Author: Denis Avetisyan
New research explores how quantum entanglement can be propagated between two seemingly disconnected universes using wormhole-like connections, potentially offering insights into the nature of quantum information transfer.
This study investigates the propagation of entanglement entropy through wormholes using the AdS/CFT correspondence and localized operator quenches in coupled conformal field theories.
The conventional understanding of information transfer faces limitations when considering strongly coupled systems and the emergence of spacetime geometry. In the paper ‘Holographic Entanglement Propagation Through Wormholes’, we investigate the propagation of energy and entanglement between two coupled conformal field theories using a holographic framework, revealing a mechanism for signal transmission through an effective wormhole geometry. Our calculations demonstrate that localized excitations can enhance mutual information, counterintuitively reversing the typical expectation of entanglement scrambling, and suggesting a connection to quantum teleportation. Could this framework provide insights into the fundamental relationship between entanglement, geometry, and information transfer in quantum gravity?
The Entanglement Echo: A Fragile Foundation
The efficient transmission of quantum information represents a foundational challenge in modern physics, yet conventional methods often falter when confronted with the intricate correlations inherent in many-body systems. These correlations, arising from the interconnectedness of numerous quantum particles, create complexities that quickly overwhelm classical computational approaches and limit the effectiveness of standard quantum communication protocols. Unlike simple, isolated qubit transfers, realistic quantum systems exhibit entanglement across multiple degrees of freedom, necessitating a deeper understanding of how information is encoded, propagated, and potentially degraded within these highly correlated environments. Consequently, researchers are increasingly focused on exploring novel theoretical frameworks and experimental platforms capable of handling these complex quantum relationships, paving the way for more robust and scalable quantum technologies.
Researchers are employing the framework of conformal field theories (CFTs) to model and investigate the complex evolution of quantum entanglement. CFTs, known for their inherent symmetries and mathematical tractability, provide an ideal platform for studying how entanglement-a cornerstone of quantum mechanics-changes over time. By examining the dynamics within these theoretical systems, scientists aim to understand the fundamental principles governing information transfer and potential loss in quantum systems. This approach allows for controlled experiments, albeit simulations, where the interplay between entanglement and the propagation of quantum information can be carefully scrutinized, offering insights into scenarios ranging from black hole physics to the behavior of many-body systems. The use of CFTs provides a powerful tool for deciphering the subtle mechanisms that dictate how quantum correlations evolve and potentially degrade, a crucial step toward harnessing the power of quantum information.
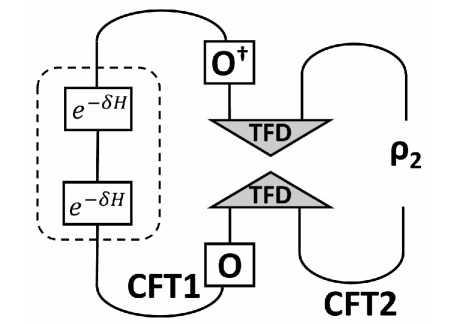
A precise definition of the system’s starting conditions is paramount when investigating quantum dynamics, and this research employs a specialized initial state known as a localized thermofield double state, or LocalizedTFDState. This state represents a form of maximal entanglement between two identical conformal field theories, effectively linking their quantum properties at a specific point in spacetime. By concentrating the initial entanglement in a localized region, researchers can meticulously track how quantum information disperses and evolves over time, offering a controlled environment to study the subtle mechanisms of information propagation and potential loss within complex quantum systems. The LocalizedTFDState serves as a crucial foundation, enabling detailed analysis of entanglement dynamics and providing insights into the fundamental limits of quantum information transfer.
The carefully constructed initial state serves as a crucial laboratory for investigating the fate of quantum information. By initiating the system with a localized entanglement – a precise correlation between two seemingly separate conformal field theories – researchers can meticulously track how this shared information evolves over time. This allows for the examination of subtle processes where information, rather than being perfectly preserved, might spread into inaccessible regions, effectively appearing lost, or conversely, be potentially recovered through complex correlations and interactions within the system. Understanding this dynamic – the propagation, potential loss, and possible retrieval of information – is central to addressing fundamental questions about the nature of quantum mechanics and its implications for black hole physics and the broader universe.
Holographic Projections: A Dubious Shortcut
Holographic CFT (Holographic Conformal Field Theory) establishes a duality between a quantum field theory and a gravitational theory in one fewer dimension. This correspondence, often referred to as AdS/CFT, allows for the translation of strongly coupled quantum systems – those difficult to analyze using conventional perturbative methods – into a weakly coupled gravitational system where calculations are more tractable. Specifically, the holographic approach facilitates the study of quantum dynamics by mapping problems in the quantum field theory to equivalent problems involving gravity in an Anti-de Sitter (AdS) space. This framework leverages the principle that all information about a volume of space can be encoded on its boundary, thus enabling the analysis of quantum phenomena through a gravitational description and vice versa. The utility of this approach lies in its ability to provide insights into quantum systems that are inaccessible through purely quantum mechanical calculations.
The AdSBTCZ black hole is utilized as a gravitational dual within the holographic framework to model strongly coupled quantum systems; this approach leverages the Anti-de Sitter/Conformal Field Theory (AdS/CFT) correspondence. This specific black hole solution in AdS_{3} space allows for the calculation of quantum observables on the boundary CFT through corresponding gravitational calculations in the bulk. The AdSBTCZ black hole, characterized by its mass and spin, provides a classical gravity description that can elucidate dynamical properties and correlation functions which are analytically intractable using purely quantum field theory methods. This dual representation effectively transforms complex many-body quantum problems into equivalent, but often more manageable, gravitational calculations, providing insights into phenomena such as thermalization and transport properties.
The SaddlePointApproximation is employed as a computational technique to manage the complexity arising from calculations within this framework. This method involves identifying the stationary points of the relevant functional or integral, effectively finding the dominant contribution to the overall result. While a full evaluation of the integral – often involving infinite-dimensional functional integration – is intractable, the SaddlePointApproximation provides a leading-order solution by focusing on the region near these stationary points. The approximation is valid when the function being integrated changes slowly in the vicinity of the saddle point, allowing for a Gaussian expansion around it. This simplification significantly reduces computational demands while preserving the essential physics and qualitative features of the system being modeled, providing an accurate approximation for many relevant observables.
The utilization of FreeScalarCFT provides a complementary analytical pathway distinct from the gravitational dual approach using AdSBTCZBlackHole. This non-gravitational framework allows for the investigation of quantum dynamics without reliance on the holographic correspondence, serving as a valuable point of comparison and potential validation for results obtained via the gravitational model. Specifically, FreeScalarCFT, being a conformal field theory with free scalar fields, simplifies calculations by avoiding interactions and allows for exact solutions in certain scenarios, offering insights into the system’s behavior that may be obscured by the complexity of the gravitational calculations. This approach facilitates the isolation and examination of specific quantum effects, and serves as a crucial test of the holographic principle itself by providing an independent calculation of quantities also accessible through the gravitational dual.
Perturbing the Void: A Delicate Disturbance
A localized excitation is introduced into the system via the application of a LocalOperatorQuench. This process involves applying a time-dependent perturbation to a specific region of the system, effectively creating a disturbance that propagates outwards. This method is employed to simulate a signal propagation scenario, allowing for the observation of how quantum information spreads and evolves within the system. The LocalOperatorQuench serves as the initial condition for investigating the subsequent dynamics and analyzing key observables, such as energy density, to track the excitation’s movement and influence on the system’s state.
The \text{EnergyDensity} observable quantifies the spatial distribution of energy within the system following the introduction of a localized excitation via the LocalOperatorQuench. Specifically, it measures the average energy per lattice site as a function of time and position, allowing for direct visualization of the excitation’s propagation. Tracking the temporal evolution of the \text{EnergyDensity} profile is critical for characterizing the dynamics of the excitation, determining its velocity, and identifying any spatial regions where energy is concentrated or dissipated. Variations in the \text{EnergyDensity} indicate the transfer of energy from the initial excitation point to other parts of the system, providing a key metric for analyzing the system’s response to the perturbation.
The observed excitation process shares characteristics with quantum teleportation, specifically in the transfer of quantum states between spatially separated regions of the system. While not a direct implementation of teleportation protocols requiring pre-shared entanglement and classical communication, the dynamics demonstrate a non-local spread of quantum information originating from the initial localized excitation. This transfer is evidenced by changes in the EnergyDensity observable, indicating that the quantum state associated with the excitation is effectively being “reconstructed” in distant locations within the system, similar to the state transfer achieved in quantum teleportation experiments.
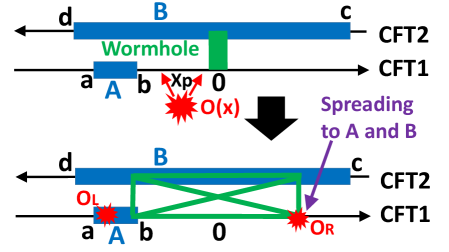
Analysis of the system’s dynamic evolution following localized excitation reveals competing effects on quantum information. While a \text{ScramblingEffect} consistently leads to information loss as the initial perturbation disperses, a counteracting \text{DescramblingEffect} unexpectedly enhances information accessibility in certain regions. This enhancement is quantitatively demonstrated by a positive \Delta I_{AB} > 0, representing a measurable increase in mutual information between subsystems A and B. This positive value indicates that, despite the overall trend towards scrambling and information dispersal, specific correlations are amplified during the dynamic process, a key finding characterizing the system’s non-equilibrium behavior.
Entanglement’s Grip: A Spacetime Connection (Or Illusion?)
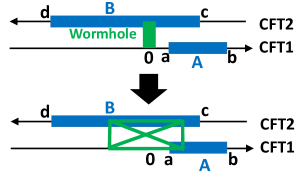
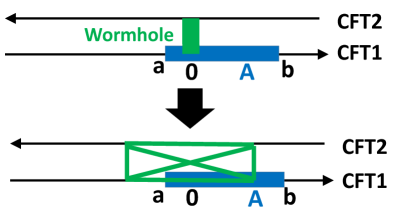
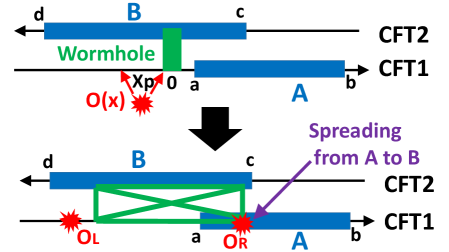
Recent analysis suggests a profound connection between quantum entanglement and the very fabric of spacetime, revealing that entanglement can be geometrically interpreted through the emergence of a wormhole within a gravitational dual. This isn’t a wormhole in the traditional sense of a traversable passage, but rather a topological feature arising in the AdS/CFT correspondence, where strongly coupled quantum field theories are equivalent to gravitational theories in Anti-de Sitter space. The degree of entanglement between two quantum systems is directly manifested as the size and shape of this wormhole; stronger entanglement corresponds to a larger, more pronounced geometric connection. Essentially, the analysis demonstrates that entangled particles are not merely correlated, but connected via a minuscule bridge through a higher-dimensional spacetime, providing a novel perspective on how quantum information might underpin the structure of the universe itself. This geometric manifestation allows for the quantification of entanglement using tools from general relativity, opening new avenues for exploring the interplay between quantum mechanics and gravity.
The emergence of a traversable Wormhole isn’t merely a topological curiosity within the gravitational dual, but a fundamental support structure for quantifying EntanglementEntropy between the two Conformal Field Theories (CFTs). Specifically, the geometry of this Wormhole – its length and shape – directly correlates with the amount of entanglement shared between the CFTs; a longer, more substantial Wormhole signifies a higher degree of entanglement. This connection isn’t simply observational; calculations demonstrate that the EntanglementEntropy can be precisely determined by measuring geometric properties within the Wormhole, effectively translating a quantum information property into a classical geometric one. This establishes a tangible, measurable link, suggesting that entanglement isn’t just described by spacetime geometry, but is actively sustained by it, offering a novel pathway to understand and potentially manipulate quantum correlations through geometric control.
Recent dynamics reveal a surprising interplay between information loss and recovery within entangled systems, prompting a reconsideration of established principles regarding information preservation. Observations indicate that information, while appearing to vanish during specific interactions, is demonstrably recoverable through enhanced energy transmission – a phenomenon particularly pronounced with increasing ratios of \delta/s. This suggests that information isn’t necessarily destroyed, but encoded in subtle correlations and accessible through energetic pathways. The study challenges the conventional understanding that information loss equates to genuine erasure, implying instead a dynamic process of information scrambling and subsequent reconstruction, potentially mediated by the underlying geometry of spacetime and offering a new perspective on the black hole information paradox.
Recent investigations reveal a profound connection between quantum information and the very fabric of spacetime, demonstrating that entanglement – a cornerstone of quantum mechanics – isn’t merely in spacetime, but appears to fundamentally shape it. Specifically, research indicates a period of enhanced mutual information – a measure of the information shared between two systems – occurring within a defined temporal window, where t < |a| + x_{P}. This temporal constraint suggests a limited timeframe during which quantum correlations can significantly influence, and potentially warp, the geometric properties of spacetime. The observation isn’t simply a correlation; it implies that information transfer, driven by entanglement, can dynamically alter the relationship between spacetime points, offering a novel perspective on how quantum phenomena might give rise to emergent gravitational effects and challenging conventional understandings of information preservation in highly energetic systems.
The pursuit of entanglement propagation, as detailed in this work, feels predictably circular. It’s a testament to the universe’s fondness for reusing old ideas with a fresh coat of paint. The researchers attempt to finesse entanglement through wormholes, essentially building increasingly elaborate Rube Goldberg machines to achieve quantum teleportation. As Niels Bohr observed, “The opposite of a trivial truth is also true.” Here, the ‘trivial truth’ is that information wants to travel; the increasingly complex methods simply delay the inevitable-and introduce a whole new class of errors production will gleefully expose. The study highlights the delicate balance between enhancing entanglement and succumbing to scrambling, which is just a fancy way of saying ‘things fall apart,’ a phenomenon well-understood by anyone who’s deployed code before.
What’s Next?
The persistent appeal of simulating spacetime with entangled states-conjuring wormholes from CFTs-should give anyone pause. It began as a neat mathematical trick, and now there’s talk of ‘information transfer’. They’ll call it AI and raise funding, naturally. The crucial point, consistently overlooked, is that any attempt to scale this beyond a carefully constructed, highly idealized system will inevitably run aground on the shoals of decoherence. The ‘mutual information’ they so diligently calculate will become, in a practical setting, a measure of how quickly the signal degrades into noise.
The authors correctly identify the delicate balance between enhancing and scrambling entanglement. But the conditions for ‘enhancement’ seem suspiciously… pristine. A local operator quench is one thing; a rogue cosmic ray is quite another. The system ‘used to be a simple bash script’ before they introduced the holographic duality, and now it’s a sprawling codebase with no unit tests.
Future work will undoubtedly focus on ‘robustness’ and ‘error correction’. This is code for ‘trying to glue a fundamentally fragile concept back together after production breaks it’. The documentation lied again, promising a seamless bridge between theory and reality. Perhaps the next step isn’t to refine the model, but to honestly assess the limitations. Tech debt is just emotional debt with commits, after all.
Original article: https://arxiv.org/pdf/2601.21604.pdf
Contact the author: https://www.linkedin.com/in/avetisyan/
See also:
- Best Controller Settings for ARC Raiders
- Ashes of Creation Rogue Guide for Beginners
- Stephen Colbert Jokes This Could Be Next Job After Late Show Canceled
- DCU Nightwing Contender Addresses Casting Rumors & Reveals His Other Dream DC Role [Exclusive]
- 7 Home Alone Moments That Still Make No Sense (And #2 Is a Plot Hole)
- 10 X-Men Batman Could Beat (Ranked By How Hard It’d Be)
- Is XRP ETF the New Stock Market Rockstar? Find Out Why Everyone’s Obsessed!
- Disney’s $1 billion investment in OpenAI brings Mickey Mouse to Sora AI’s doorstep — will it redefine Hollywood’s future?
- 10 Most Brutal Acts Of Revenge In Marvel Comics History
- Gigi Hadid, Bradley Cooper Share Their Confidence Tips in Rare Video
2026-02-01 06:15