Seeing Beyond the Limit: Quantum Light Amplifies Photothermal Microscopy
A new microscopy technique harnesses the power of quantum squeezing to dramatically enhance sensitivity, offering unprecedented detail in label-free imaging.
A new microscopy technique harnesses the power of quantum squeezing to dramatically enhance sensitivity, offering unprecedented detail in label-free imaging.
![The model captures the complexities of pion-pion scattering through partial fits to experimental data-specifically, Protopopescu [Pro73], Ishida [Ish97], and Estabrooks [Est74]-by decomposing the total phase φ into resonant and background components, where the background phase [latex]\phi_{B}[/latex] represents a constant difference defining the underlying interaction.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.20816v1/x2.png)
New phase shift analysis reveals that the long-enigmatic f0(500) meson behaves as a standard resonance, its unusual properties stemming from its unique position near a particle threshold.
New research reveals limitations in the ability of topological quantum field theories to distinguish between different shapes of spheres, challenging long-held assumptions at the intersection of mathematics and physics.

Moiré materials, with their intricate nanoscale structures, are emerging as a powerful platform for engineering exotic electronic phases.
New research explores how Gödel’s rotating universe solution fares when fundamental symmetries of spacetime are explicitly violated by modified gravity theories.
![The evolution of a dimensionless scalar displacement, [latex]\frac{\phi-\phi_{\ast}}{M_{\rm Pl}}[/latex], consistently dampens and relaxes towards zero as expressed by [latex]N = \ln a[/latex], indicating a progressive suppression of composition-dependent fifth forces and deviations from the equivalence principle within the Damour-Polyakov regime, where ambient matter coupling scales proportionally to this displacement.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.20156v1/dp_full_x_of_N.png)
New research uses dynamical systems to explore how the evolution of a fundamental field in string theory impacts the equivalence principle-a cornerstone of general relativity.
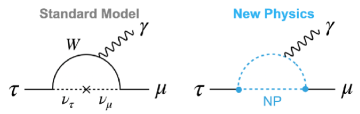
A next-generation Super Tau-Charm Factory promises unprecedented precision in measurements of the tau lepton and its potential to reveal new physics beyond the Standard Model.
[/latex], with ‘a’ and ‘b’ quantifying these operations.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.20759v1/images/diam_nums_cut.png)
A new approach uses geometric principles to reveal hidden structures within mathematical reasoning systems.
![The study demonstrates that a dimensionless quantity [latex]K_3[/latex], representing a deviation from classical limits, exceeds the established upper bound of one-defined by the Localized Gravity Interpretation (LGI)-for specific values of the dimensionless parameter [latex]\lambda\,\Delta t[/latex], where [latex]\lambda = \sqrt{2}B/M_{\rm P}[/latex], indicating a violation of the LGI under those conditions.](https://arxiv.org/html/2601.20436v1/x1.png)
New research suggests that the conversion of photons into gravitons within a magnetic field exhibits distinctly non-classical behavior, hinting at the quantum nature of gravity.

A new approach elegantly compresses the complexities of open quantum systems, offering a streamlined path to understanding their behavior.