Beyond Kohn-Sham: A New Path for Simulating Matter Under Pressure
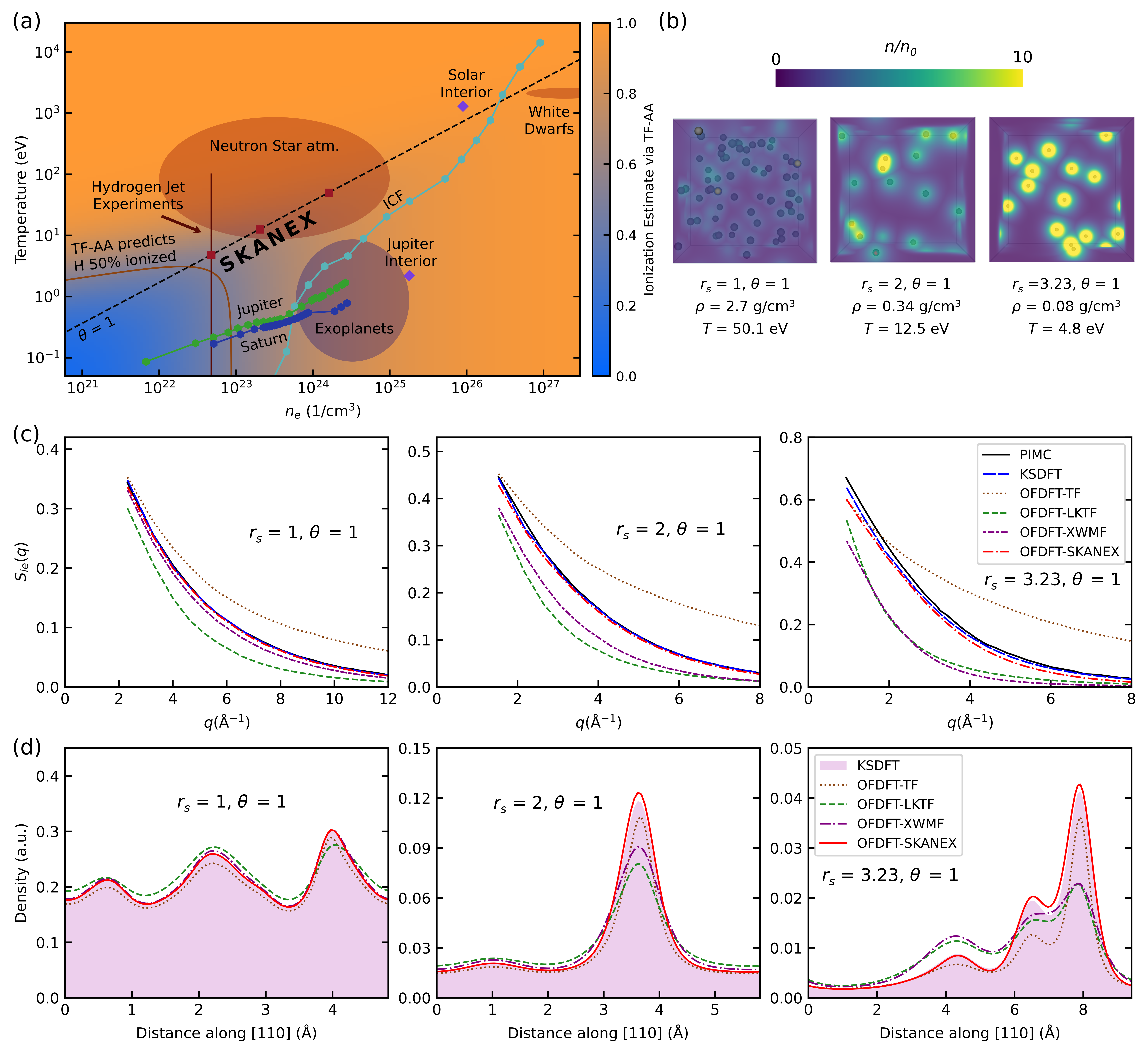
Researchers have developed a novel orbital-free density functional theory method offering a computationally efficient way to model the electronic structure of materials at extreme temperatures and densities.
![The study demonstrates how sensitivities to specific GMP parameters-under the hypothesis of [latex]\varepsilon=1[/latex] and [latex]\varphi\_{12}=\varphi\_{13}=0[/latex]-reveal distinct responses when contrasted with sensitivities derived from a prior three-year DeepCore analysis, highlighting an evolution in system behavior over time.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.22374v1/x3.png)
![Analysis of the [latex]D^{0}\overline{D}^{0}[/latex] and [latex]D_{0}\overline{H}[/latex] correlator matrix, utilizing hexaquark and dibaryon interpolating operators, demonstrates that an unconstrained fit reveals no bound state, whereas a constrained fit-guided by the model in Eq. (74)-identifies the existence of one.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.22272v1/x73.png)
![The study demonstrates that diminished scalar amplitude values correlate with reduced Wigner negativity-a reversal of the trend observed in prior analyses-when computations are constrained to the perturbative regime [latex]|\epsilon\_{2}H\chi\_{0}|<1[/latex].](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.22219v1/perturbative.png)

![The study demonstrates the existence of coupled exceptional points within the system, evidenced by the numerical analysis of eigenvalues-with real components shown in blue and imaginary in orange-and further substantiated by the observed [latex]\varepsilon^{-1/8}[/latex] scaling in eigenvector projections onto the (0,0,0,1) mode, where coinciding curves (red) represent the upper eigenvalues and confirm the theoretical predictions.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.22733v1/x4.png)