As a seasoned tech enthusiast with countless hours spent troubleshooting and optimizing systems, I can confidently say that Task Manager is one of the most underestimated tools in any PC user’s arsenal. It’s not just about ending processes or monitoring system resources; it’s about understanding your machine, keeping it healthy, and squeezing every last drop of performance out of it.
The Task Manager app has long been one of the most essential tools in the operating system, offering a glimpse into the inner workings of your computer. On Windows 11, the tool has been reimagined with a modern design and new enhancements that make managing your computer a little easier.
Although you might already be acquainted with Task Manager, it offers a range of underutilized features that could give you enhanced system management abilities. These include Efficiency Mode, memory dumps, drive monitoring, network details, firmware boot time information, wait chain analysis, desktop widgets, always-on-top functionality, and more.
In this step-by-step tutorial, I’ll be providing you with some under-the-radar suggestions to maximize your experience with the Task Manager in Windows 11.
Collection of tips to make you more productive on Task Manager
The Task Manager has received numerous upgrades, boasting capabilities that might elude even seasoned users. Here’s a peek at some hidden gems and less popular tricks:
1. Quick shortcut
Although you can open Task Manager from the Taskbar context menu, you can always use the “Ctrl + Shift + Esc” keyboard shortcut for even quicker access.
As a tech-savvy individual, when you’re ready to kick off your tool using the Run command or Command Prompt, give the trusty old `taskmgr` command a try!
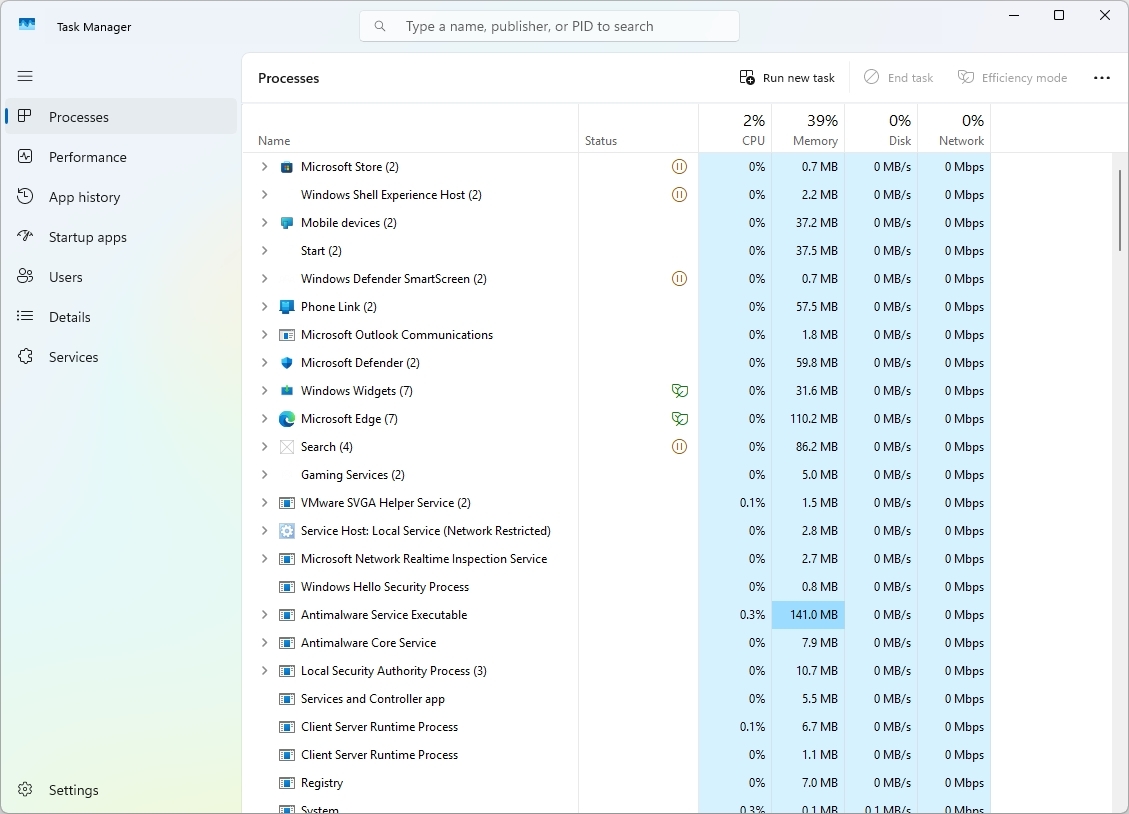
2. Efficiency mode
In the Task Manager, Efficiency Mode functions as an integrated tool that enhances both system performance and energy conservation. It does this by giving priority to foreground apps while minimizing the resource usage of running background tasks.
Activating Efficiency Mode for a certain task means the system gives less attention to it. Essentially, this implies that fewer system resources are allocated towards that particular task, thus making more resources available for your currently running applications. This action not only optimizes overall performance but also saves power and prolongs battery life, particularly on devices with limited hardware capabilities.
To activate Efficiency Mode for a process in Task Manager, first click on the “Processes” tab, then right-click the desired process, select “Efficiency Mode” from the menu, and finally hit the “OK” button.
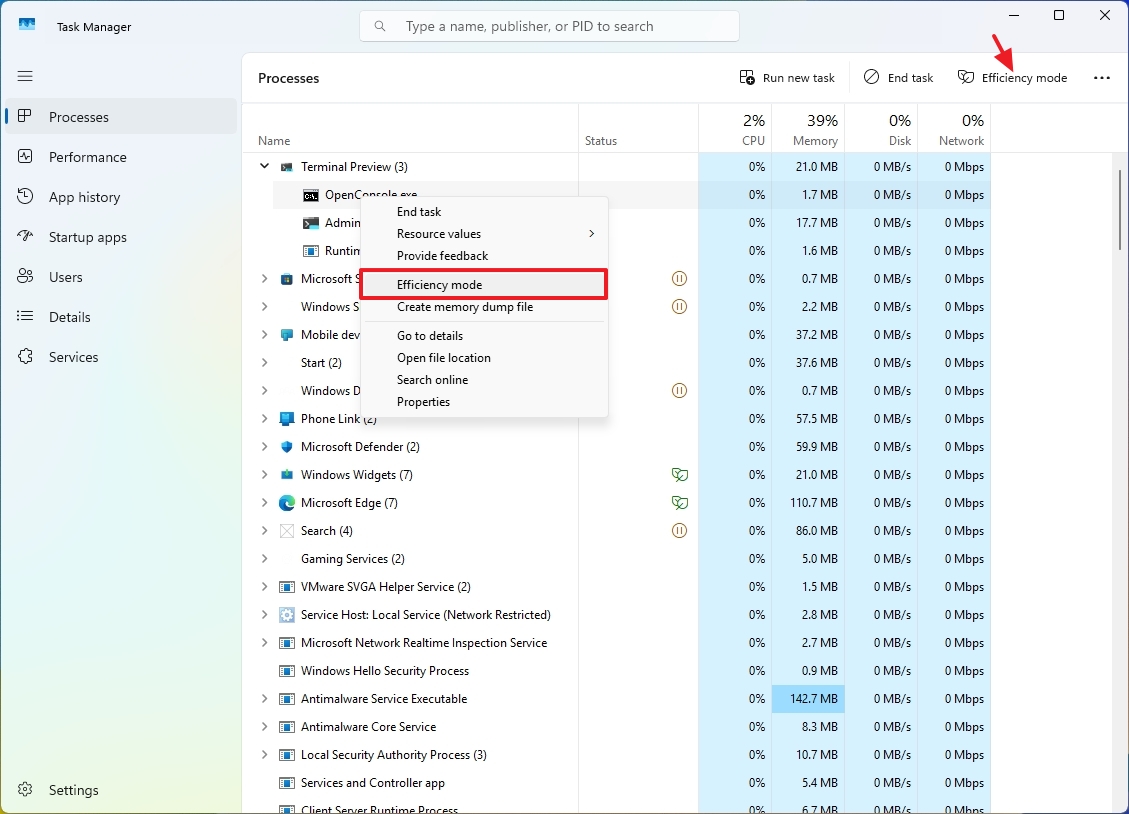
The feature is only available for specific applications. If the option isn’t available, it’s not supported for that particular item.
It’s advisable to utilize this function with caution, as decreasing an application’s process priority might impact the overall system performance and stability.
As a tech enthusiast, if you’d like to revert the modifications, simply right-click the ongoing process and opt for the “Efficiency Mode” once more to remove the tick.
3. Show command line
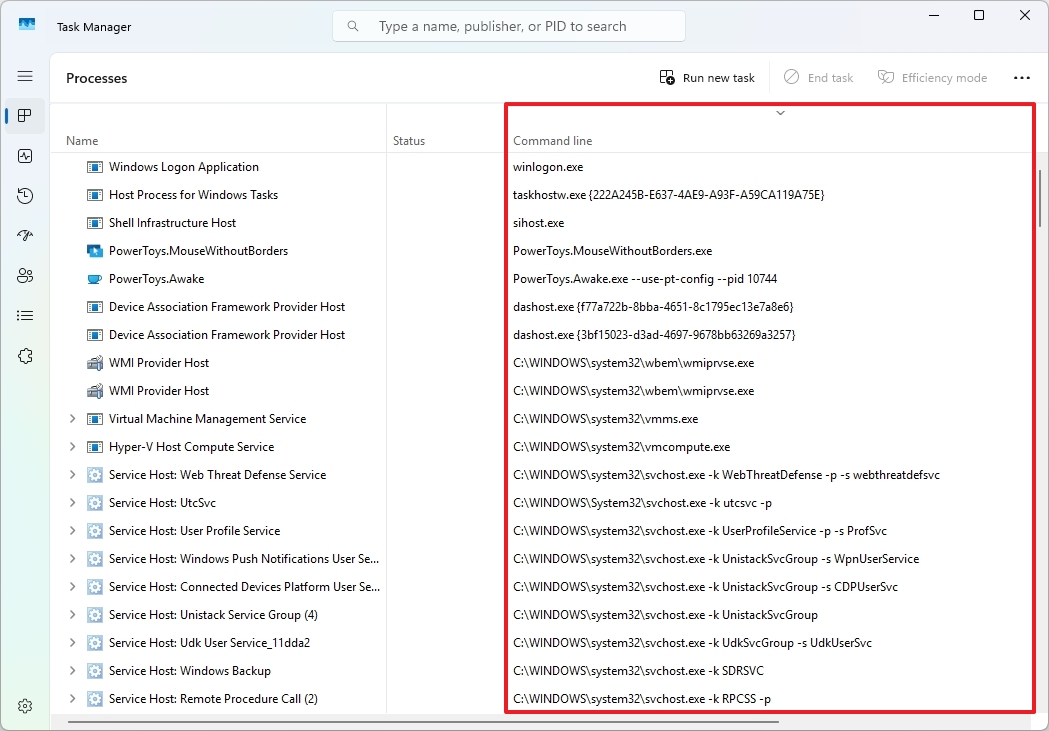
The “Processes” tab has the ability to display the exact command line utilized to initiate a specific process, making it useful for problem-solving purposes.
Click on the “Processes” tab, then right-click the column header, and select the “Command Line” option to display the command line for each process.
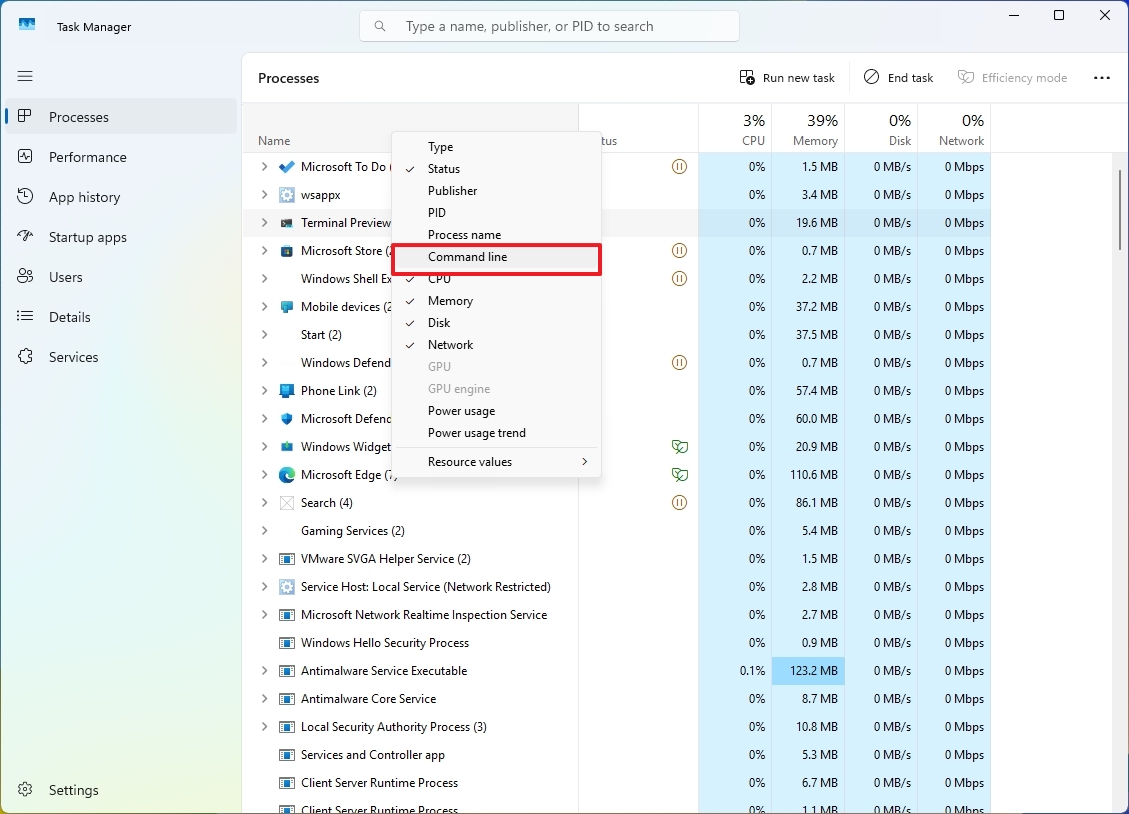
Once you activate the setting, you’ll notice the appearance of a fresh “Command Line” column displaying the command that initiated the process execution.
4. Create memory dump
On Windows 11, a memory dump is essentially a picture of the system’s memory at a particular point in time. This tool can prove incredibly useful when dealing with crashes, application malfunctions, or overall performance concerns. The Task Manager gives you the ability to generate memory dumps specifically for certain processes, which can be invaluable in identifying and resolving software-related issues.
To save a memory snapshot of a specific process using Task Manager, navigate to the “Processes” tab, right-click on the targeted process, then choose the “Generate Memory Dump File” option.
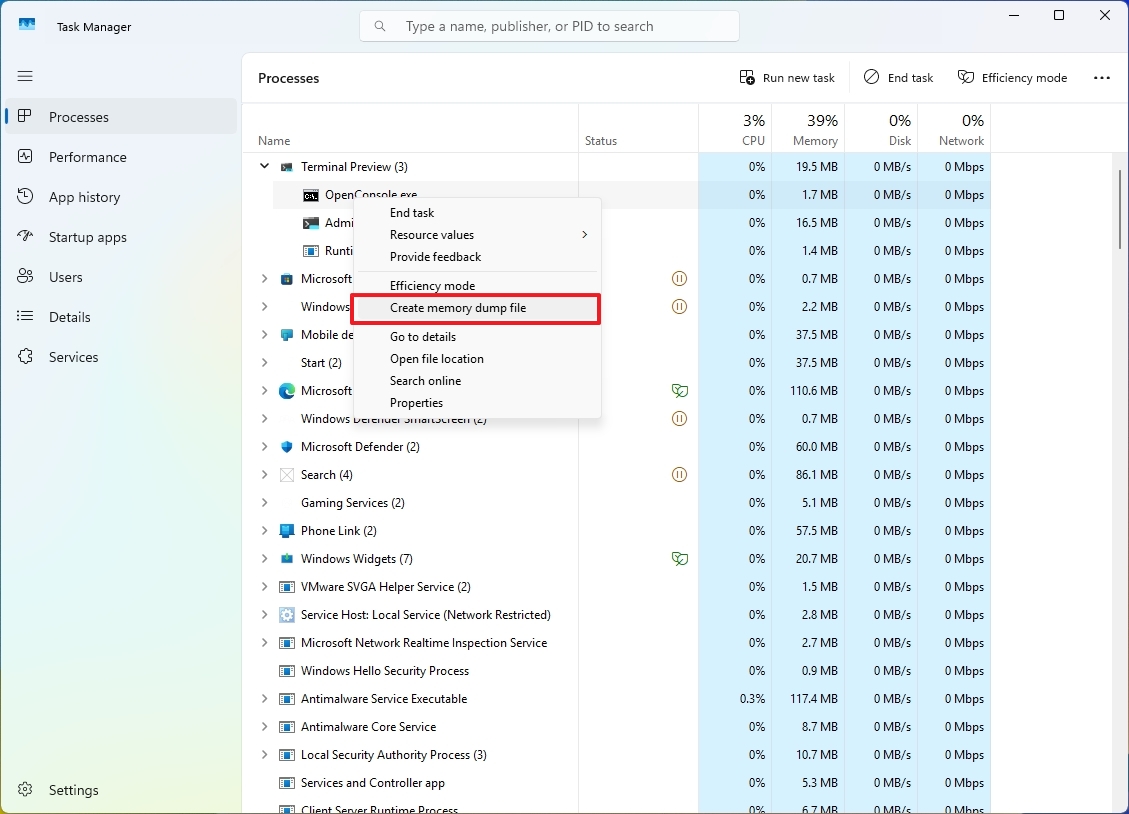
After generating the dump file, Task Manager will provide the location of the corresponding “.dmp” file for you. You can either copy this location directly or use the “Open file location” button instead.
Although this is a powerful tool, analyzing a memory dump often requires specialized tools and knowledge.
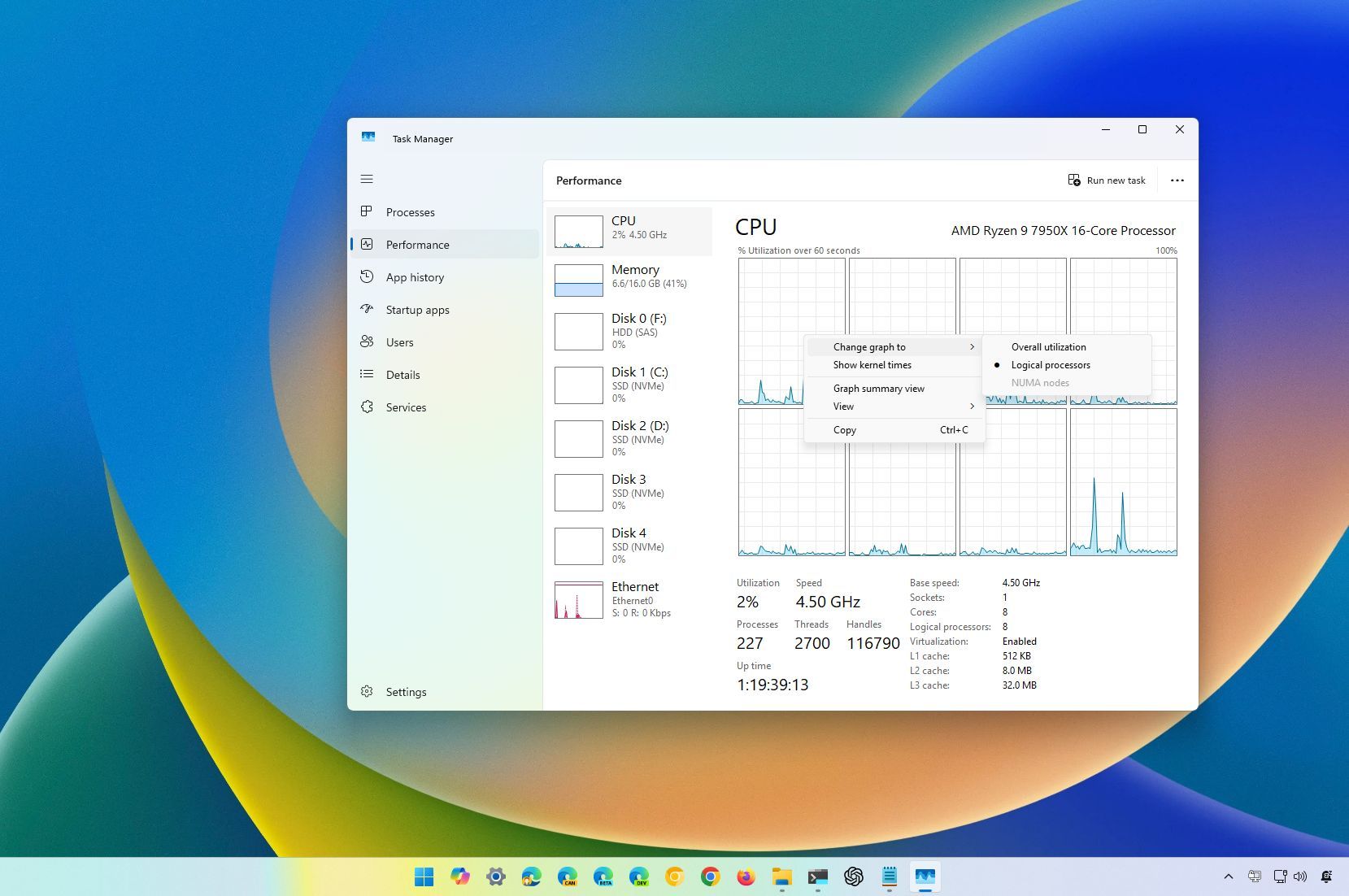
5. Show every core in the processor
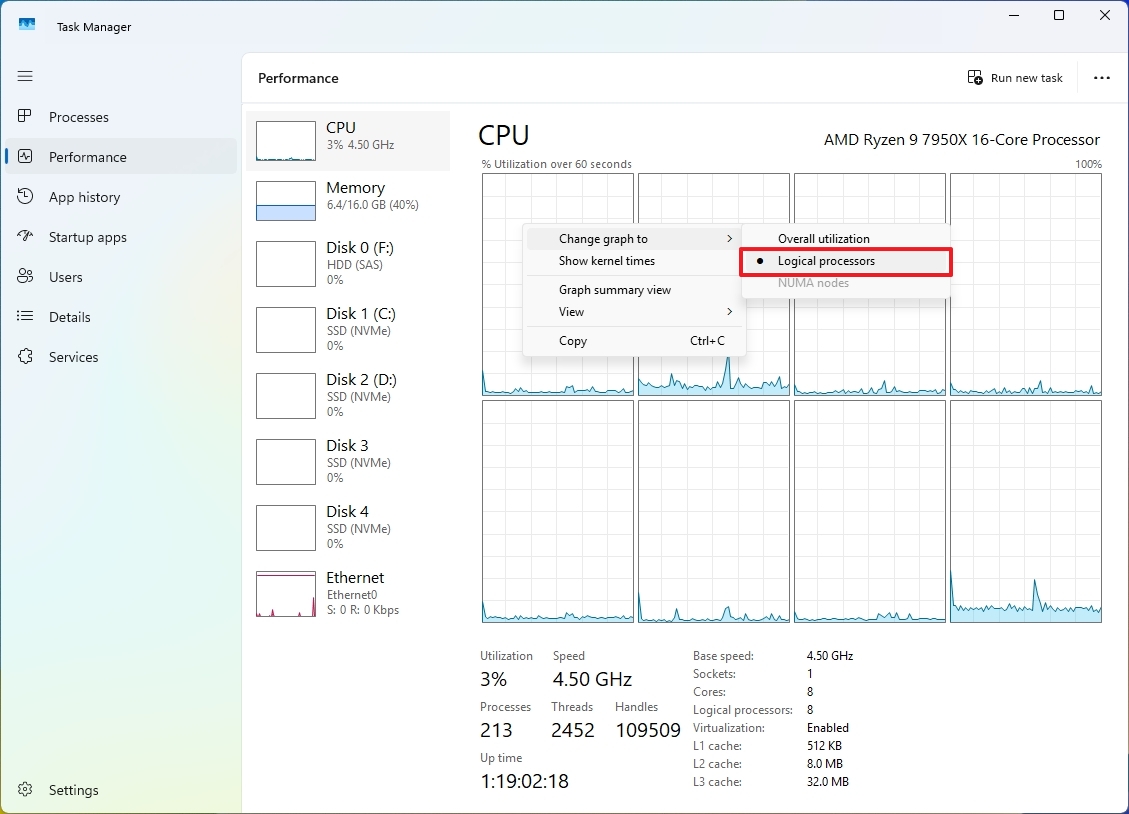
In the “Performance” section, under “CPU” details, you’ll typically find an “Overall Utilization” perspective displaying the collective activity across your whole processor. But don’t forget that you can switch to a view showcasing the activity of each individual core instead.
To monitor the activity of individual cores within your processor, simply click the right mouse button on the CPU graph located in the “Performance” tab, then pick the “Modify graph as…” option followed by choosing the “Logical Processors” selection.
6. Check graphics temperature
Under the “Performance” tab, you’ll additionally discover the graphics card’s temperature. This could be useful for individuals dealing with gaming PC troubleshooting or thermal management when utilizing rendering software such as photo and video editing tools.
To find out the GPU temperature, simply navigate to the “Graphics Processing Unit (GPU)” section, where you’ll spot the temperature reading either below the tab title or somewhere on the displayed page.
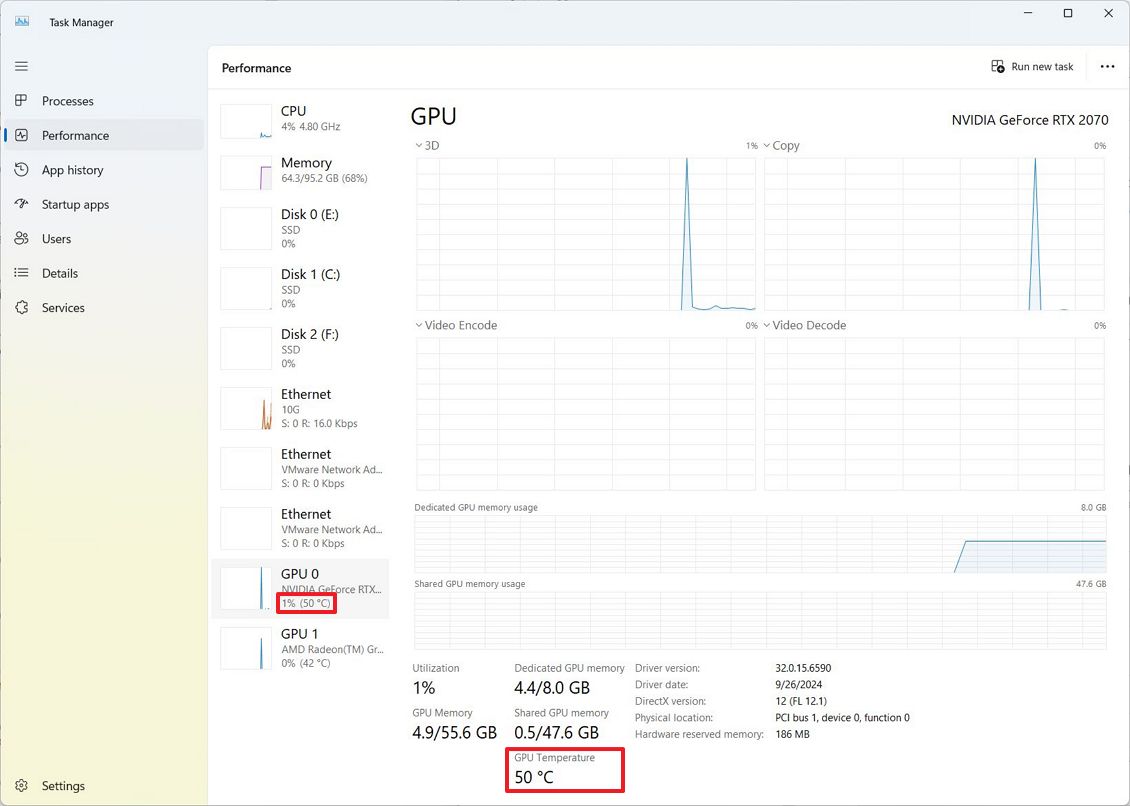
It’s quite common for this data not to be accessible on all types of graphics cards, especially with older models or those used in virtual environments.
Typically, temperatures that fall between 65 degrees Fahrenheit (F) and 85 degrees F are normal, however, if the temperature consistently exceeds 212 degrees F (which is 100 degrees Celsius), it’s important to consider it as overheating.
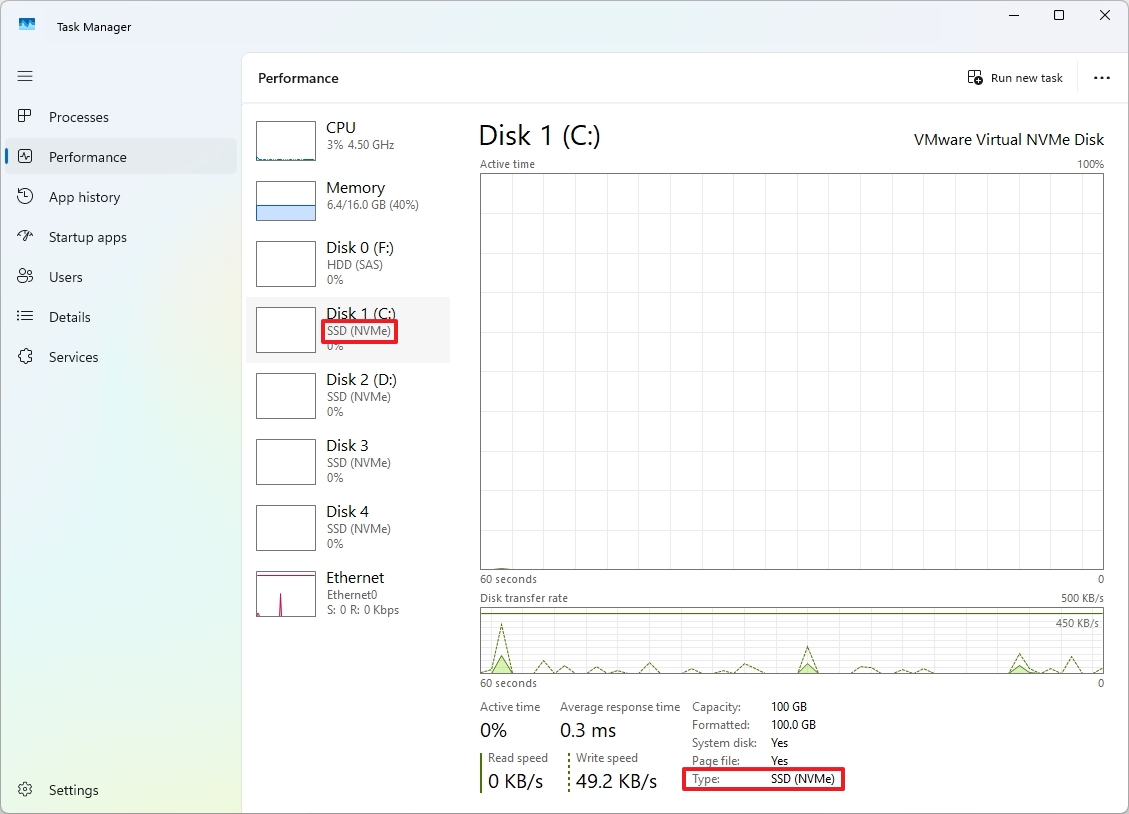
7. Check drive media type
You no longer need to explore various methods to determine the kind of storage linked to your device; instead, simply use the Task Manager, which will inform you whether the drive uses SATA, NVMe, and other types.
To find out what kind of drive is installed on your computer, navigate to the “Performance” tab, then click on the specific drive. The drive’s type details will appear below the tab title and on the screen within the “Type section.
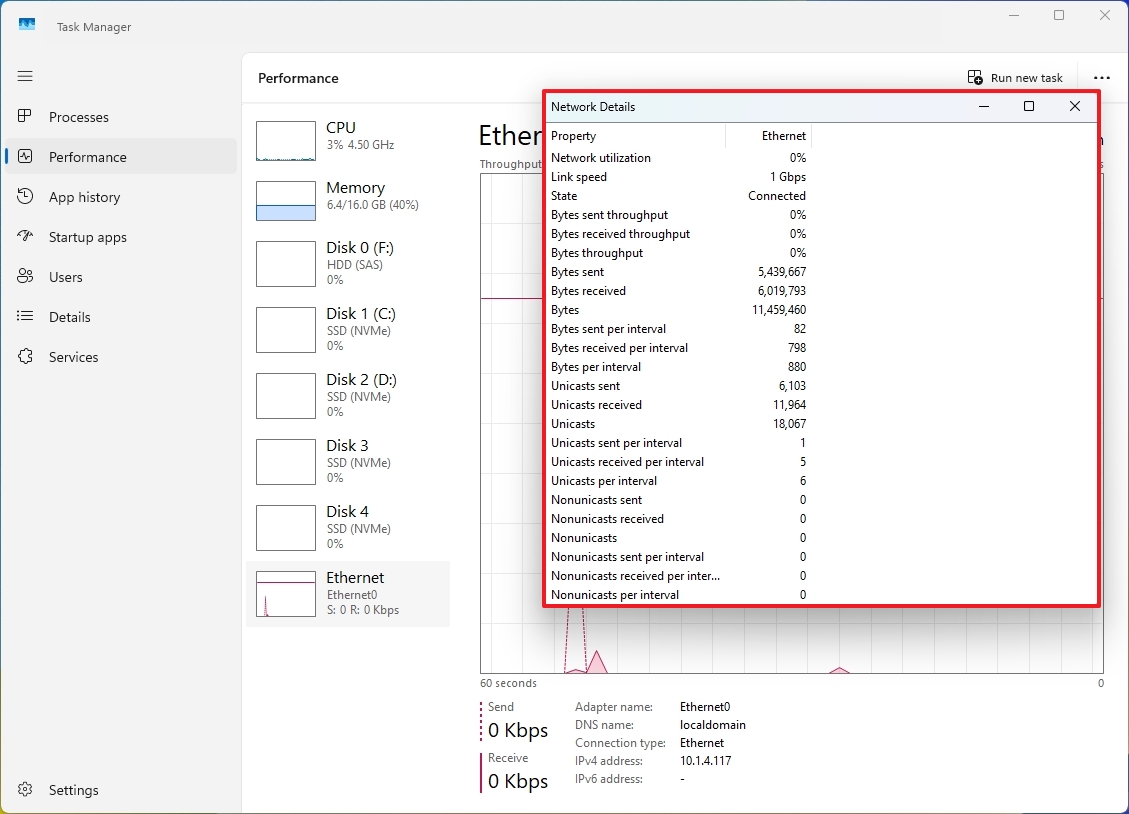
8. Show network details
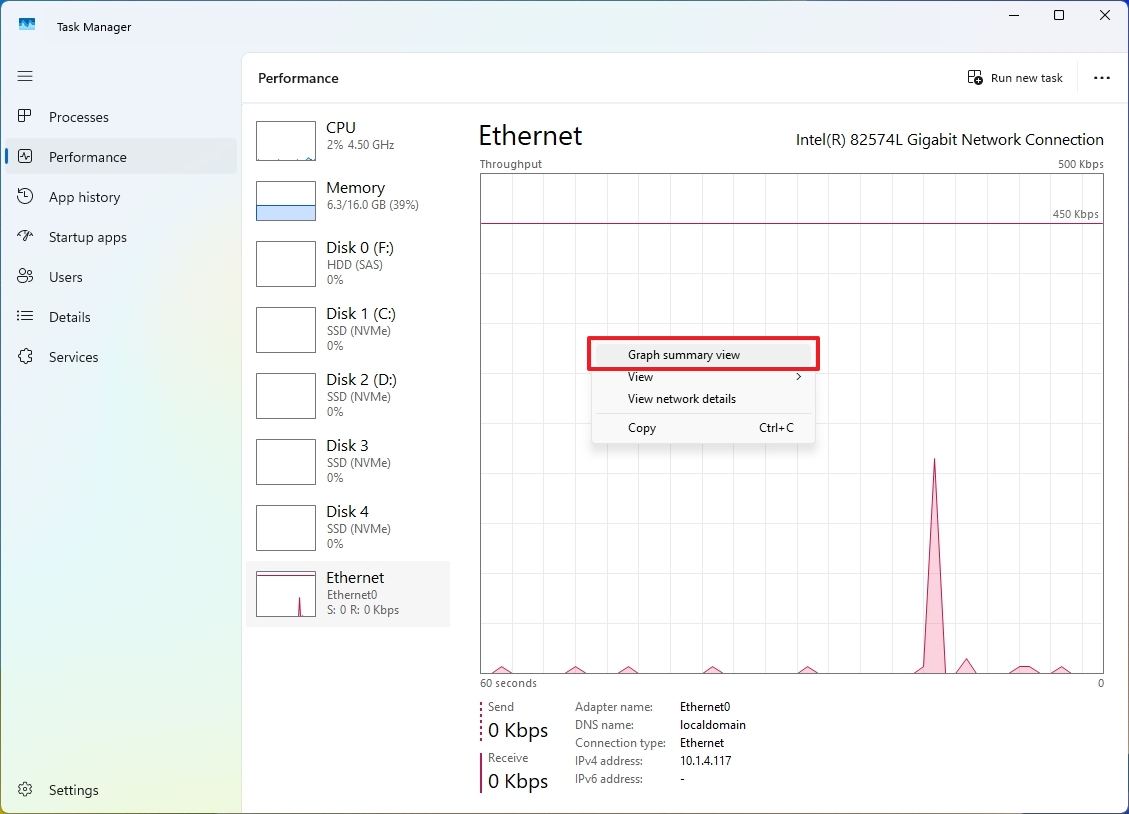
As an analyst, I’d like to point out an interesting fact about the Network Adapter activity under the “Performance” tab: while it primarily showcases the throughput of sent and received packets, there’s a hidden treasure trove of additional network details that you might not be aware of. These include network utilization, state, detailed statistics for sent and received bytes, as well as insights into unicast packets. These extra pieces of information can prove incredibly useful when it comes to diagnosing issues or keeping a close eye on your network connection.
In the “Performance” tab, you can explore detailed information about a particular network adapter by clicking on the selected Ethernet or Wi-Fi icon, then right-clicking its graph and selecting the option called “‘Display network properties’“.
9. Disable startup apps
You have the ability to control which apps start up when your computer boots, but you can also use the Task Manager to identify and prevent most applications from launching automatically at startup.
To manage apps that start up automatically from within the Task Manager app, navigate to the “Startup items” section, click on the “Startup impact” column header to arrange the apps according to their influence on system performance, choose an app, then press the “Disable” button.
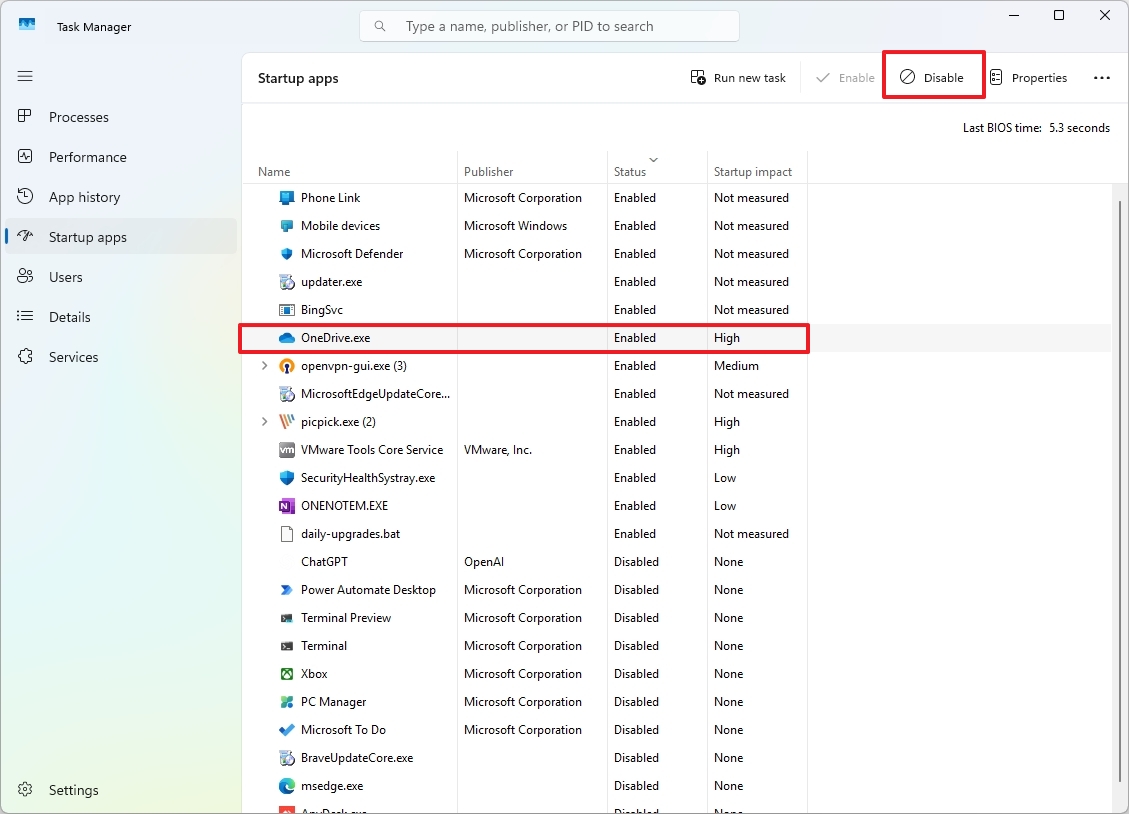
You can also select an app and click the “Enable” button to allow the app to run a startup.
10. Check boot speed time
In the “Startup apps” section, you’ll find details about when the Basic Input/Output System (BIOS) was last started. This info is displayed at the upper right corner of the screen.
The “Last BIOS Time” shown indicates the duration taken by your computer’s BIOS (or Unified Extensible Firmware Interface, UEFI) to set up your hardware, perform the Power-On Self-Test (POST), and ultimately transfer control to the operating system.
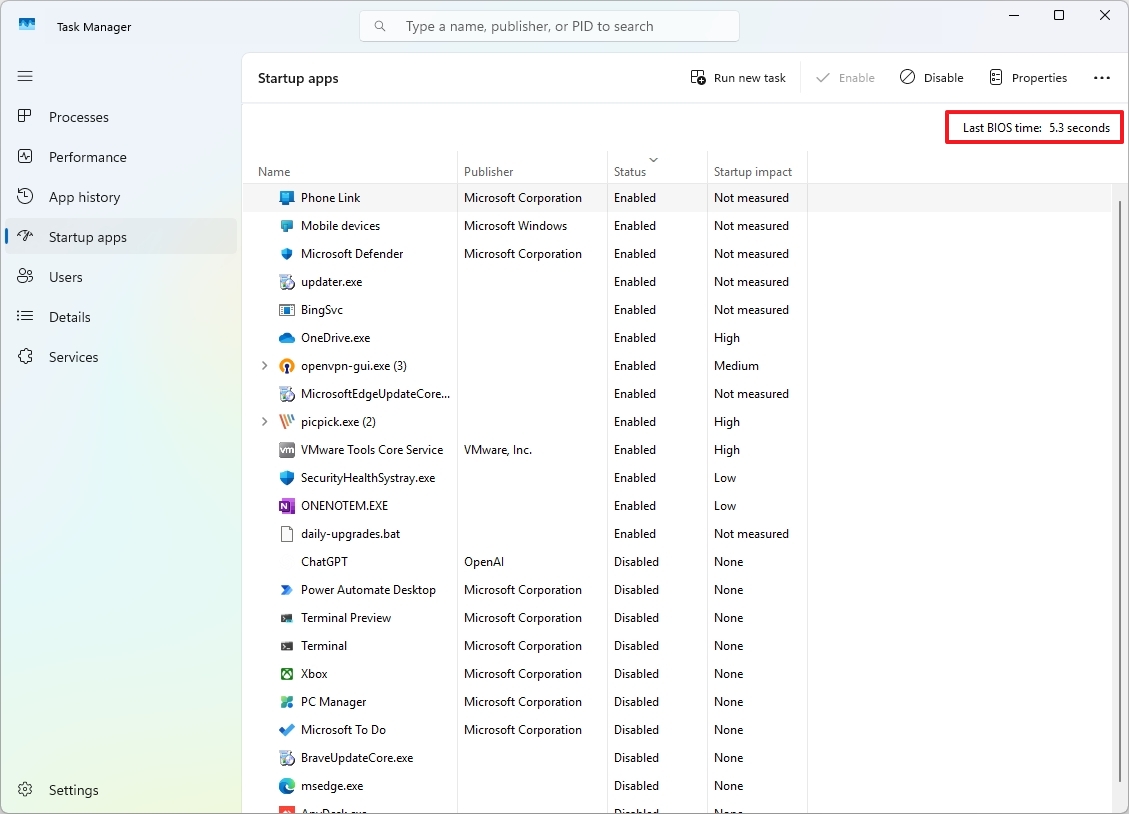
As a tech enthusiast, I’ve found this info incredibly useful whenever I encounter slow startup issues, when I want to compare boot speeds across various devices, during benchmarking tests, or simply to gauge the overall well-being of my system.
11. Real-time drive monitoring
In simpler terms, the “Details” section gives you a complete look at all the tasks currently being run by your system. It provides specific details about each task, helping you locate heavy-duty tasks that might be causing performance problems, diagnose issues, and improve your system’s efficiency.
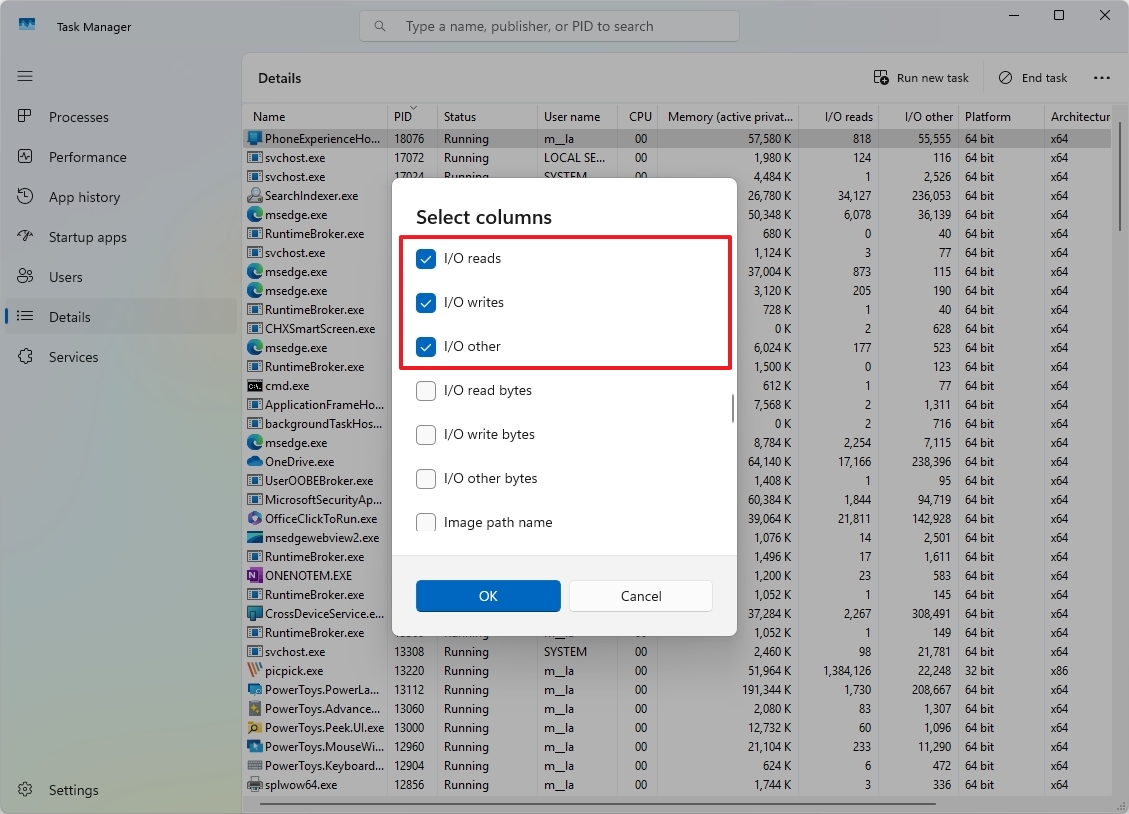
Additionally, you have the option to adjust the view to display “I/O Reads,” “I/O Writes,” and “I/O Other.” These metrics offer valuable insights into a process’s interaction with your system’s storage devices. This feature is particularly useful when diagnosing drive issues, such as during instances where the hard drive appears to be operating at 100% utilization.
To display Input/Output (I/O) details in Task Manager, follow these steps:
12. Troubleshoot unresponsive apps
If an application seems unresponsive, you can terminate it and then reopen it to reset its status, usually resolving the issue. But if you’d like to delve deeper into the problem, the Task Manager offers a “Analyze Wait Chain” feature to help detect and address app hang-ups and freezes.
This characteristic shows the visual depiction of the processes that are pending resources, allowing you to identify precisely where the problem originates from.
To utilize this function, navigate to the “Details” tab, long-press on the unresponsive application, and select the “Investigate Wait Chain” option instead.
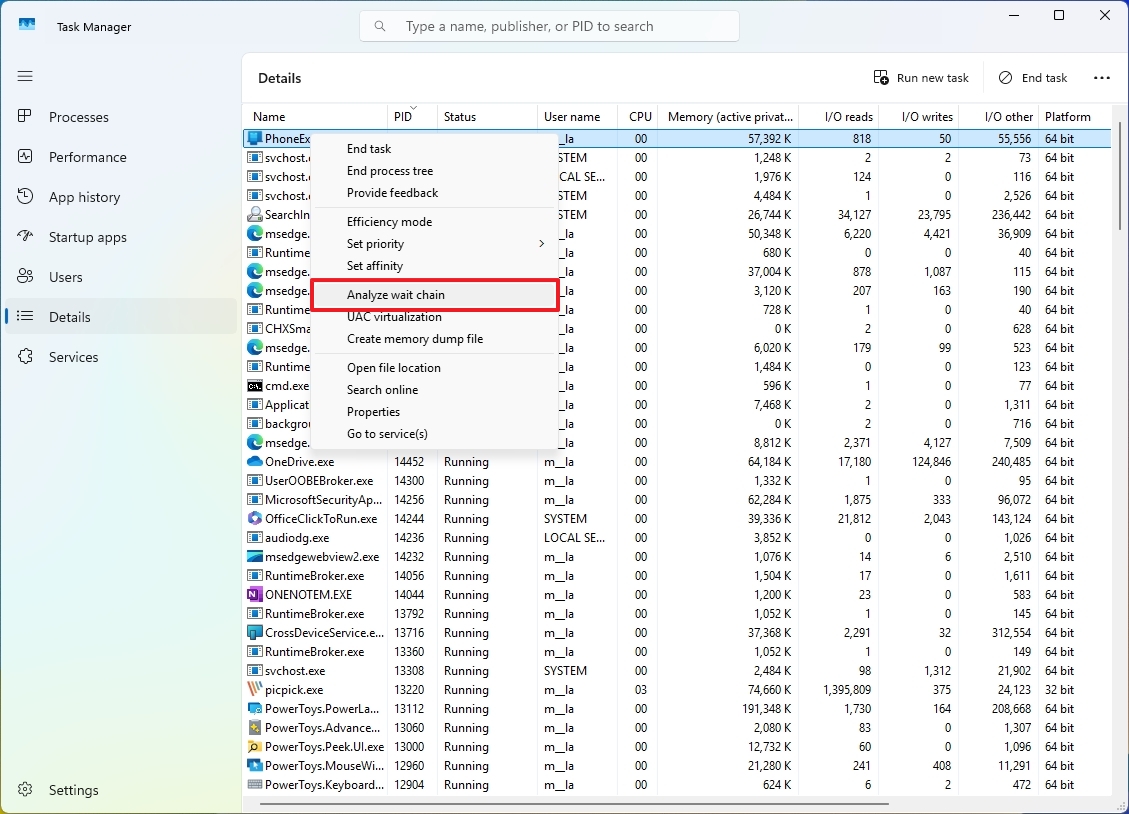
As a researcher, when you choose this option, you’ll find a tree structure unfolding before your eyes. Each branch on this tree symbolizes a distinct process, while the connections between these branches signify that one process is waiting for another to complete, much like the sequential steps in a recipe or an assembly line.
Although this feature can be handy to troubleshoot an unresponsive application, it’s worth noting that it may not always provide a definitive answer. In some cases, the problem can be more complex and challenging.
13. Log off other users from your account
If multiple people use the same computer and one user’s account is still active, you might find it difficult to access their specific account, but you can either log them out or manage their ongoing tasks with ease through the Task Manager.
To examine and assess a currently logged-in user’s services, navigate to the “Users” tab and simply click twice on the specific user to open their details.
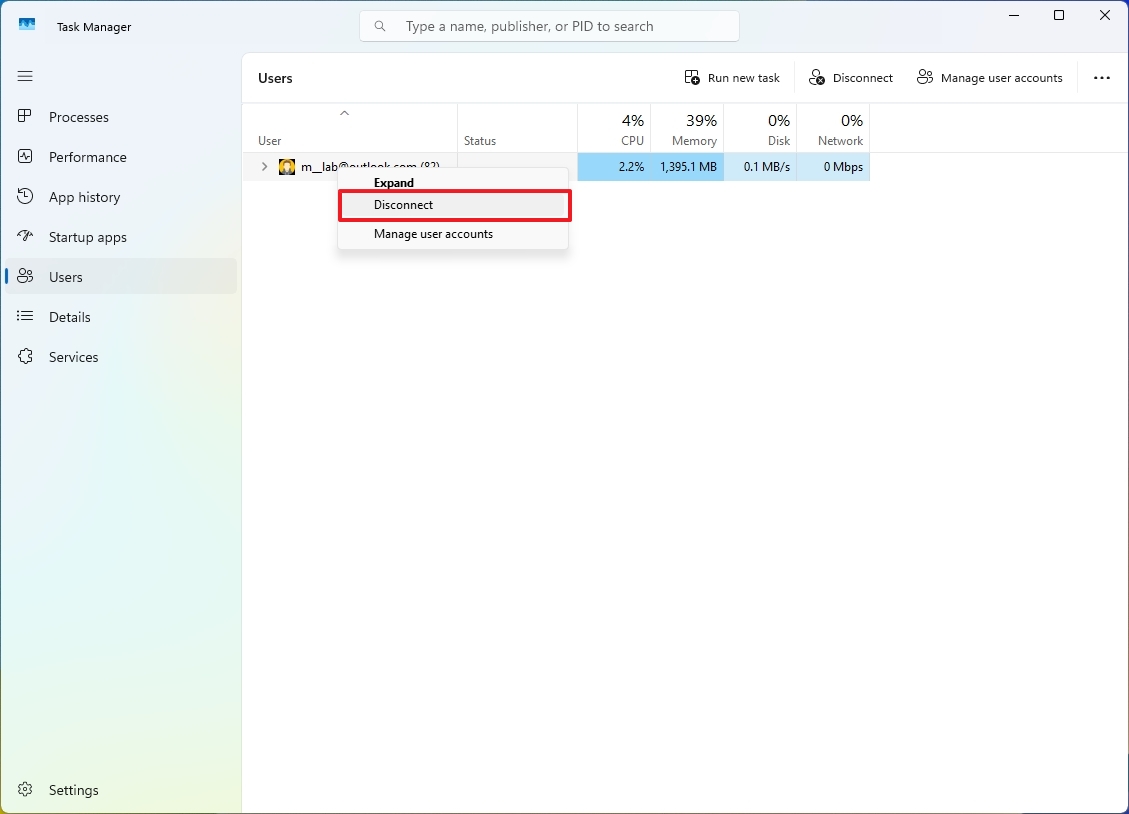
To log a user out of the computer, simply click on the “Users” tab, then right-click the specific user account, followed by selecting the “Log off” or “Sign Out” option instead.
14. Confirm process identification
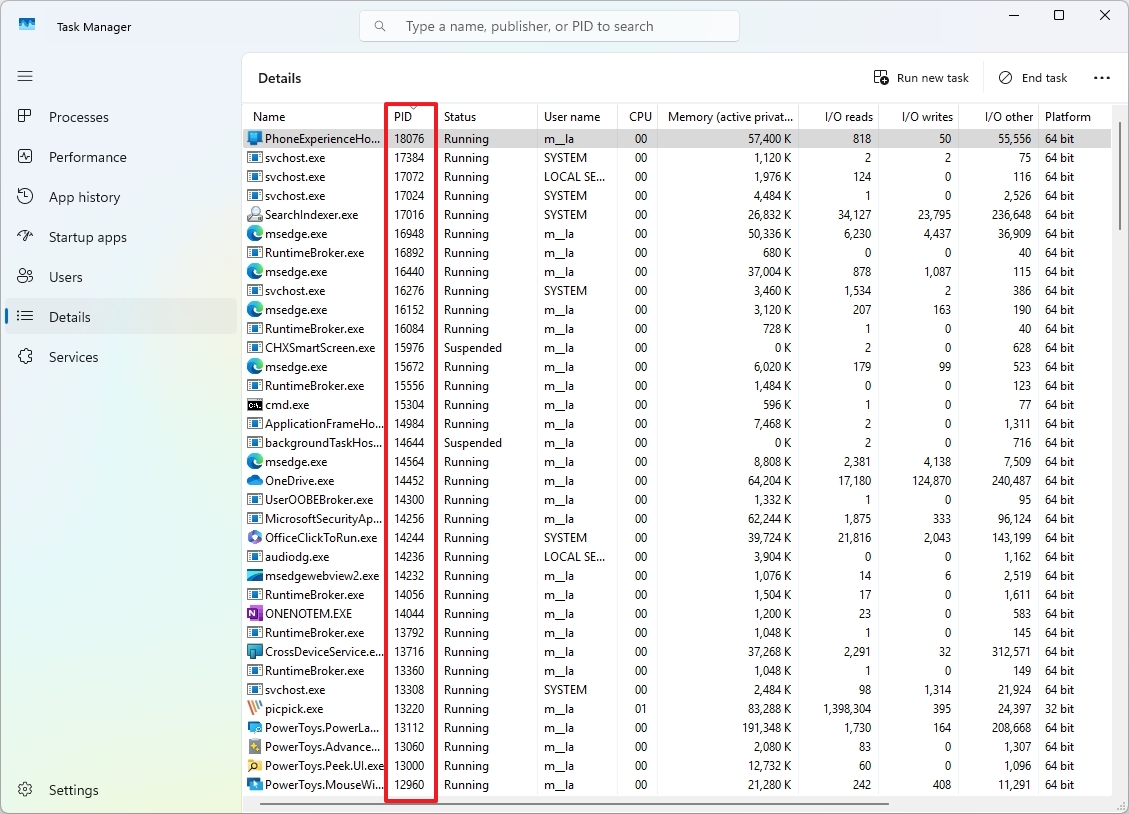
In the context of using Task Manager, the Process Identifier (PID) is a distinctive number given to every active process on your computer. This number serves as a helpful tool for locating a specific process or for terminating one immediately with the “taskkill” command when dealing with troubleshooting issues.
To locate the Process ID (PID) for a particular process, simply navigate to the “Details” tab and verify the Process Identifier listed under the “Process ID” column.
The system is capable of labeling multiple services running on your computer with a Process ID (PID), which you can locate in the “‘Services’” tab by checking the ‘PID’ column.
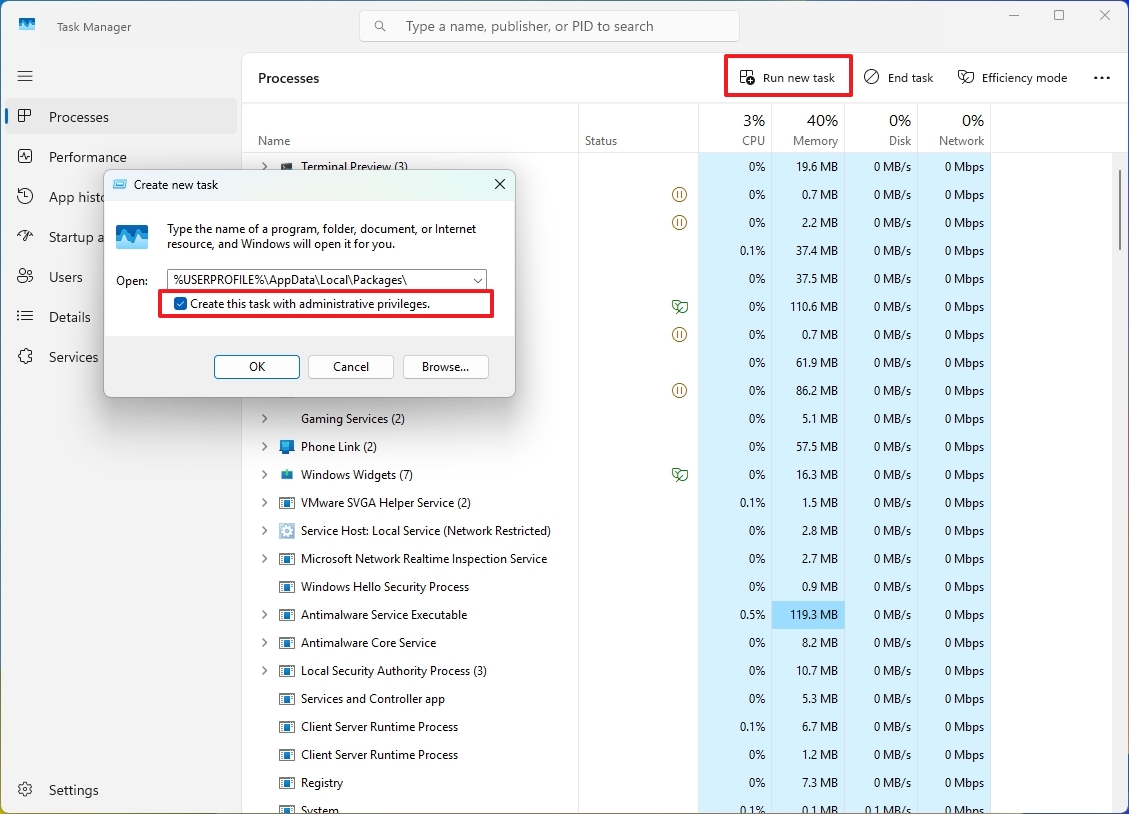
15. Run apps as admin
On Windows 11, there are multiple methods to launch an app or task with administrative privileges, such as using the Task Manager.
To launch a new application or task using Task Manager, look for the “Run new task” button located at the upper right corner from any tab. If needed, select the “Run as administrator” option before entering the command for the app or task you wish to run. Finally, hit the “OK” button to proceed.
16. Show always on top
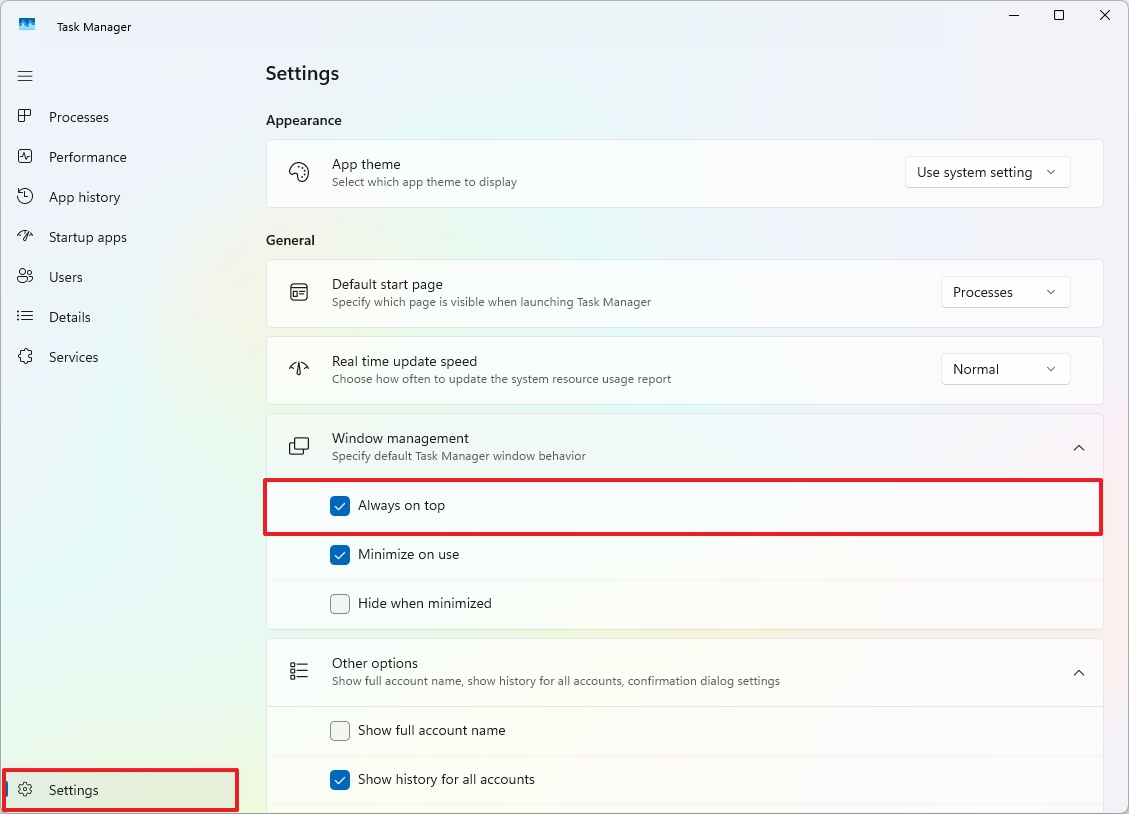
The “Always on Top” option keeps the Task Manager window visible over other active windows on your screen, making it convenient for observing system resources or controlling processes, even when you’re using other applications, particularly those running in full-screen mode.
To ensure that Task Manager stays at the top of your screen at all times, click the “Settings” button located in the left panel, then tick the “Always on top” box found under the “Window management” setting.
Once you enable the option, the Task Manager app will restart automatically.
You can always undo the changes by clearing the “Always on top” option under the “Window Management” setting.
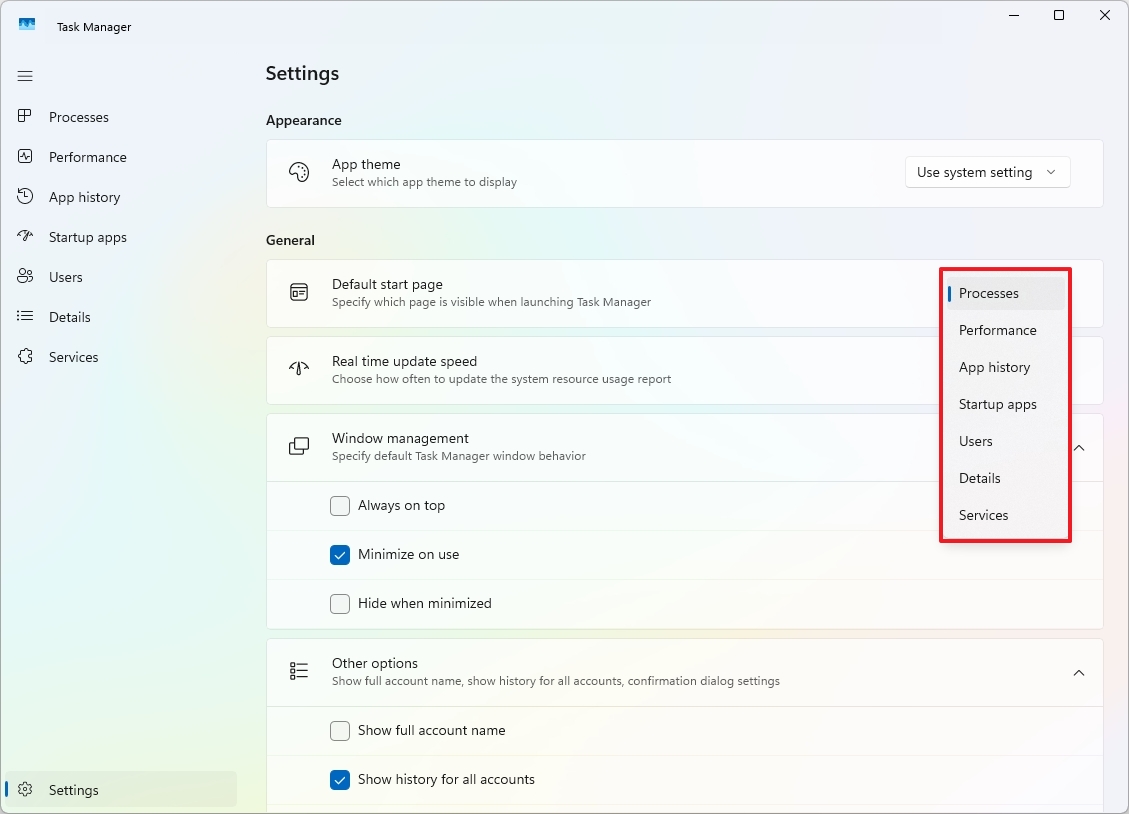
17. Change default startup page
If you often use Task Manager and usually switch to a different tab instead of the “Processes” tab, you have the option to adjust it so that your chosen tab opens automatically whenever you start the program.
To make a specific page appear whenever you open Task Manager, simply click on the “Settings” button located in the left panel, then select your preferred page under the “Startup” or “Default start page” option.
18. Other useful shortcuts
Unbeknownst to many, Task Manager, similar to most apps, offers keyboard shortcuts for seamless navigation around its interface.
General shortcuts:
- Tab: Switch between elements on the screen.
- Ctrl + Tab: Cycle through the tabs.
- Ctrl + Shift + Tab: Cycle through open tabs in reverse order.
- Alt + N – opens the dialog to run a new task.
- Ctrl+F: Open the search bar to find specific processes.
Processes tab:
- Spacebar and Enter: Opens and closes the selected process tree.
- Delete, Enter, and Alt + E: End the selected processes.
- Alt + V: Turns “Efficiency Mode” on or off.
19. Create desktop widget
To closely track specific aspects like network usage, CPU, memory, or disk activity in real time, simply double-click on any graph within the Task Manager to generate a movable window for more detailed monitoring.
Additionally, you can access the same view by simply right-clicking on the graph and choosing the “Summary of Graph” option.
After you finish observing, you can simply double-click the graph once more to return the Task Manager to its initial state or default interface.
More resources
Read More
- PI PREDICTION. PI cryptocurrency
- Gold Rate Forecast
- WCT PREDICTION. WCT cryptocurrency
- LPT PREDICTION. LPT cryptocurrency
- Guide: 18 PS5, PS4 Games You Should Buy in PS Store’s Extended Play Sale
- Solo Leveling Arise Tawata Kanae Guide
- Despite Bitcoin’s $64K surprise, some major concerns persist
- Clarkson’s Farm Season 5: What We Know About the Release Date and More!
- Planet Coaster 2 Interview – Water Parks, Coaster Customization, PS5 Pro Enhancements, and More
- Chrishell Stause’s Dig at Ex-Husband Justin Hartley Sparks Backlash
2024-11-26 14:10