Mapping the Edge of Order: A New Look at Quantum Criticality
![The scaling dimension [latex]\Delta\phi[/latex] is calculated across different [latex]\mathrm{Sp}(10)[/latex] and [latex]\mathrm{Sp}(4)[/latex] models using conformal 2-pt correlators [latex]\mathscr{C}_T[/latex], revealing its dependence on both [latex]\gamma_{12}[/latex] and [latex]R[/latex], and consistently approaching the expected value of [latex]\Delta_J = 2[/latex] while aligning with the critical point previously identified through crossing symmetry.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.11255v1/x8.png)
Researchers are using innovative simulations on a ‘fuzzy sphere’ to explore the behavior of quantum systems at the brink of phase transitions.
![The scaling dimension [latex]\Delta\phi[/latex] is calculated across different [latex]\mathrm{Sp}(10)[/latex] and [latex]\mathrm{Sp}(4)[/latex] models using conformal 2-pt correlators [latex]\mathscr{C}_T[/latex], revealing its dependence on both [latex]\gamma_{12}[/latex] and [latex]R[/latex], and consistently approaching the expected value of [latex]\Delta_J = 2[/latex] while aligning with the critical point previously identified through crossing symmetry.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.11255v1/x8.png)
Researchers are using innovative simulations on a ‘fuzzy sphere’ to explore the behavior of quantum systems at the brink of phase transitions.
![The Sondheimer frequency exhibits a clear dependence on doping concentration, transitioning predictably across the overdoped to underdoped regime under a perpendicular magnetic field-a relationship governed by parameters including a perpendicular transfer integral of [latex]3 \times 10^{-3} \text{eV}[/latex], zero phase shift [latex]\eta = 0[/latex], and a layer thickness ratio of [latex]d/a = 40[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.11252v1/x6.png)
New research demonstrates that subtle changes in electrical resistance under a magnetic field can be used to chart the complex electronic structure of high-temperature superconductors.
New research reveals that the fundamental nature of spacetime in loop quantum gravity allows for both fermionic and bosonic behavior in the excitations of the gravitational field.
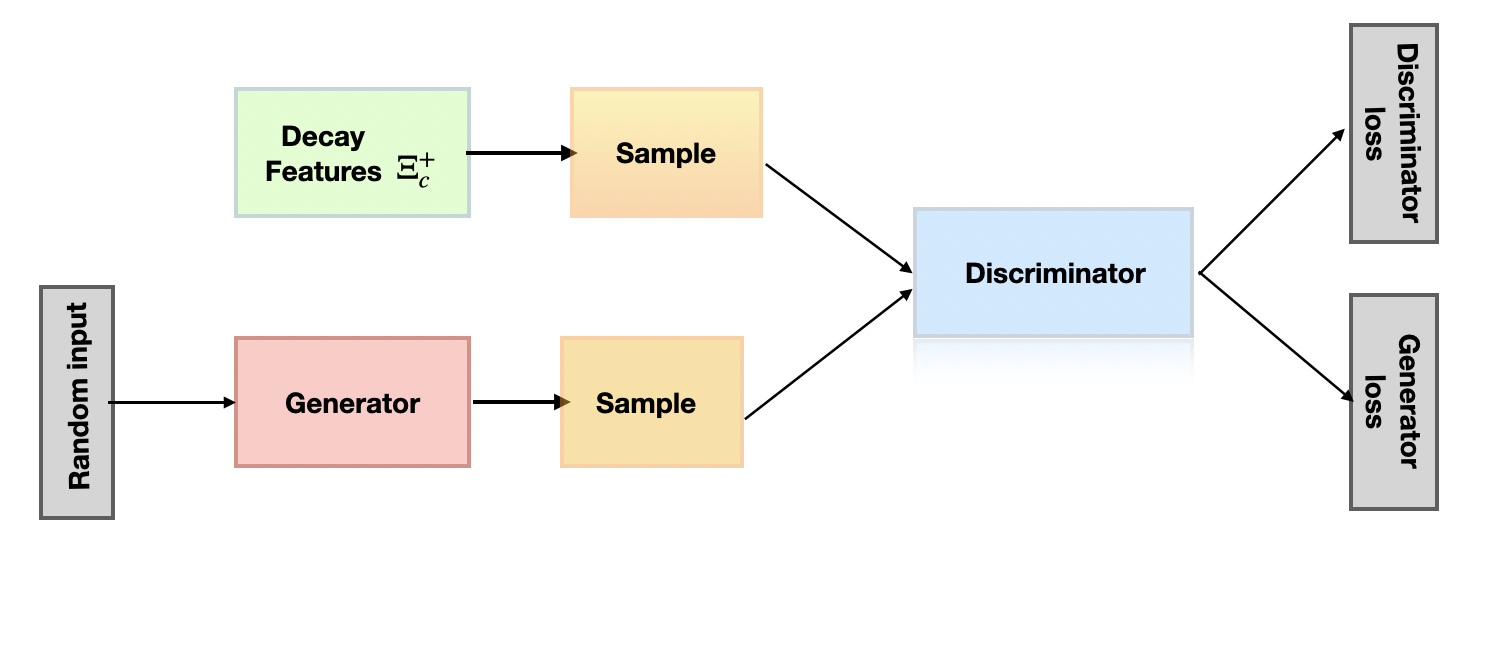
A new approach leveraging generative AI is enhancing the search for rare particles created in the extreme conditions of heavy-ion collisions.
![A search for minimal extensions to the Standard Model, constrained by parity violation limits and experimental data from NA64 and KLOE-2, reveals a landscape of viable neutron and proton couplings-specifically [latex]\epsilon_{n}^{V},\epsilon_{n}^{A},\epsilon_{p}^{V},\epsilon_{p}^{A}[/latex]-that simultaneously accommodate ATOMKI measurements at 99% confidence, potentially explaining the PADME excess through corresponding electron coupling values [latex]\epsilon_{e}^{V}[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.11263v1/x5.png)
New research explores the potential role of a previously undetected vector boson, the X17, in explaining anomalies observed in nuclear decays.
^{2}[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.11405v1/feynman_GammaD_To_chi_chi.png)
A new analysis tightens the constraints on dark axion interactions, leveraging both searches for invisible particles and precise measurements of fundamental asymmetries.
New research explores how strong magnetic fields and particle density affect the behavior of the fundamental matter described by quantum chromodynamics.
![Recent determinations of the ratio [latex]V_{ub}/V_{cb}[/latex] - calculated from decays of [latex]B_s[/latex] and [latex]\Lambda_b[/latex] baryons using form factors from HPQCD, FNAL/MILC, DM, and LCSR calculations - are presented alongside experimental averages and theoretical predictions for [latex]R_D[/latex] and [latex]R_{D^{*}}\[/latex], offering a comprehensive view of the parameters governing the Standard Model and potential avenues for new physics.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.11997v1/x6.png)
Recent experiments are challenging our understanding of how beauty and charm quarks decay, revealing intriguing discrepancies that could point to new physics.
This review details a refined theoretical approach to magnetic resonance, enhancing both the precision of nuclear moment measurements and the potential for control in quantum computing applications.
![The relationship [latex]\delta(\Delta)[/latex] reveals how the Barrow-Tsallis model-and its simplification to the extensive limit-define a distribution generated through Monte Carlo methods, all while remaining constrained by specific cosmographic parameters [latex]q_0 = -0.580[/latex] and [latex]j_0 = 0.745[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.12077v1/x3.png)
A novel framework connects the microscopic structure of spacetime with the large-scale behavior of the universe through a shared entropic foundation.