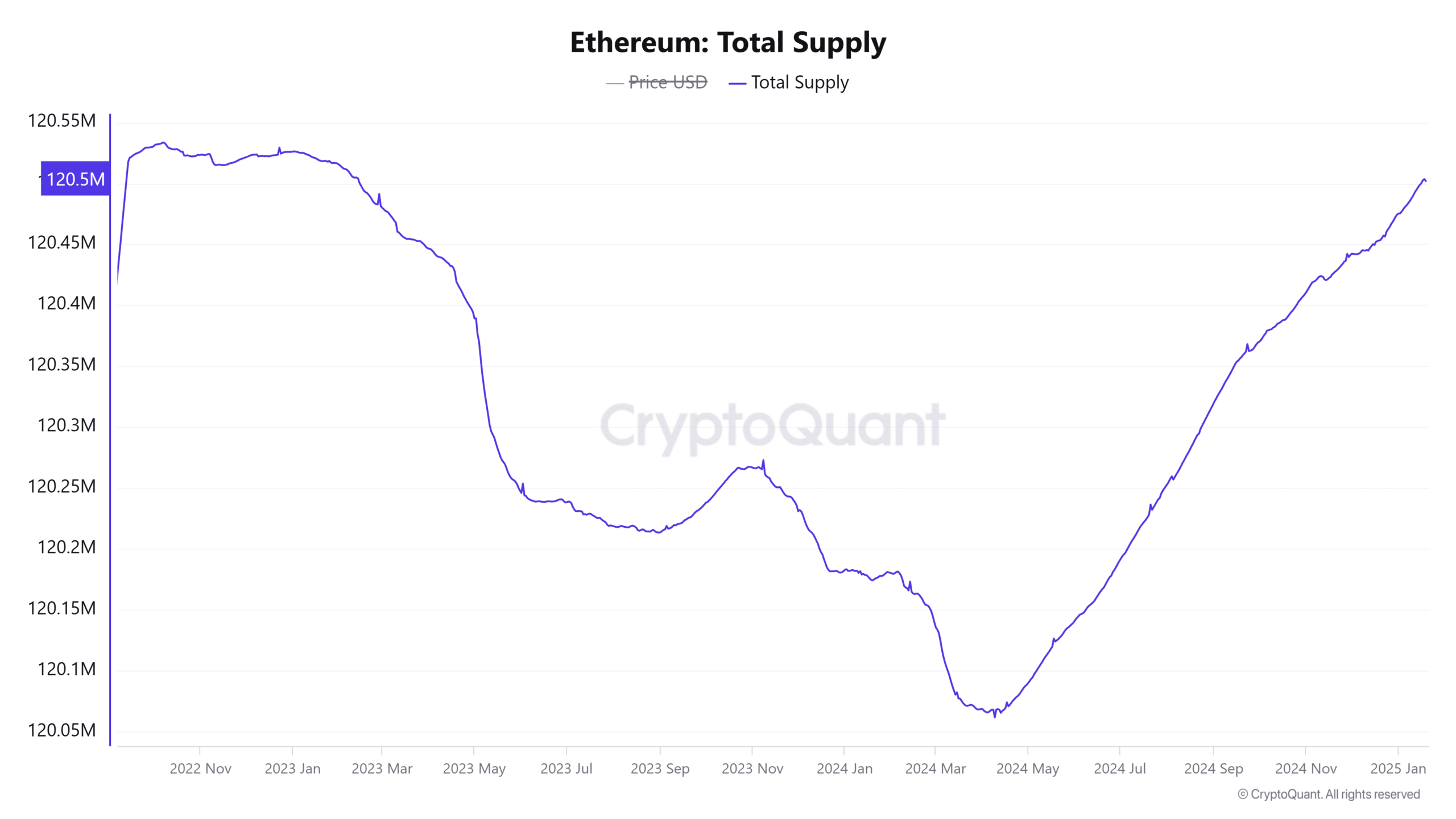
- Ethereum’s supply has surged to 120,501,906, and it is currently approaching its highest level in nearly two years.
- The number of validators on the network has also dropped by around 2% in the last three months.
Over the past while, the amount of Ethereum (ETH) in circulation has significantly grown, nearing its highest point in almost four years.
Due to an increase in its availability, Ethereum’s capacity to increase in value may be restricted, as it has fallen behind Bitcoin [BTC] and leading alternative coins in terms of performance over the past few months.
ETH supply nears two-year high
According to CryptoQuant’s latest findings, the current Ethereum supply has reached a peak of 120,501,906 units, marking a high not seen since February 2023.
If this rise continues, it could soon reach the level it was before the Ethereum Merge.
The transition of Ethereum, known as The Merge, aimed to create a deflationary state for Ether (ETH). This change reduced the daily issuance of ETH from approximately 13,000 ETH to around 1,700 ETH, with the exact amount depending on staking participation.
In contrast, data from Ultrasound Money reveals a 45,724 ETH increase in Ethereum’s supply within thirty days. Such an increase in supply when demand is low may signal potential downward trends.
Dropping validator count suggests…
In the Ethereum’s Proof-of-Stake framework, validators are essential participants who must deposit Ether (ETH) as a form of guarantee to authenticate transactions.
Over these past three months, there’s been a decrease of approximately 2% in the number of validators on the network, leaving us with about 1,057,356 active validators.
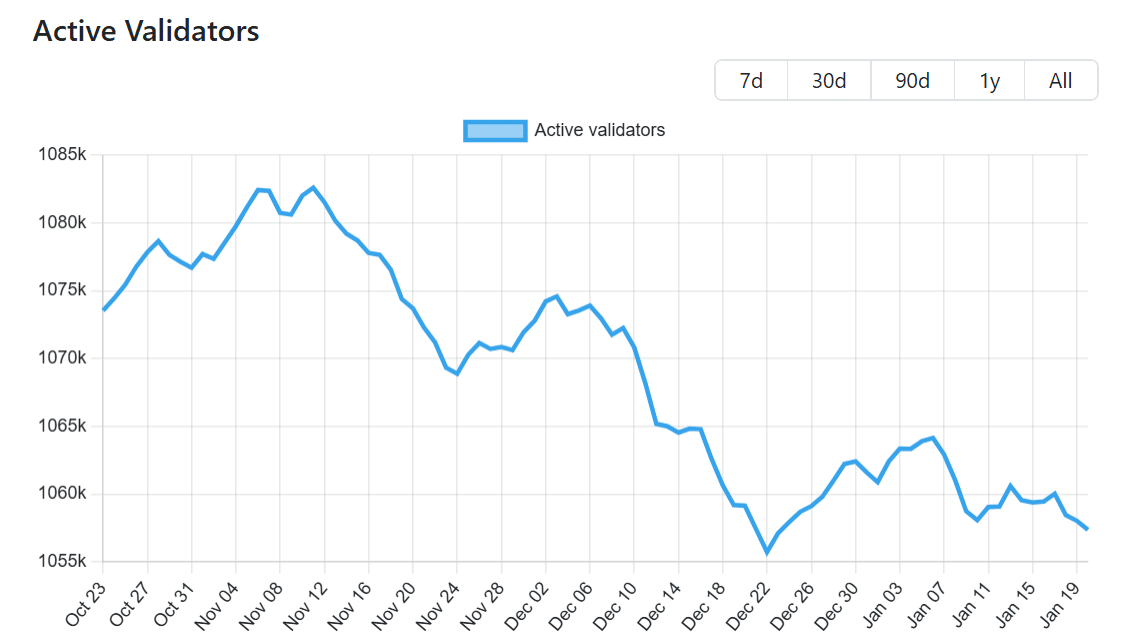
This decrease indicates an increase in the rate at which Ethereum is being unlocked for use (unstaking), thereby boosting the total available supply. As per the Validator Queue, the current staked ETH amounts to approximately 27% of Ethereum’s total circulating amount.
Declining activity on the Ethereum mainnet
In addition to the decline in Ethereum (ETH) staking interest, it’s possible that decreased usage on the Ethereum primary network might be causing an increase in ETH supply. Every Ethereum transaction involves a base fee payment in ETH, which gets destroyed or “burned” later on.
The purpose of this burning process is to make Ethereum scarce by reducing its supply. But when there’s less action on the main network, fewer tokens get destroyed, leading to an expansion of the total supply.
According to L2Beat statistics, there’s been a significant shift in activities from the Ethereum primary network to layer two systems. To illustrate, the number of transactions on Base stands at approximately 312 million over the past thirty days, which is almost ten times greater than Ethereum’s 36 million.
If an increasing number of users opt for Ethereum’s layer two networks instead of the mainnet, there may be less triggering of the burn process. This could potentially slow down the reduction in the total supply of Ether circulating in the market.
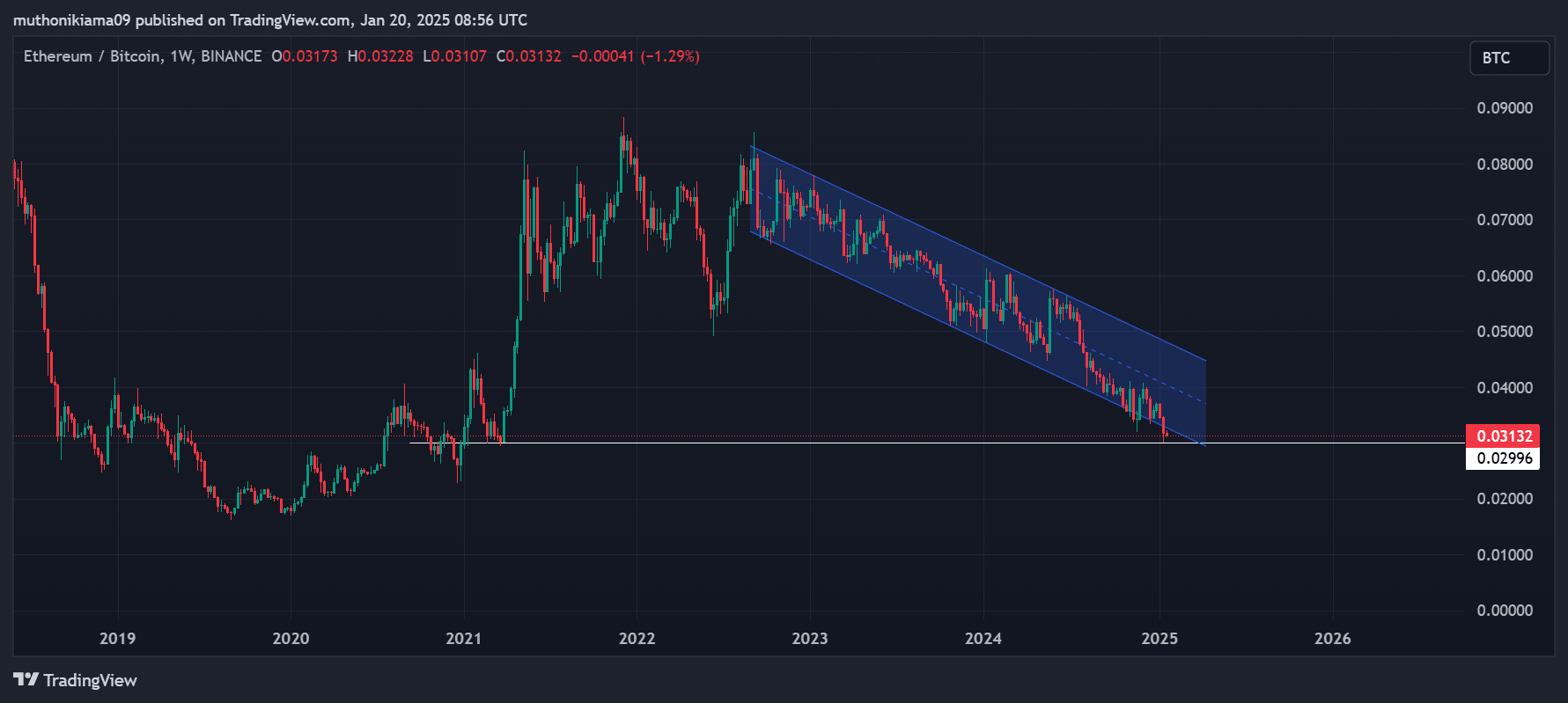
ETH/BTC hits lowest level since 2021
In my observation as a financial analyst, the supply dynamics within Ethereum seem to be affecting its price negatively, while Bitcoin continues to surpass it. The ETH/BTC ratio has dipped to 0.02996, reaching its lowest point since March 2021, indicating that one Bitcoin is worth more than 29.96 Ether at the moment.
Read Ethereum’s [ETH] Price Prediction 2025–2026
ETH/BTC has been trading within a descending parallel channel on its weekly chart.
After the recent drop, it has fallen below the lower boundary of its channel pattern, implying that Ethereum is experiencing a downward trend and may reach even lower prices.
Read More
- Gold Rate Forecast
- PI PREDICTION. PI cryptocurrency
- Rick and Morty Season 8: Release Date SHOCK!
- Discover the New Psion Subclasses in D&D’s Latest Unearthed Arcana!
- Masters Toronto 2025: Everything You Need to Know
- We Loved Both of These Classic Sci-Fi Films (But They’re Pretty Much the Same Movie)
- Mission: Impossible 8 Reveals Shocking Truth But Leaves Fans with Unanswered Questions!
- SteelSeries reveals new Arctis Nova 3 Wireless headset series for Xbox, PlayStation, Nintendo Switch, and PC
- Eddie Murphy Reveals the Role That Defines His Hollywood Career
- LPT PREDICTION. LPT cryptocurrency
2025-01-20 15:04