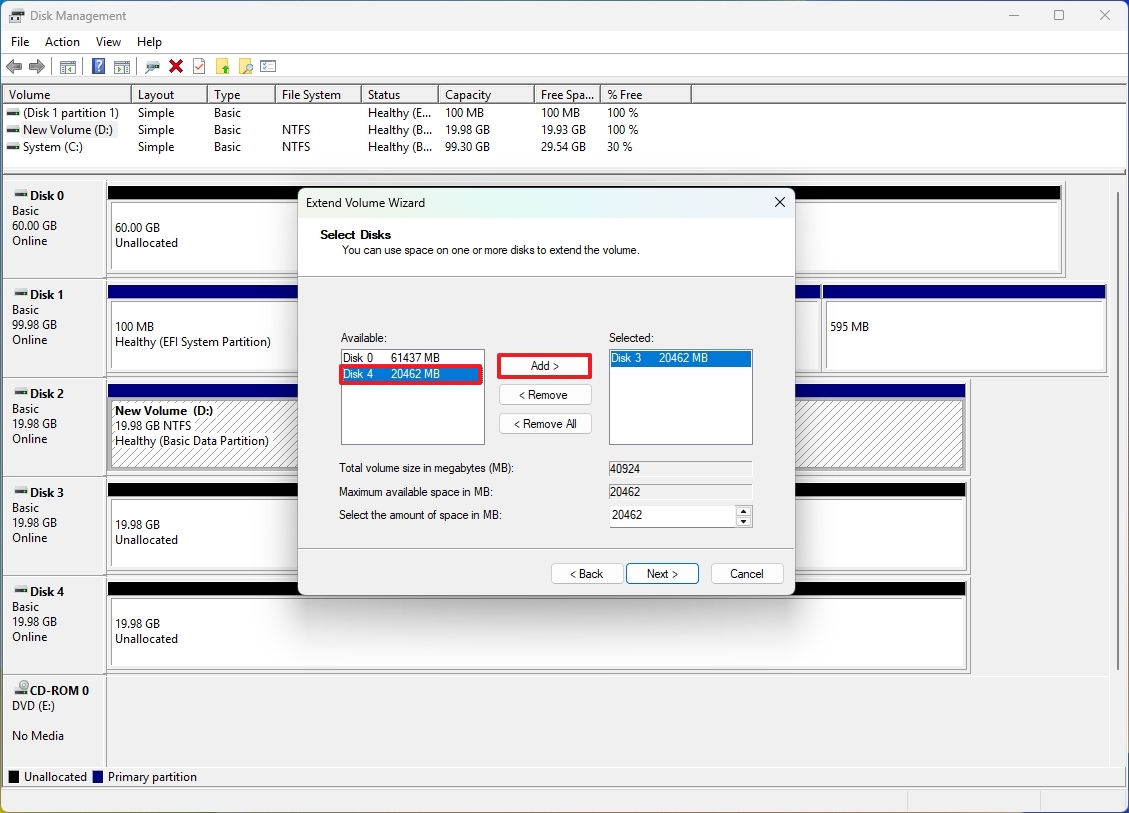
- Click the Next button.
- Click the Finish button.
- Click the Yes button to convert the drives to dynamic disks.
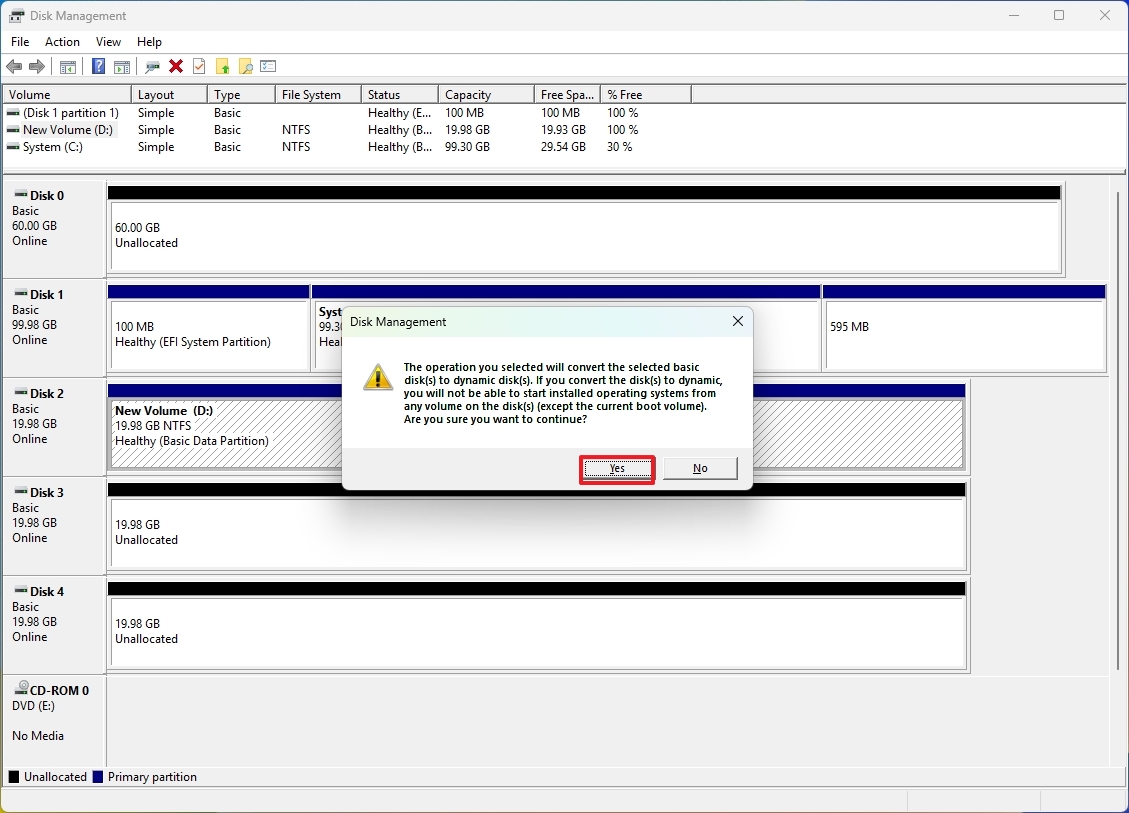
Once you finish the process, the volume will expand to the drives you chose, preserving any existing data on those drives.
Even though it’s a non-damaging method, I’d strongly advise you to make a copy of your data before continuing just to be on the safe side.
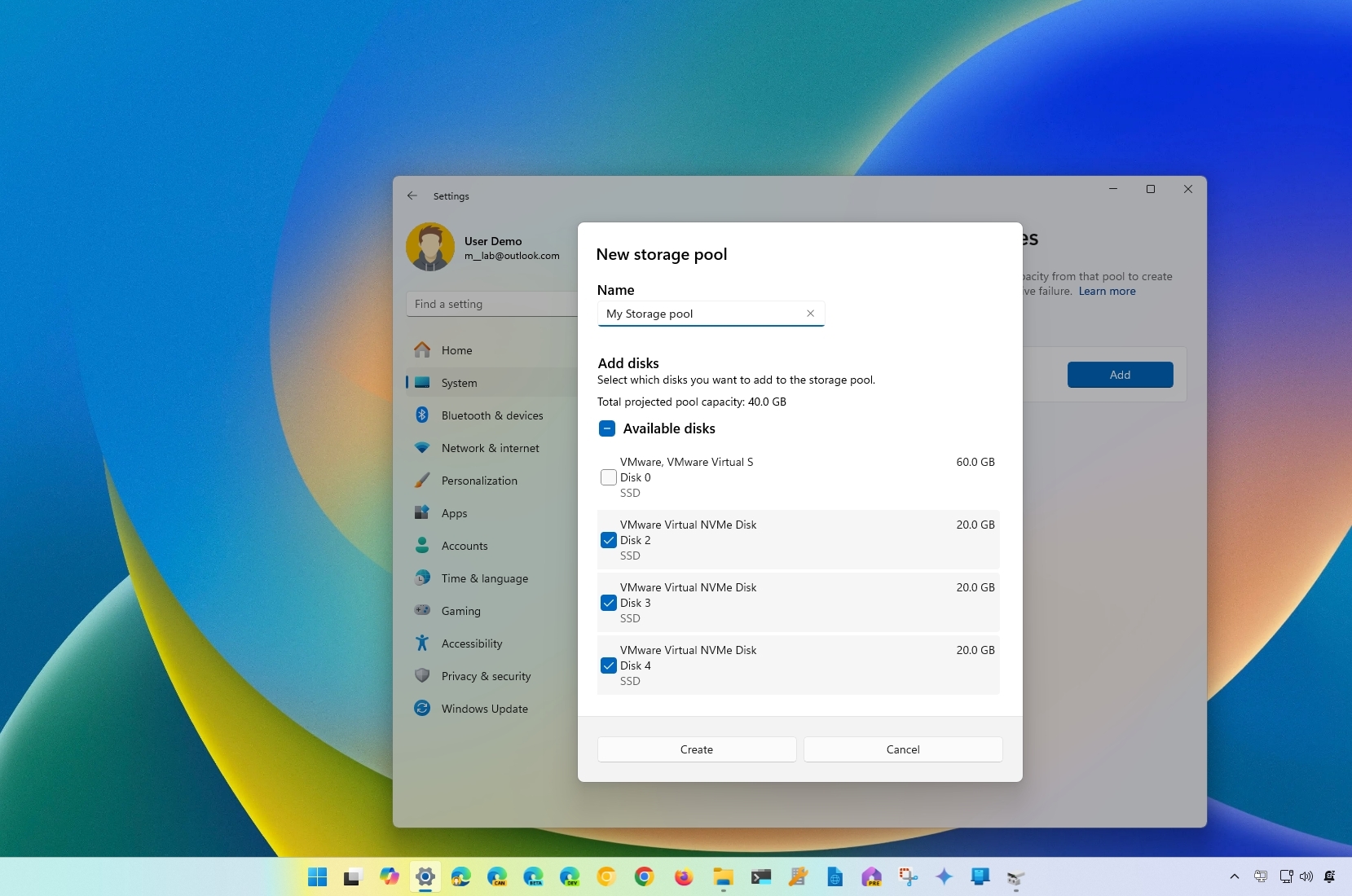
How to span volume across drives using Settings
To combine multiple drives into a single large volume through the Settings app, use these steps:
- Open Settings.
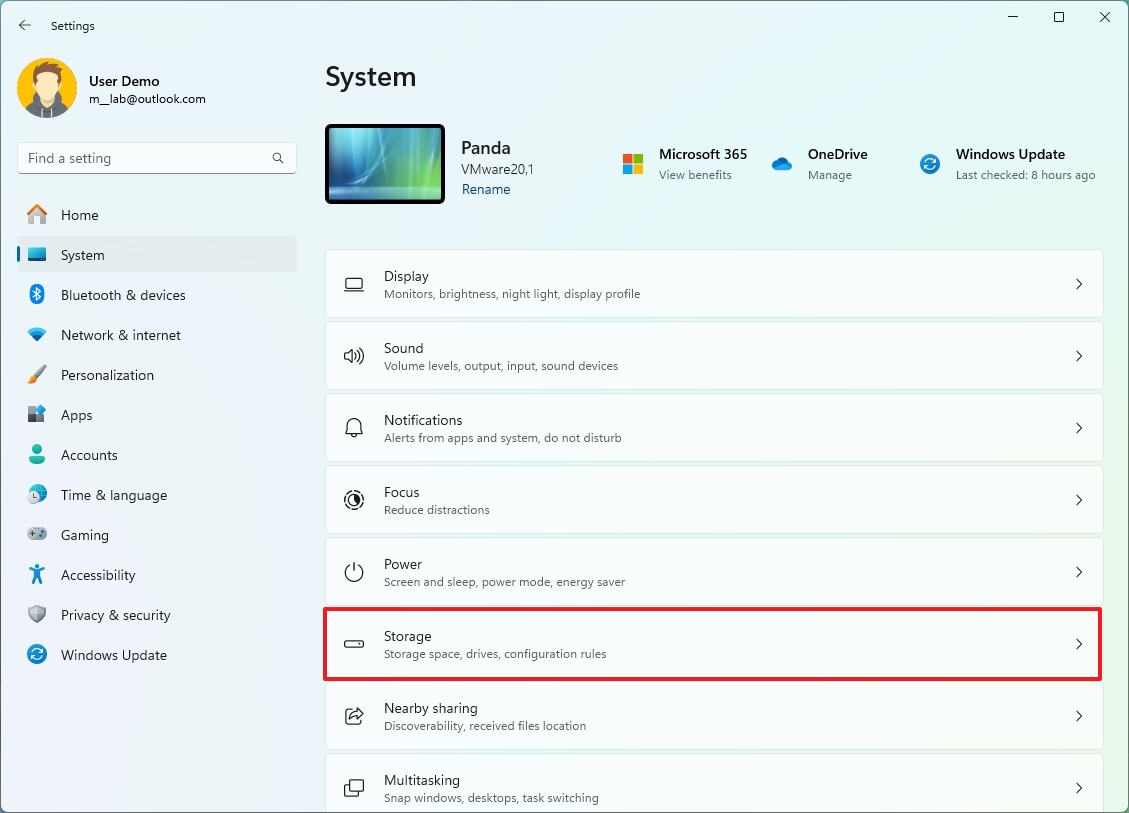
- Click on System.
- Click the Storage page on the right side.
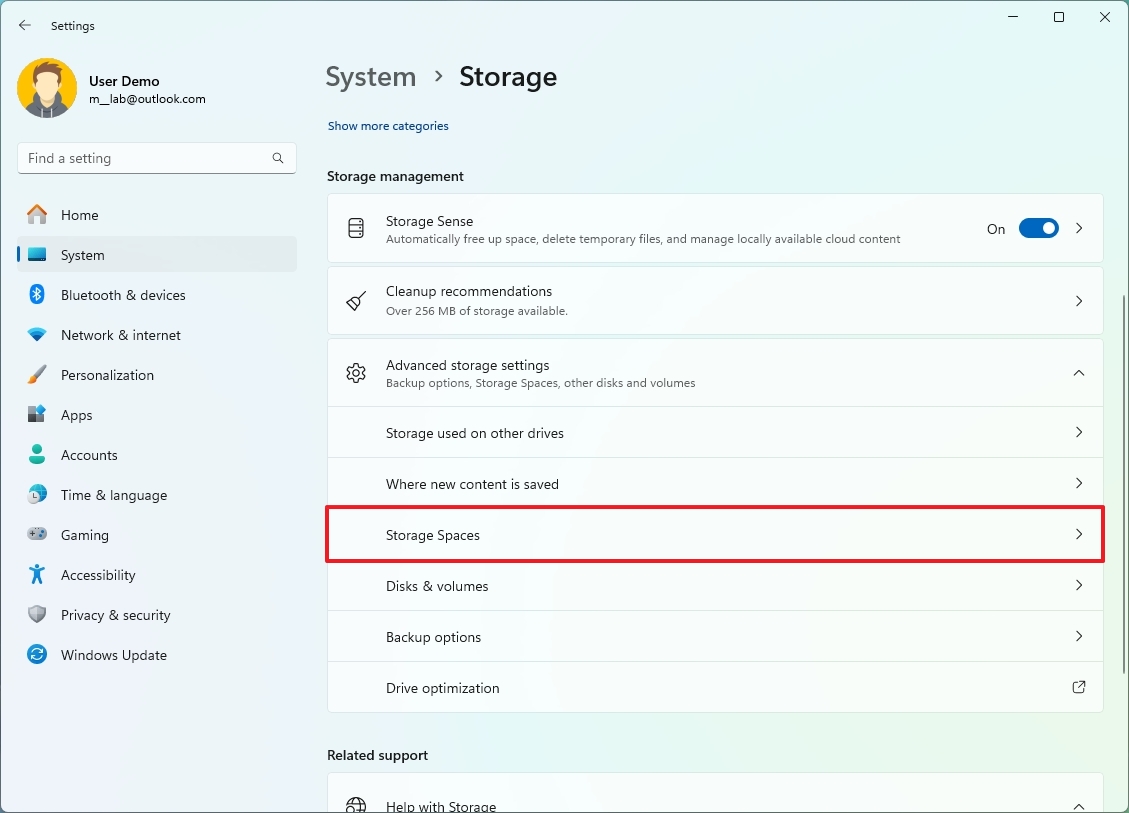
- Click on “Advanced storage settings” under the “Storage management” section.
- Click the Storage Spaces setting.
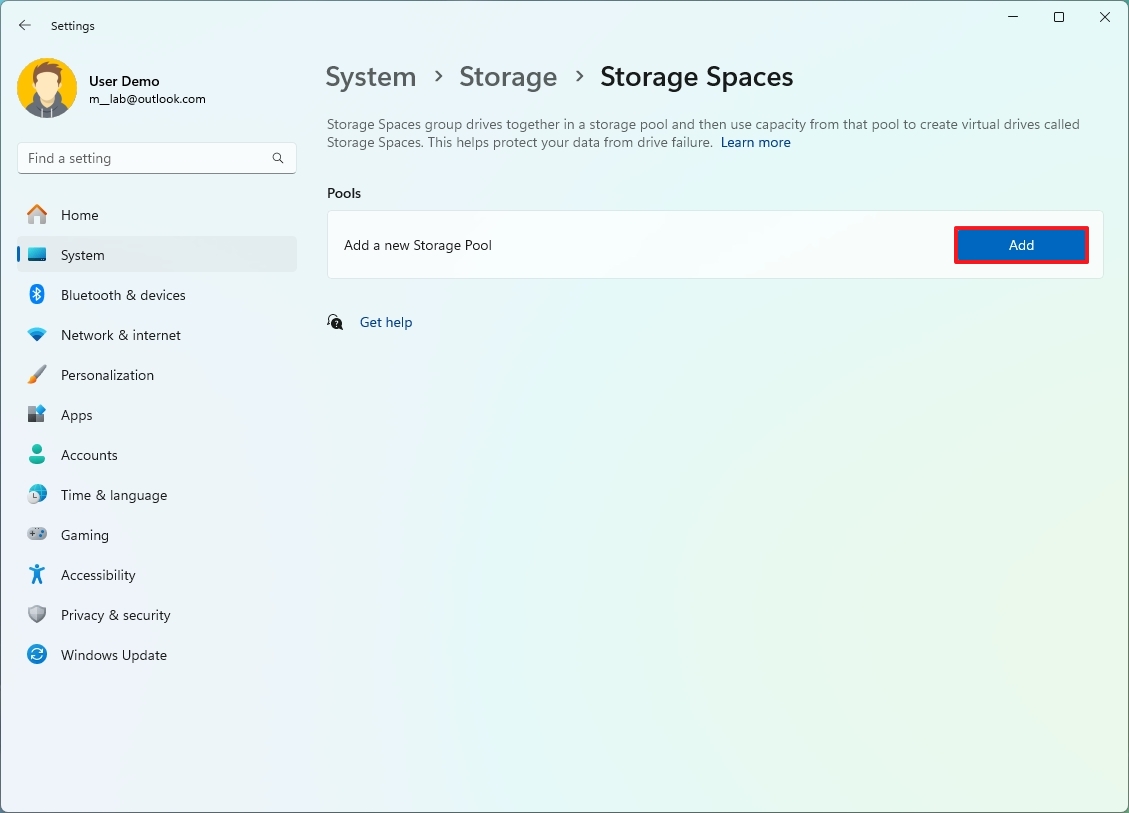
- Click the Add button under the “Pools” section.
- Confirm a name for the pool, such as “My Storage Pool.”
- Select the drives you want to combine into a single volume.
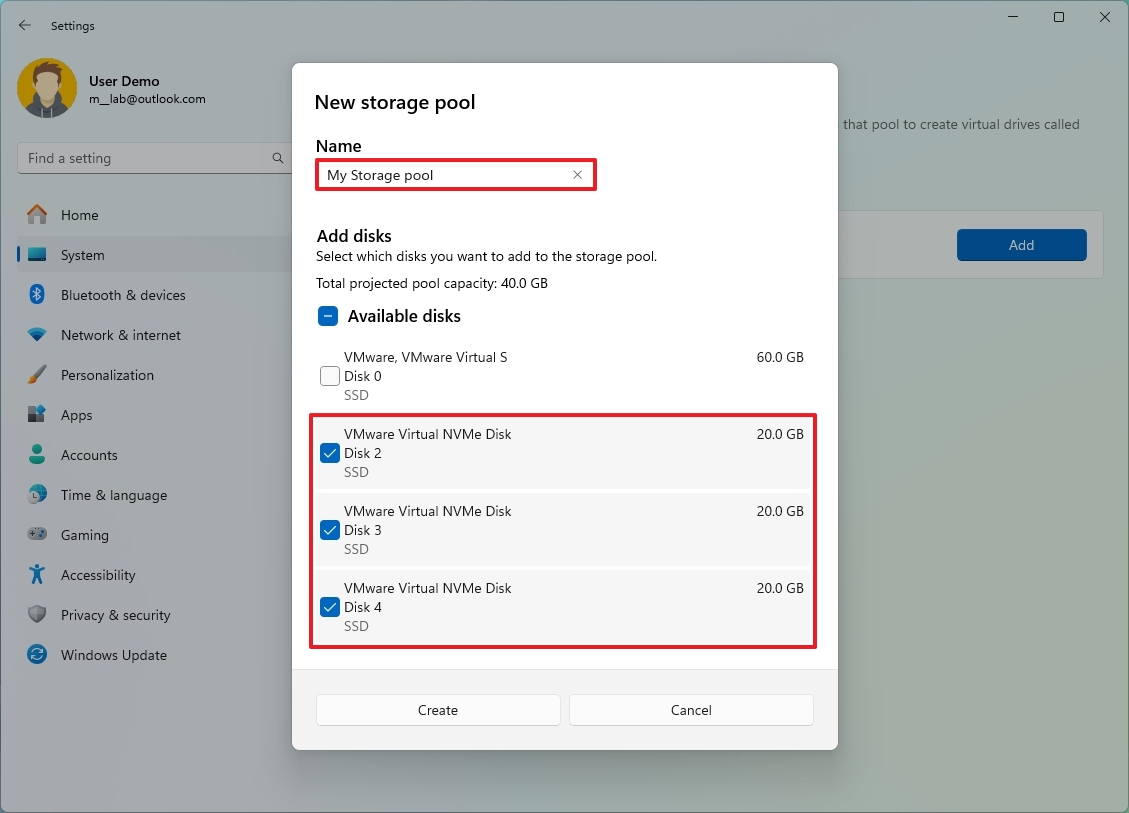
- Click the Create button.
- Confirm a name for the space, such as “My Storage Space.”
- Use the default (total) capacity in the “Size & resiliency” setting.
- Choose the “Simple (no resiliency)” (or the Parity) option.
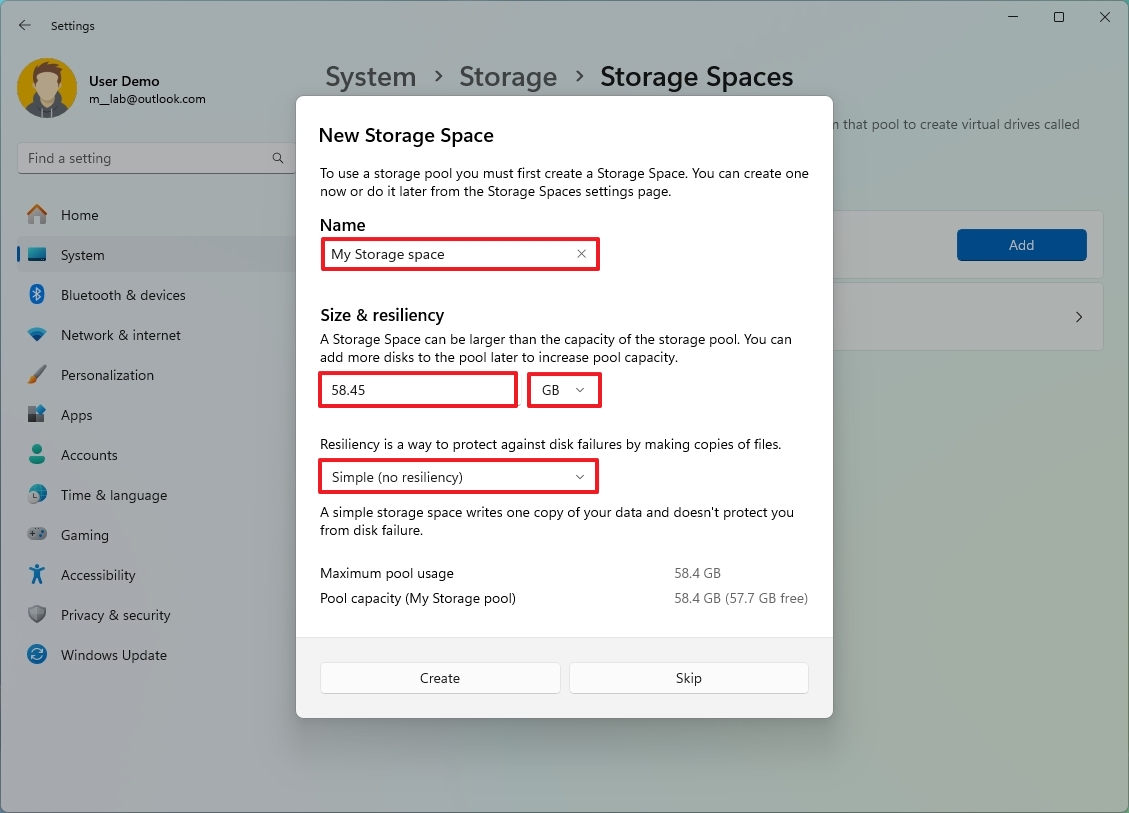
- Click the Create button.
- Confirm a label for the volume.
- Select a drive letter.
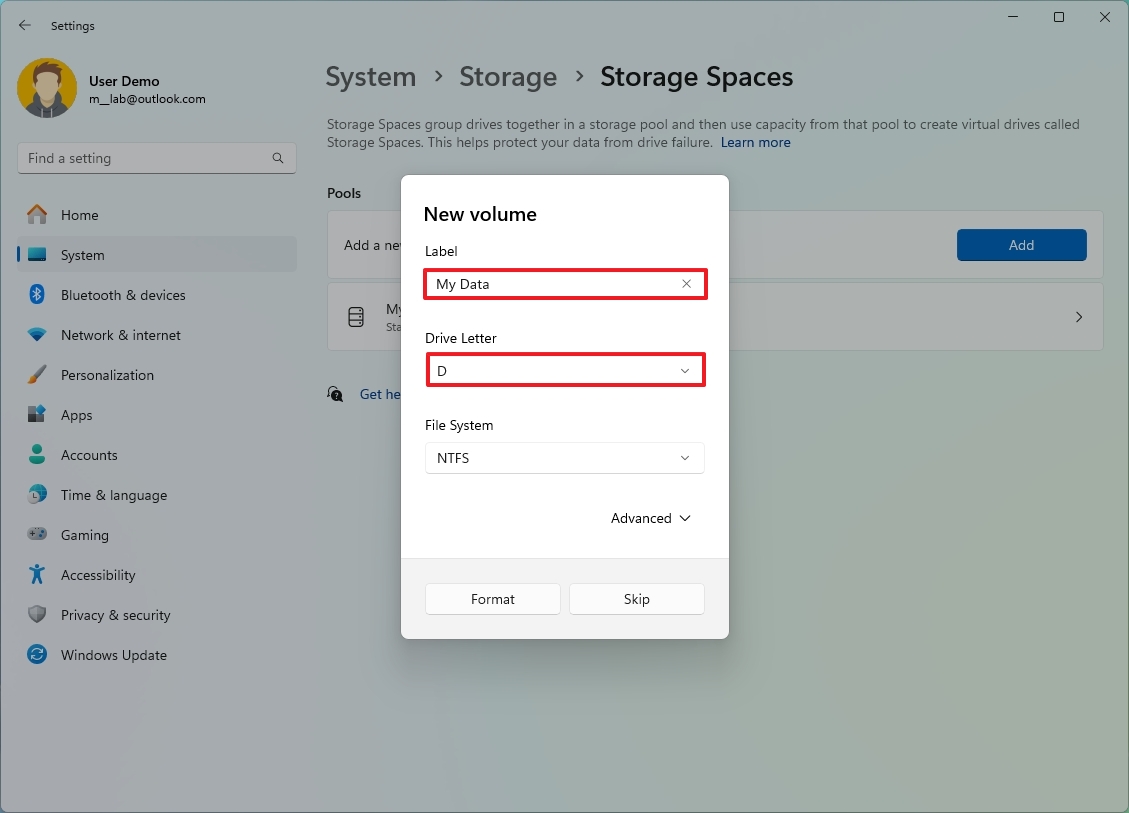
- Choose the NTFS option for the file system.
- Click the Format button.
Once you’ve finished the procedures, the Storage Spaces function will create a substantial pool by merging the drives, utilizing the chosen redundancy option.
With the “Storage Spaces” feature, choosing the “Simple” setting merges multiple drives to form a substantial volume. The system perceives this combined entity as a single drive. Yet, it’s important to note that this setup does not provide protection for your data in case of hardware malfunction.
This option necessitates a minimum of three storage devices. It distributes your data along with parity information across these other devices. In case one drive malfunctions, you can swap it out, and the system will be capable of recreating the lost data using the stored parity information.
As a researcher, I find that Storage Spaces could serve as an alternative approach to traditional RAID technology, despite some differences in functioning. For instance, much like RAID, Storage Spaces allows multiple physical drives to be amalgamated into a single logical entity. However, unlike RAID, Storage Spaces offers both hardware and software implementation options. Once set up, the configuration of RAID remains fixed, making it somewhat complex to manage.
The Storage Spaces solution is a software-only implementation, but it’s more flexible, allowing for dynamic changes after setup and easier to manage. However, the hardware RAID solution can offer more performance than Storage Spaces.
You can only use these instructions on secondary drives. This approach won’t work on the boot drive. If you want to use redundancy on the drive where the operating system resides, you will be better off using a RAID solution. Usually, motherboards for desktop computers come with some sort of RAID solution. You can always check with your manufacturer for more information. (This example shows the RAID compatibility on Asus motherboards.)
More resources
Read More
- We Ranked All of Gilmore Girls Couples: From Worst to Best
- Gaming News: Why Kingdom Come Deliverance II is Winning Hearts – A Reader’s Review
- Jujutsu Kaisen Reveals New Gojo and Geto Image That Will Break Your Heart Before the Movie!
- Why Tina Fey’s Netflix Show The Four Seasons Is a Must-Watch Remake of a Classic Romcom
- How to Get to Frostcrag Spire in Oblivion Remastered
- Assassin’s Creed Shadows is Currently at About 300,000 Pre-Orders – Rumor
- First U.S. Born Pope: Meet Pope Leo XIV Robert Prevost
- Kylie & Timothée’s Red Carpet Debut: You Won’t BELIEVE What Happened After!
- Whale That Sold TRUMP Coins Now Regrets It, Pays Double to Buy Back
- Taylor Swift Denies Involvement as Legal Battle Explodes Between Blake Lively and Justin Baldoni
2024-11-14 17:13