- Ethereum mainnet gas fees drop amid low network demand.
- We assess the role of Ethereum layer 2s in the declining gas fees and decongesting the mainnet.
As a seasoned crypto investor who’s weathered numerous market cycles and witnessed the evolution of Ethereum [ETH], it’s refreshing to see gas fees finally dropping to levels we haven’t seen since 2017! The decline in network activity, coupled with the maturity of Layer 2 solutions, has significantly eased congestion on the mainnet.
Over time, Ethereum (ETH) has gained a reputation for its high transaction costs, leading numerous users to opt for Layer 2 networks instead.
But, recent findings reveal that Ethereum gas fees have been declining.
High transaction costs on the Ethereum blockchain have acted as a deterrent, causing some individuals to reconsider engaging in Decentralized Finance (DeFi) within the main network due to these expenses.
On the other hand, it has been discovered that gas fees have plummeted to their lowest points in the past five years.
On August 11th, AMBCrypto reported that gas fees had dropped to a low of 1.38 Gwei. To put this into perspective, the average base gas fee across the network peaked at 91.51 Gwei on March 5th.
This was just before prices peaked in March, followed by a strong pullback.
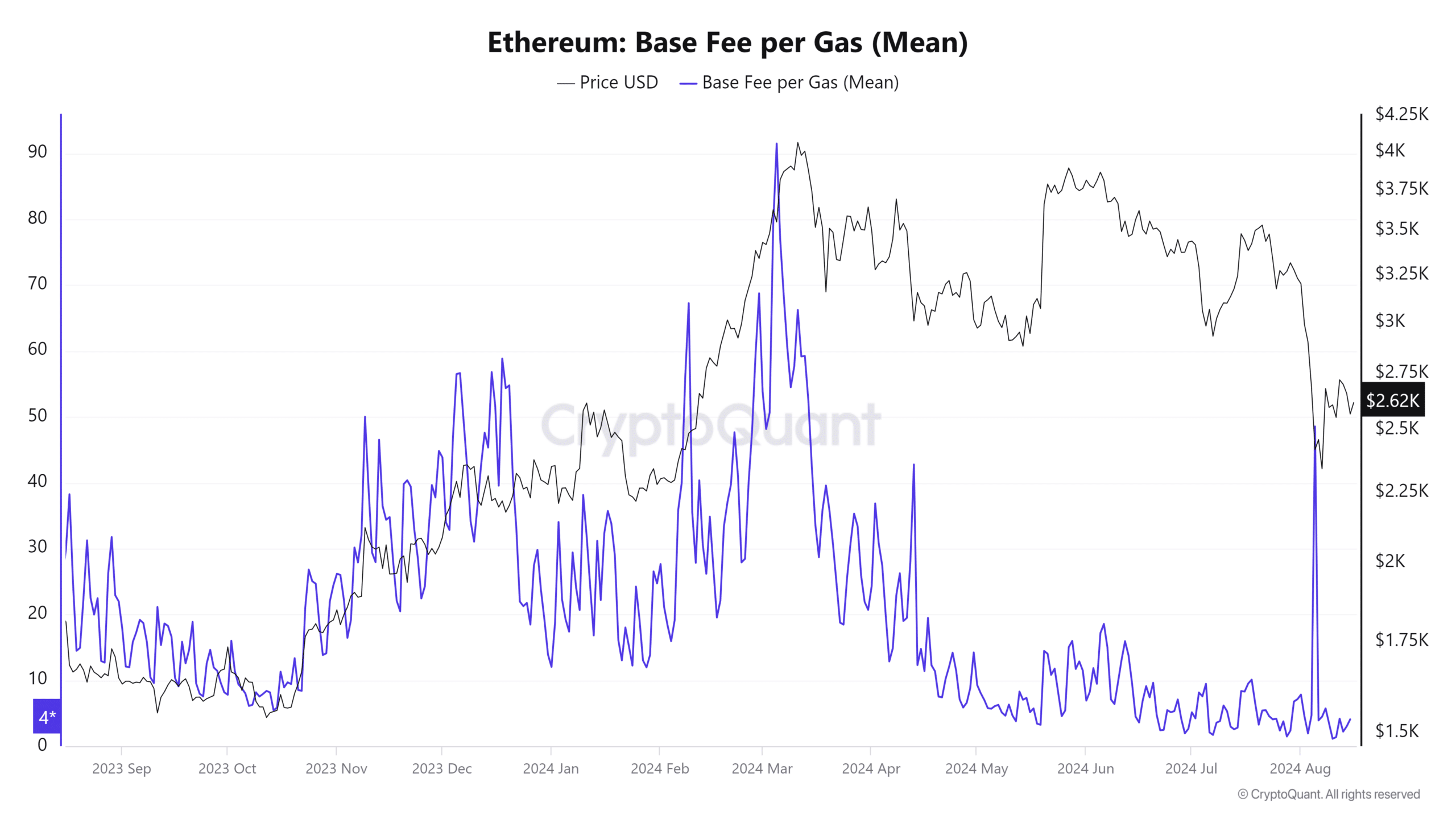
Why are Ethereum gas fees declining?
A likely reason behind this result could be the decrease in network usage or traffic. The costs for transactions on Ethereum (gas fees) are primarily driven by market forces such as supply and demand, and this relationship is particularly noticeable when there’s a lot of activity on the network.
As a crypto investor, I’ve noticed that gas fees tend to surge when there’s an increase in demand or transactions, such as when people are buying or selling a lot of Ethereum. Conversely, when demand decreases, so does the gas fee. This pattern became particularly clear during the recent market crash, where a significant rise in ETH selling transactions coincided with a spike in gas fees.
This resulted in a gas fee surge.
Ethereum gas fees hitting a new low may have also been influenced by Layer 2 activity.
In comparison to 2018, the Ethereum Layer 2 ecosystem has significantly advanced, which helps alleviate the mainnet congestion that previously led to increased prices. This progress can be seen clearly in the surge of transactions within the Ethereum network.
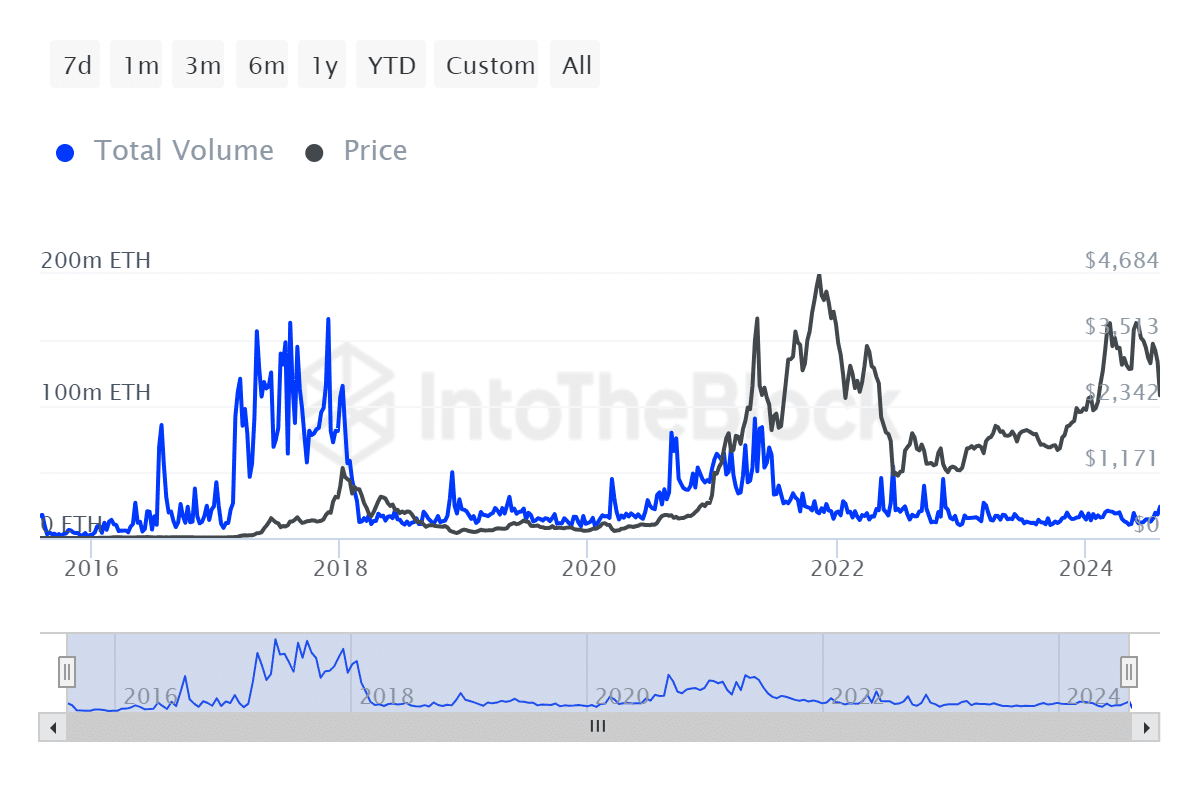
During the 2017 cryptocurrency surge, Ethereum transaction volume reached an astounding 165.97 million Ether. However, this number was notably lower during the 2021 bull run, peaking at only 90.44 million Ether.
In 2024, the greatest number of Ethereum transactions ever transacted within a single year was approximately 20.19 million, which occurred right before the altcoin attained its Year-to-Date peak.
It’s evident from the increasing transaction volumes that the expanding Ethereum layer 2 ecosystem is having a substantial influence on the Ethereum primary network.
Read Ethereum’s [ETH] Price Prediction 2024-25
Over the past couple of years, I’ve noticed a significant decrease in network congestion, which translates to lower gas fees. This reduction wasn’t just because of luck, but also due to the consistent increase in transactions, fueled by an influx of new users who have embraced cryptocurrencies.
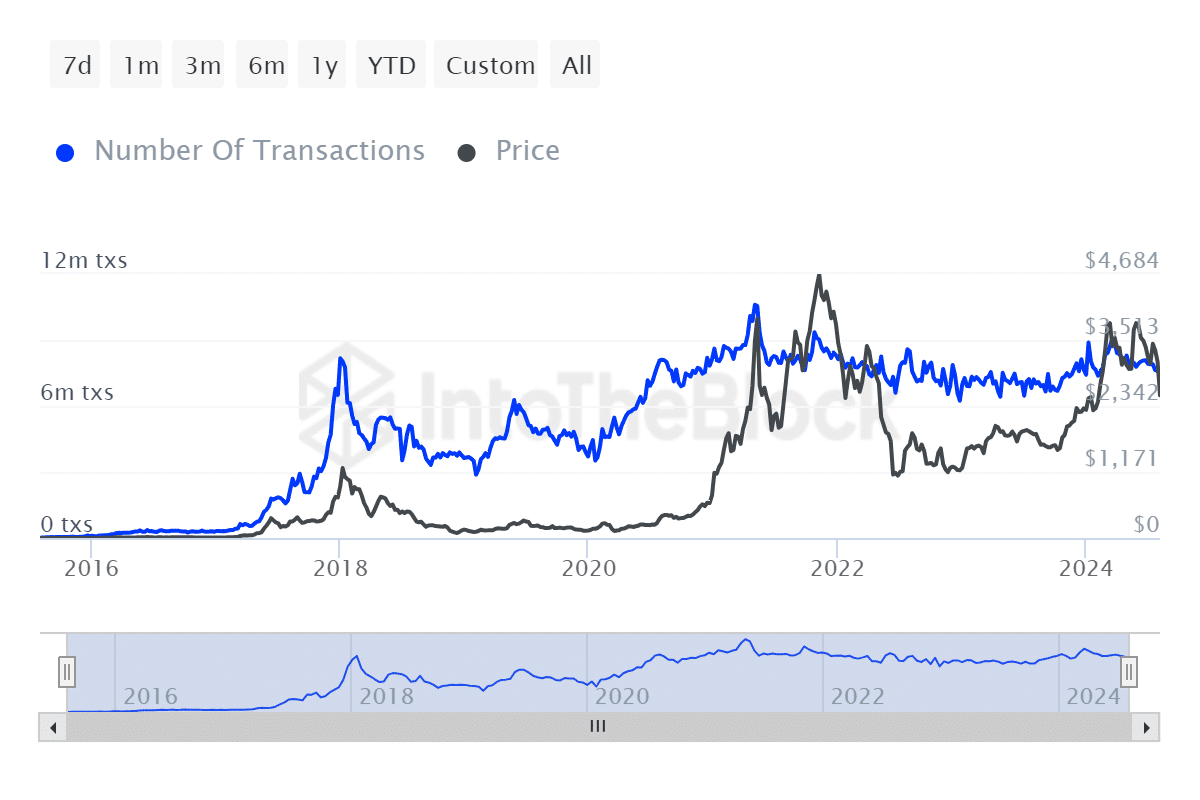
Over the years, Ethereum transactions generally followed an upward trend. Interestingly, this growth trend seems to be inversely related to gas fees, suggesting that layer 2 networks may have a significant influence on transaction costs.
Read More
- PI PREDICTION. PI cryptocurrency
- Gold Rate Forecast
- Rick and Morty Season 8: Release Date SHOCK!
- Discover Ryan Gosling & Emma Stone’s Hidden Movie Trilogy You Never Knew About!
- Discover the New Psion Subclasses in D&D’s Latest Unearthed Arcana!
- Linkin Park Albums in Order: Full Tracklists and Secrets Revealed
- Masters Toronto 2025: Everything You Need to Know
- We Loved Both of These Classic Sci-Fi Films (But They’re Pretty Much the Same Movie)
- Mission: Impossible 8 Reveals Shocking Truth But Leaves Fans with Unanswered Questions!
- SteelSeries reveals new Arctis Nova 3 Wireless headset series for Xbox, PlayStation, Nintendo Switch, and PC
2024-08-17 01:43