Hunting New Physics in Rare B Meson Decays
![The differential decay rate of [latex]B \to K_{0}^{*}(1430) \ell^{+} \ell^{-} [/latex] is analyzed within both the Standard Model and a scalar Lepton Quark (LQ) scenario, demonstrating that for [latex] \tau^{+} \tau^{-} [/latex] decays, the accessible momentum transfer squared, [latex] q^{2} [/latex], is limited by the tau mass, effectively precluding observation of the decay spectrum in the low-[latex] q^{2} [/latex] region.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.06892v1/x3.png)
A new analysis of the B meson’s decay into a K₀*(1430) and pairs of leptons offers a sensitive probe for deviations from the Standard Model and potential evidence for leptoquarks.
![The differential decay rate of [latex]B \to K_{0}^{*}(1430) \ell^{+} \ell^{-} [/latex] is analyzed within both the Standard Model and a scalar Lepton Quark (LQ) scenario, demonstrating that for [latex] \tau^{+} \tau^{-} [/latex] decays, the accessible momentum transfer squared, [latex] q^{2} [/latex], is limited by the tau mass, effectively precluding observation of the decay spectrum in the low-[latex] q^{2} [/latex] region.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.06892v1/x3.png)
A new analysis of the B meson’s decay into a K₀*(1430) and pairs of leptons offers a sensitive probe for deviations from the Standard Model and potential evidence for leptoquarks.
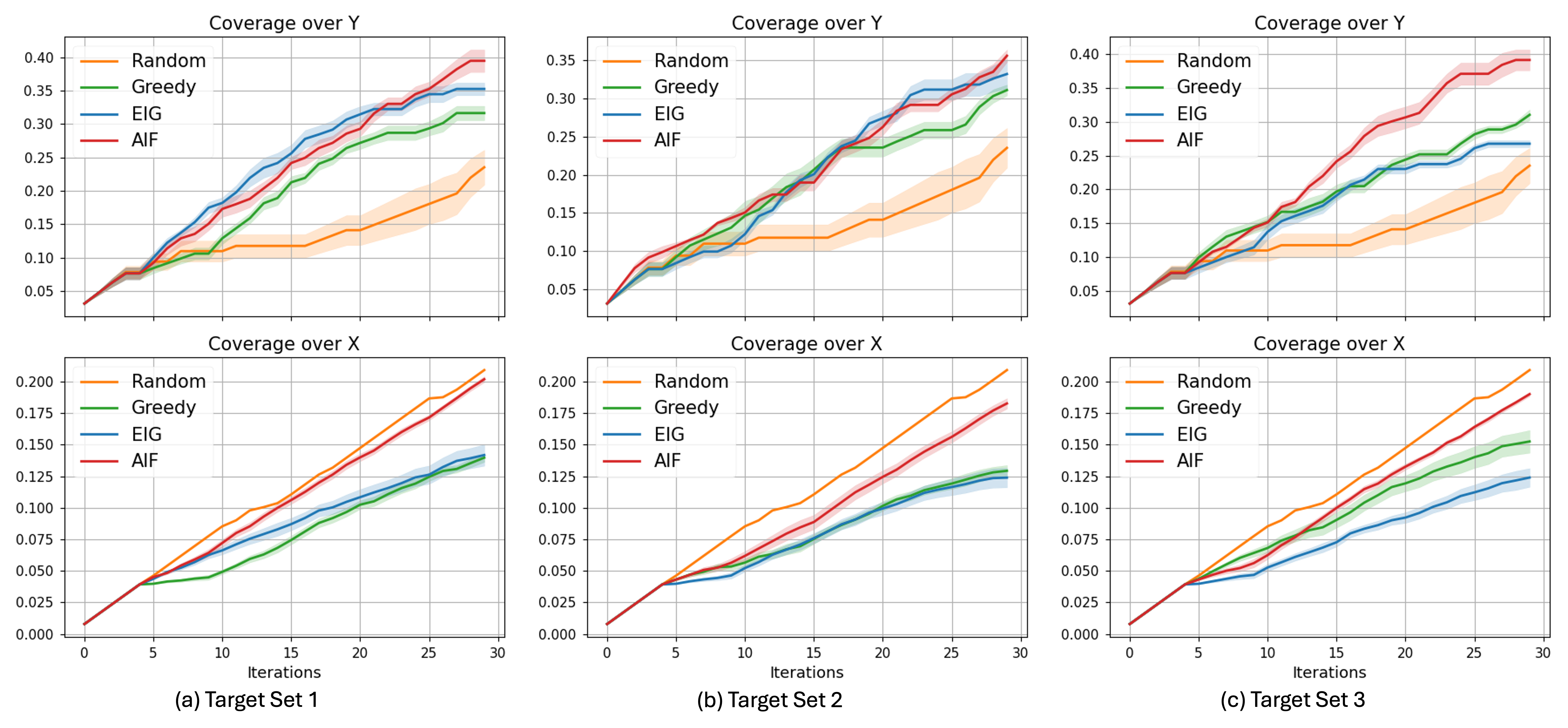
A new approach unifies curiosity-driven learning with goal-directed optimization, enabling agents to both acquire knowledge and actively pursue objectives.

A 1969 paper proposed that electromagnetic fluctuations and plasma formation could explain the forces binding atomic nuclei, offering a radical alternative to emerging strong interaction theories.
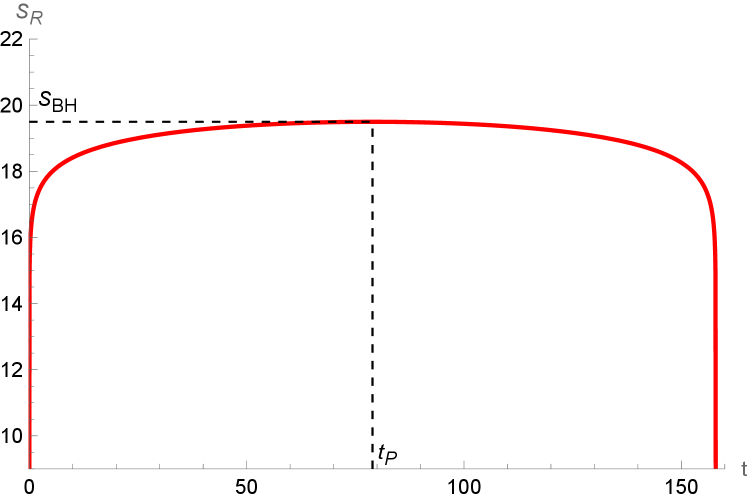
A new theoretical framework suggests information seemingly destroyed by black hole evaporation is actually encoded in the temporal correlations within Hawking radiation.
New research explores how observations of these stellar remnants are pushing the boundaries of our understanding of matter at extreme densities.
A new study reveals that specific tensors at the edge of spacetime uniquely determine the geometry of asymptotically flat universes, offering a powerful tool for understanding gravitational fields.
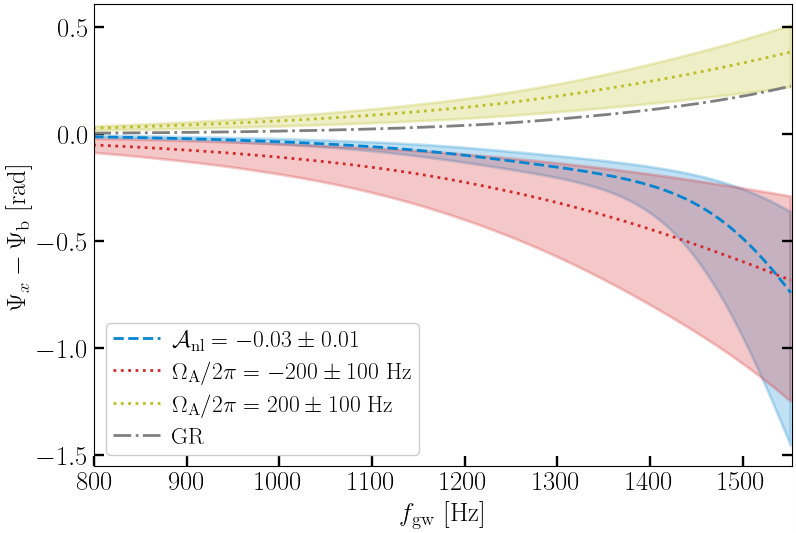
New research reveals that subtle effects from neutron star spin and relativistic hydrodynamics significantly impact our ability to determine the matter composition of these extreme objects.
New research highlights the crucial link between thermodynamic consistency in black hole systems and the precise definition of boundary conditions used in calculations.
A new technique dynamically adjusts ultrasound focusing to overcome distortions and improve image clarity in challenging media.
![The energy spectrum of an isolated commensurate Aubry-Andérson chain undergoes distinct transformations dependent on modulation phase, exhibiting merged zero-energy edge states and a central bulk band at [latex]\phi_{\lambda} = 0[/latex], while a complete band narrowing occurs at [latex]E = 0[/latex] eV for [latex]\phi_{\lambda} = \pi/2[/latex]-shifts coinciding with critical modulation strengths of [latex]\delta_{t} = W_{c1} = \frac{2}{\sqrt{3}}[/latex] and [latex]\delta_{t} = W_{c2} = 2[/latex], which govern the opening and closing of the central bulk gap, and ultimately demonstrate the system's sensitivity to subtle shifts in its foundational parameters.](https://arxiv.org/html/2602.05338v1/eg120pi2.png)
New research reveals how topology and disorder interplay in a carefully designed atomic chain to create robust and tunable charge transport.